What is the ICD 10 code for rapid AFIB?
Atrial Fibrillation: 2020 ICD-10 Code Updates Brought to you by Pinson&Tang, authors of the CDI Pocket Guide Effective October 1, 2019, there are two new ICD-10 codes for atrial fibrillation specified as “chronic” or “permanent”. Previously non-CCs, these are now CCs. Type of Afib ICD-10 code CC status Paroxysmal I48.0 Non-CC Long-standing
How to confirm atrial fibrillation?
Oct 17, 2018 · Atrial Fibrillation (AFIB) ICD 10 Atrial Fibrillation (AFIB) ICD 10 October 17, 2018 by Kelly Frey Martin The code for types of atrial fibrillation (afib) and flutter in the ICD-10 is I48. It is located within the section known as “other forms of heart disease” which includes codes I30-I52. Definition: What is an ICD code?
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified atrial fibrillation. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I48.91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I48.91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can AFIB reverse itself?
Jan 20, 2020 · ICD-10 Codes to report Atrial Fibrillation. In 2019, there were four codes to report AF: I48.0 Paroxysmal AF; I48.1 Persistent; I48.2 Chronic; I48.91 Unspecified; On October 1, 2020, category I48 was expanded, with more specific options for persistent and chronic atrial fibrillation as follows: I48 Atrial fibrillation and flutter; I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
What is the correct ICD-10 code for atrial fibrillation?
ICD-10 code I48 for Atrial fibrillation and flutter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What I48 91?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48. 91: Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for atrial fibrillation and flutter?
I482022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48: Atrial fibrillation and flutter.
What is diagnosis code I48 21?
21: Permanent atrial fibrillation.
What is unspecified atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart.Oct 19, 2021
What is ICD-10 code I10?
Essential (primary) hypertension: I10 That code is I10, Essential (primary) hypertension. As in ICD-9, this code includes “high blood pressure” but does not include elevated blood pressure without a diagnosis of hypertension (that would be ICD-10 code R03. 0).
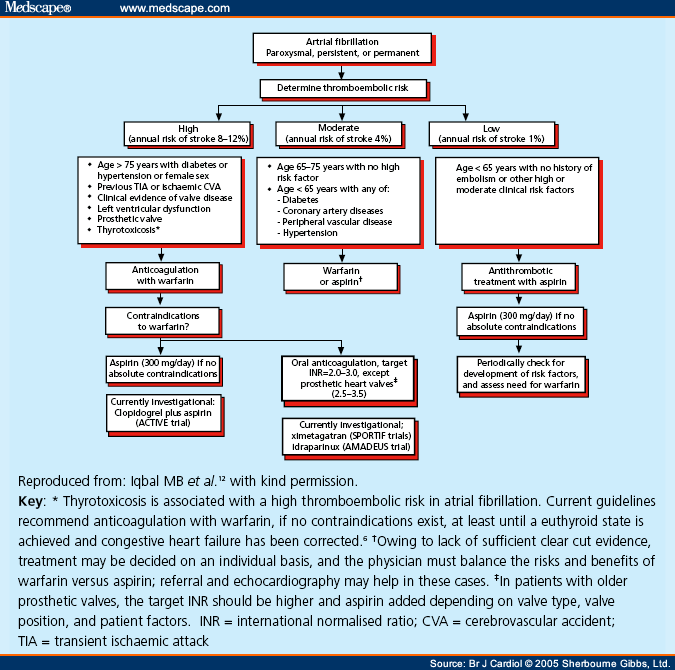
Can you code atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter together?
When the diagnosis is atrial flutter/fibrillation, assign both the code for atrial flutter (I48. 92) and atrial fibrillation based on the specific type of atrial fibrillation. The correct CC status of each specified AF type must be captured.Jan 20, 2020
Is atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation the same?
In atrial fibrillation, the atria beat irregularly. In atrial flutter, the atria beat regularly, but faster than usual and more often than the ventricles, so you may have four atrial beats to every one ventricular beat.
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response?
AFIB with RVR ICD 10 code is I48. This abnormal heartbeat is referred to as “atrial fibrillation” or “AFIB” by doctors.
What I48 19?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48. 19: Other persistent atrial fibrillation.
What is the ICD-10 code for atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response?
Using the ICD 10 code I48. 91, you may identify a diagnosis that is eligible for reimbursement. For example, AFib with slow ventricular response ICD 10 code is 148.91.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
I63.99.
How long does a persistent atrial fibrillation last?
Other persistent atrial fibrillation – usually documented as “chronic persistent” or “persistent NOS,” Other persistent atrial fibrillation is that which lasts longer than a week, but less than a year; requires pharmacologic treatment or electrical cardioversion.
How do you know if you have AF?
AF can exist without any symptoms and remain undetected until the person has a medical check-up. The common signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation are: Palpitations – fast irregular heartbeat, pounding, fluttering or flip-flops in the chest. Dizziness. Shortness of breath.
Why is AF a problem?
It is caused by problems with the heart’s electrical system. AF can lead to longer ICU stay and is associated with an increased risk of mortality. The American Heart Association estimates that about 2.7 million Americans are living with AF. Effective October 1, 2019, ICD-10 category 148 Atrial fibrillation has been expanded from four codes ...
What happens when your heart beats too fast?
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often abnormally fast heartbeat that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. Normally, the heart contracts and relaxes to a regular beat (between 60 and 100 beats a minute) when the person is resting.
Is AF common after cardiac surgery?
AF is wide spread among older patients admitted to ICU with chronic conditions who are at risk for critical illness. New-onset AF has been found to be a common complication after cardiac surgery and also occurs among critically ill patients with a high incidence of renal failure and sepsis.
How long does AFIB last?
There are different types of afib based on how long it lasts. Persistent – Lasts more than 7 days and it needs an intervention to restore the rhythm. Chronic (Permanent) – Chronic stays more than 12 months and it is called permanent when the abnormal heart rhythm cannot be restored.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
Common symptoms occur are palpitation, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness and reduced ability to exercise.
Is AFIB fatal?
Atrial Fibrillation is an irregular (often rapid) heartbeat which may lead to blood clot in the heart and travel to other parts of the body and make blocks. Afib itself is not fatal but it is critical when it leads to stroke or heart failure. Hence Afib needs to be managed.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for glaucoma bilateral unspecified
- 2. icd 9 code for allergic reaction to bee sting
- 3. icd 10 code for 2 vessel umbilical cord in pregnancy
- 4. icd 10 cm code for sti screening
- 5. icd 10 code for rheumatoid arhritis
- 6. icd 10 code for sprain of right dorsal paraspinous groups
- 7. icd 10 code for monitoring of therapuetic medications
- 8. icd 10 code for left hip flexor tendonitis
- 9. icd 10 code for laceration left heel
- 10. icd 10 code for muscle spasm of right lower extremity