Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What are the common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
What are ICD-10 diagnostic codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes
| A00.0 | B99.9 | 1. Certain infectious and parasitic dise ... |
| C00.0 | D49.9 | 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) |
| D50.0 | D89.9 | 3. Diseases of the blood and blood-formi ... |
| E00.0 | E89.89 | 4. Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic ... |
| F01.50 | F99 | 5. Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopme ... |
What does ICD - 10 stand for?
The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
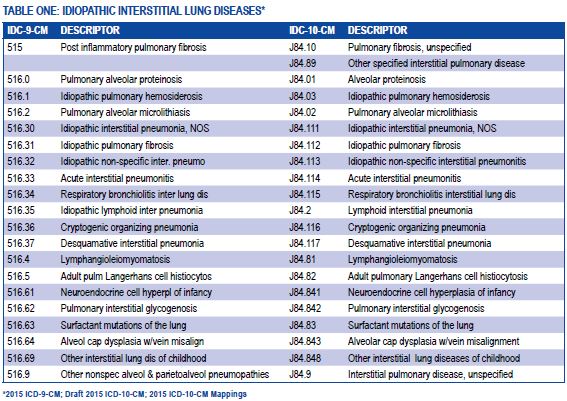
What is the ICD-10 code for lung scarring?
Mayo Clinic defines Pulmonary Fibrosis as lung disease that occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. If the scarring is an imaging finding then that will be integral to the actual condition of fibrosis, so only code J84. 10 will be needed.
What causes pulmonary fibrosis?
Causes of pulmonary fibrosis include environmental pollutants, some medicines, some connective tissue diseases, and interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease is the name for a large group of diseases that inflame or scar the lungs. In most cases, the cause cannot be found.
What happens in lung fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. This thickened, stiff tissue makes it more difficult for your lungs to work properly. As pulmonary fibrosis worsens, you become progressively more short of breath.
What's the code for hepatic fibrosis?
ICD-10 Code for Hepatic fibrosis- K74. 0- Codify by AAPC.
Does COVID-19 cause pulmonary fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a feared complication of respiratory infections. We found that among survivors of severe COVID-19, 20% of non-mechanically ventilated and 72% of mechanically ventilated individuals had fibrotic-like radiographic abnormalities 4 months after hospitalisation.
What's the difference between COPD and pulmonary fibrosis?
COPD is an umbrella term for several types of lung diseases, including emphysema. What they have in common are damaged air sacs or collapsed tubes that may leave you feeling breathless. IPF, on the other hand, is when your lung tissue gets scarred and stiff.
How serious is fibrosis of the lungs?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious, lifelong lung disease. It causes lung scarring (tissues scar and thicken over time), making it harder to breathe. Symptoms may come on quickly or take years to develop. No cure exists.
Can you recover from lung fibrosis?
There is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis. Current treatments are aimed at preventing more lung scarring, relieving symptoms and helping you stay active and healthy.
What is the treatment for fibrosis?
Currently, two drugs are FDA-approved for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), which is the most common form of PF. These include nintedanib (Ofev®) and pirfenidone (Esbriet®).
What causes hepatic fibrosis?
The most common causes of hepatic fibrosis are hepatitis B and C, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and alcohol abuse. Fibrosis does not cause symptoms unless it progresses to cirrhosis. Liver biopsy, although imperfect, is the gold standard diagnostic test but has been increasingly supplanted by noninvasive alternatives.
What is portal fibrosis?
Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis is a syndrome of obscure etiology, characterized by 'obliterative portovenopathy' leading to PHT, massive splenomegaly and well-tolerated episodes of variceal bleeding in young adults from low socioeconomic backgrounds, having near normal hepatic functions.
What are the stages of liver fibrosis?
There are five stages (F0: no scarring (no fibrosis); F1: minimal scarring; F2: scarring has occurred and extends outside the liver area (significant fibrosis); F3: fibrosis spreading and forming bridges with other fibrotic liver areas (severe fibrosis); F4: cirrhosis or advanced scarring).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right ear lump
- 2. what is the icd 10 code for nonexcisional debridement of buttock ulcer
- 3. icd 10 code for anca associated vasculitis
- 4. icd 10 code for right hemiplegia traumatic injury
- 5. icd 10 code for allergic reaction
- 6. what is the icd 9 code for right ventricular dysfunction
- 7. icd 10 cm code for dysphagia elevated blood pressure reading
- 8. icd 9 code for nerve conduction study
- 9. icd 10 cm code for right indirect inguinal hernia
- 10. icd 10 code for enterovirus