What is the ICD 10 code for Barrett esophagus without dysplasia?
Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia 1 K22.70 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K22.70 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K22.70 - other international versions of ICD-10 K22.70 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal cancer?
Disease of esophagus, unspecified. K22.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM K22.9 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K22.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 K22.9 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal hernia?
K22.70 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K22.70 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K22.70 - other international versions of ICD-10 K22.70 may differ. hiatus hernia ( K44.-) esophageal varices ( I85.-)
What is the symptomatology of Barrett esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus. The symptomatology of barrett esophagus is that of gastro-esophageal reflux. It is the precursor of most esophageal adenocarcinomas. (who) Syndrome including peptic ulcer of the lower esophagus, often with stricture, due to the presence of columnar lined epithelium, which may contain functional mucous cells, parietal cells,...
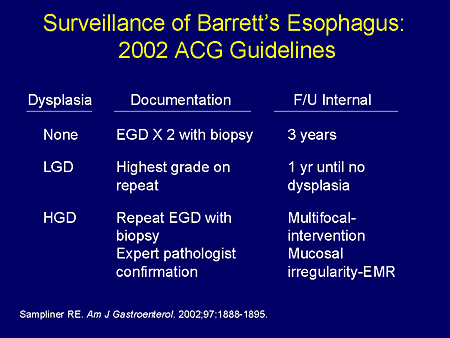
What is the ICD 10 code for Barrett's esophagus with high grade dysplasia?
K22. 711 - Barrett's esophagus with high grade dysplasia | ICD-10-CM.
What are the four stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages, or grades, of Barrett's are: Non-dysplastic, Indefinite, Low grade Dysplasia, and High Grade Dysplasia, which can lead to Intramucosal Carcinoma.
What is the ICD 9 code for Barrett's esophagus?
530.2Barrett's esophagus is a chronic complication associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease. The ICD-9-CM code used for Barrett's esophagus, 530.2, is also used for patients with “ulcer of the esophagus.”
What is Barrett's oesophagus?
Barrett's oesophagus is a medical condition where some of the cells in your oesophagus grow abnormally. If you have Barrett's oesophagus you are slightly more likely to get oesophageal cancer. But this is not common. It is sometimes called a pre-cancerous condition.
What is the survival rate for Barrett's esophagus?
During the 1960s and 1970s, only about 5% of patients survived at least 5 years after being diagnosed. Now, about 20% of patients survive at least 5 years after diagnosis.
What is the best treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Preferred treatments include: Endoscopic resection, which uses an endoscope to remove damaged cells to aid in the detection of dysplasia and cancer. Radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat to remove abnormal esophagus tissue. Radiofrequency ablation may be recommended after endoscopic resection.
What is the ICD-10 code for gastroesophageal reflux?
ICD-10 code K21. 9 for Gastro-esophageal reflux disease without esophagitis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What does diagnosis code K21 9 mean?
ICD-10 code: K21. 9 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease without oesophagitis.
What does the medical code K21 9 mean?
- K21.9 (gastro-esophageal reflux disease. without esophagitis)
What causes Barrett's disease?
Refluxed stomach acid that touches the lining of your esophagus can cause heartburn and damage the cells in your esophagus. Between 10 and 15 percent of people with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus. Obesity—specifically high levels of belly fat—and smoking also increase your chances of developing Barrett's esophagus.
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed?
How do doctors diagnose Barrett's esophagus? Doctors diagnose Barrett's esophagus with an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and a biopsy. Doctors may diagnose Barrett's esophagus while performing tests to find the cause of a patient's gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms.
Is Barrett's esophagus a serious condition?
Barrett's esophagus is a potentially serious complication of GERD, which stands for gastroesophageal reflux disease. In Barrett's esophagus, normal tissue lining the esophagus -- the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach -- changes to tissue that resembles the lining of the intestine.
How many stages does Barrett's esophagus have?
DISEASE PROGRESSION AND COMPLICATIONS There are three stages of Barrett's esophagus, which range from intestinal metaplasia without dysplasia to high-grade dysplasia.
How fast does Barrett's progress?
Barrett esophagus (BE) is a precancerous condition that progresses to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) at an estimated rate of 0.5% to 0.9% per year.
How often should you have an endoscopy if you have Barrett's esophagus?
Usually, you don't need treatment at this stage. But your healthcare provider will want to monitor the condition. You'll need to have an upper endoscopy every two to three years.
How do you keep your Barrett's esophagus from progressing?
Getting plenty of fiber in your daily diet is good for your overall health. Medical research shows that it may also help prevent Barrett's esophagus from worsening and lower your risk of cancer in the esophagus. Add these and other fiber-rich foods to your daily diet: fresh, frozen, and dried fruit.
What is a varices esophageal?
esophageal varices ( I85.-) malignant neoplasm of esophagus ( C15.-) A condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus have changed or been replaced with abnormal cells that could lead to cancer of the esophagus.
What is the name of the condition where the cells in the lower part of the esophagus have changed
malignant neoplasm of esophagus ( C15.-) A condition in which the cells lining the lower part of the esophagus have changed or been replaced with abnormal cells that could lead to cancer of the esophagus. The backing up of stomach contents (reflux) may irritate the esophagus and, over time, cause barrett's esophagus.
What is the term for a condition where the lining of the lower esophagus is damaged?
A condition with damage to the lining of the lower esophagus resulting from chronic acid reflux (esophagitis, reflux). Through the process of metaplasia, the squamous cells are replaced by a columnar epithelium with cells resembling those of the intestine or the salmon-pink mucosa of the stomach.
What is Barrett's columnar epithelium?
Barrett's columnar epithelium is a marker for severe reflux and precursor to adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Esophageal lesion lined with columnar metaplastic epithelium which is flat or villiform. Barrett epithelium is characterized by two different types of cells: goblet cells and columnar cells. The symptomatology of barrett esophagus is that ...
The ICD code K227 is used to code Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus (British English: Barrett's oesophagus), sometimes called Barrett syndrome, Barrett esophagus, or columnar epithelium lined lower oesophagus (CELLO), refers to an abnormal change (metaplasia) in the cells of the lower portion of the esophagus.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K22.719 - Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia, unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K22.719. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K22.719 and a single ICD9 code, 530.85 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is wrong with the esophagus?
You may also become aware of it when something is wrong. The most common problem with the esophagus is gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). It happens when a band of muscle at the end of your esophagus does not close properly. This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it.
What is a varices esophageal?
esophageal varices ( I85.-) A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder that affects the esophagus. Representative examples of non-neoplastic disorders include esophagitis and esophageal ulcer. Representative examples of neoplastic disorders include carcinomas, lymphomas, and melanomas.
Can GERD cause heartburn?
This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. Over time, gerd can cause damage to the esophagus. Other problems include heartburn and cancer .treatment depends on the problem. Some get better with over-the-counter medicines or changes in diet.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for erectile dysfunction due to diabetes
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for chronic pansinusitis
- 3. icd 10 code for abnormal glucose level
- 4. icd 10 code for positive fobt
- 5. icd 10 cm code for cvd
- 6. icd-10 code for active labor without delivery
- 7. icd 10 cm pcs code for primary median sternotomy incision was made, and the pericardium was opened
- 8. icd 10 code for ajovy injection
- 9. icd 10 code for flushed face
- 10. icd 10 code for multiple rib fractures unspecified