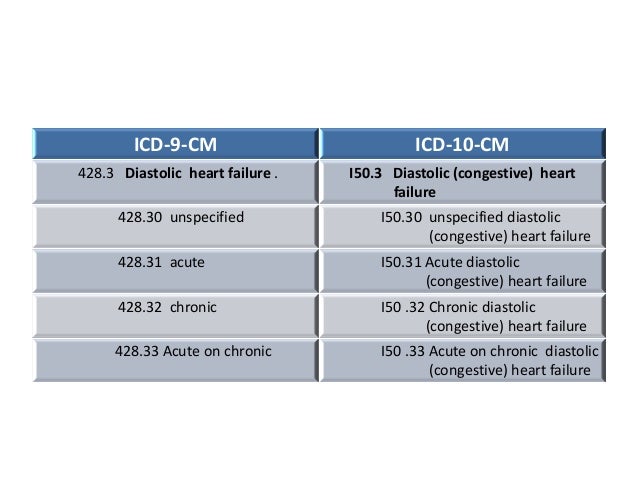
What are ICD 10 codes?
Why ICD-10 codes are important
- The ICD-10 code system offers accurate and up-to-date procedure codes to improve health care cost and ensure fair reimbursement policies. ...
- ICD-10-CM has been adopted internationally to facilitate implementation of quality health care as well as its comparison on a global scale.
- Compared to the previous version (i.e. ...
How serious is a dilated ascending aorta?
The dilated or aneurysmal ascending aorta is at risk for spontaneous rupture or dissection. The magnitude of this risk is closely related to the size of the aorta and the underlying pathology of the aortic wall. The occurrence of rupture or dissection adversely alters natural history and survival even after successful emergency surgical treatment.
What causes a mildly ectatic aorta?
A Guide to the Causes, Signs and Symptoms, and Available Treatments
- About. Mild aortic ectasia is defined as an enlargement of the aorta that is mild in degree. ...
- Risk of Rupture. Though the term ‘mild’ may indicate a lack in the seriousness of the condition, aortic aneurysms are serious.
- Echocardiography. ...
- Other Factors. ...
- Symptoms. ...
- Treatment. ...
- Summary. ...
- References. ...
What is the ICD 10 code for aortic root replacement?
The procedure code 02RX0KZ is in the medical and surgical section and is part of the heart and great vessels body system, classified under the replacement operation. The applicable bodypart is thoracic aorta, ascending/arch. 02RX0KZ replaces the following previously assigned ICD-10-PCS code (s):
See more
What is ascending aortic dilation?
An ascending aortic aneurysm is a weak spot in the top part of your aorta, which is the main artery in your body. The aneurysm bulges outward, and may cause your blood vessel wall to tear or break open. It's a life-threatening condition.
Is a dilated ascending aorta the same as an aneurysm?
Nevertheless, by common convention, aortic dilatation refers to a dimension that is greater than the 95th percentile for the normal person age, sex and body size. In contrast, an aneurysm is defined as a localized dilation of the aorta that is more than 50% of predicted (ratio of observed to expected diameter ≥ 1.5).
Is ascending aorta the same as thoracic aorta?
The entire aorta divides into two parts: the thoracic aorta and the abdominal aorta. The ascending aorta, along with the aortic arch and the descending aorta, makes up the thoracic aorta.
Is aortic dilation the same as aortic dissection?
Aortic dilatation may lead to aortic dissection or aortic rupture. The chance of aortic dissection is related to the aortic diameter. In 2002, Davies et al15 identified that the median aortic diameter at the time of rupture for the ascending or aortic arch was 6.0 cm.
What is aneurysmal dilatation of the ascending thoracic aorta?
Background: The aorta is considered pathologically dilated if the diameters of the ascending aorta and the aortic root exceed the norms for a given age and body size. A 50% increase over the normal diameter is considered aneurysmal dilatation.
How do you fix dilated ascending aorta?
How is an ascending aortic aneurysm repaired? An ascending aortic aneurysm is repaired through traditional open surgery. Your surgeon removes the weakened part of your ascending aorta and replaces it with a graft (synthetic fabric tube). This graft functions as a new lining for your artery so blood can pass through.
Is the ascending aorta Part of the heart?
The aorta is divided into four sections: The ascending aorta rises up from the heart and is about 2 inches long. The coronary arteries branch off the ascending aorta to supply the heart with blood. The aortic arch curves over the heart, giving rise to branches that bring blood to the head, neck, and arms.
What is the difference between an aortic dissection and an aortic aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm occurs when a weak spot in the wall of the aorta begins to bulge, as shown in the image on the left. An aneurysm can occur anywhere in the aorta. Having an aortic aneurysm increases the risk of a tear in the aortic lining (aortic dissection), as shown in the image on the right.
How common is aortic dilation?
66% of our patients were males and 34% females. 146 patients were found to have aortic dilatation. Therefore, the incidence of aortic dilatation was 6.8% in our study population. Conclusion The incidence of aortic dilatation in our hospital population of 6.8% was significantly higher than we expected.
What's the difference between an aortic aneurysm and an aortic dissection?
Aneurysms can occur in any vessel, most notably in the brain, heart, thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta. A dissection is a tear of the inside layer of a blood vessel wall that allows blood to flow between the layers that make up the vessel wall and separate these layers.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for problem with fiberglass cast
- 2. icd-10 code for bcc of cheek
- 3. icd 10 code for vitamin b12
- 4. 2021 icd 10 code for elevated liver enzymes
- 5. icd-10 code for visual field defect
- 6. icd 10 code for fibroglandular density breast
- 7. icd 10 code for left nephrostomy tube displaced
- 8. icd-10 code for icu admission
- 9. icd-10 code for rh negative in pregnancy
- 10. icd 10 cm code for laceration of right eyebrow