What is the code for GI bleed?
ICD-10-CM Code K92.2 Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, unspecified BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 K92.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of gastrointestinal hemorrhage, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code K922 is used to code Gastrointestinal bleeding
What is the ICD 10 code for gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Feb 15, 2020 · The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM Z85. 01 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z85. 01 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z85. Then, how do you code GI bleed? Assign code 578.1 Hematochezia for documentation of …
What is the ICD 10 code for sigmoid colon?
Oct 01, 2021 · It generally indicates bleeding of the upper gastrointestinal tract. ICD-10-CM K92.0 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 377 Gastrointestinal hemorrhage with mcc 378 Gastrointestinal hemorrhage with cc 379 Gastrointestinal hemorrhage without cc/mcc 791 Prematurity with major problems
What is the diagnosis code for upper - GI - bleed?
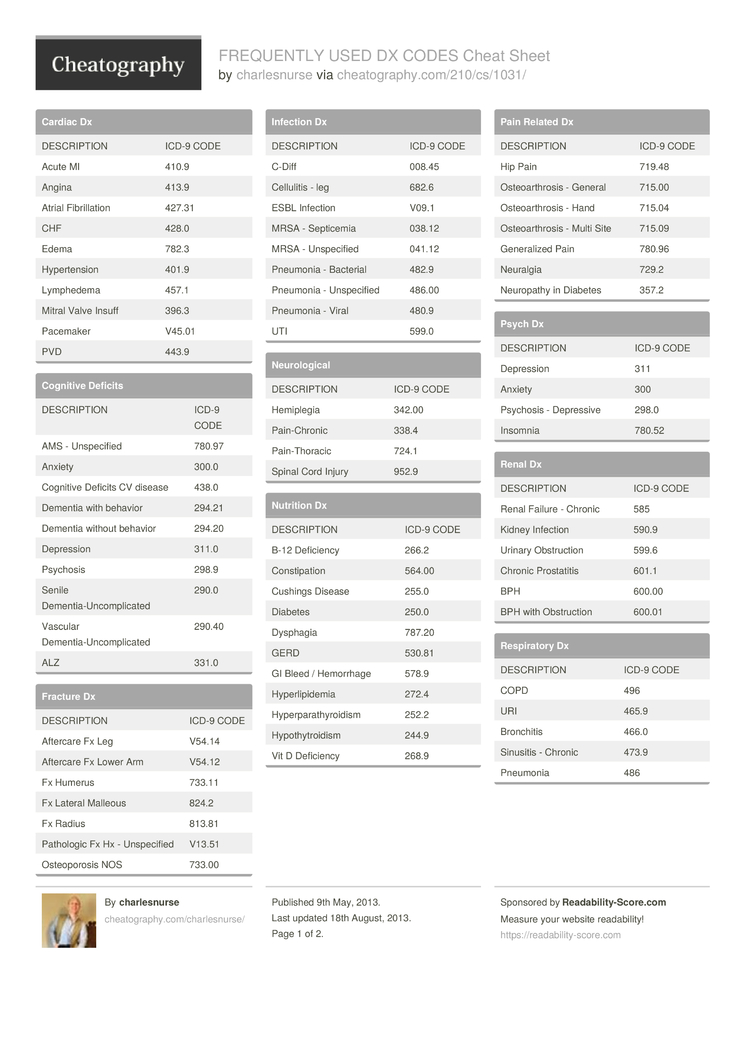
What is the 2021 ICD-10 code for GI bleed?
ICD-10 code K92. 2 for Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD 9 code for GI bleed?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 578.9 : Hemorrhage of gastrointestinal tract, unspecified.
Is GI bleed a diagnosis?
GI bleeding is not a disease, but a symptom of a disease. There are many possible causes of GI bleeding, including hemorrhoids, peptic ulcers, tears or inflammation in the esophagus, diverticulosis and diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, colonic polyps, or cancer in the colon, stomach or esophagus.
What does GI bleed stand for?
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a symptom of a disorder in your digestive tract. The blood often appears in stool or vomit but isn't always visible, though it may cause the stool to look black or tarry.Oct 15, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for gastroenteritis?
ICD-10 code A09 for Infectious gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What K57 92?
ICD-10 code: K57. 92 Diverticulitis of intestine, part unspecified, without perforation, abscess or bleeding - gesund.bund.de.
What are the three main presentations of GI bleeding?
Clinical presentations of gastrointestinal bleeding are classified as overt (acute), occult (chronic) or obscure and the corresponding diagnostic algorithms are illustrated through review of the key evidence and consensus guidelines. Upper endoscopy and colonoscopy are the mainstay of initial investigations.
How do you diagnose an upper GI bleed?
Doctors most often use upper GI endoscopy and colonoscopy to test for acute GI bleeding in the upper and lower GI tracts. Upper GI endoscopy. In an upper GI endoscopy, your doctor feeds an endoscope down your esophagus and into your stomach and duodenum.
What is upper GI bleeding?
Upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage is a medical condition in which heavy bleeding occurs in the upper parts of the digestive tract: the esophagus (tube between the mouth and stomach), the stomach or the small intestine. This is often a medical emergency.Feb 15, 2022
What does GI stand for medical term?
gastrointestinalRefers to the stomach and intestines. Also called gastrointestinal.
What is the most common cause of upper GI bleeding?
Over time, gastritis can cause ulcers or damage parts of the stomach lining, leading to bleeding. The condition can occur due to NSAID use, injury, IBD, or infection.May 10, 2021
How common are GI bleeds?
Epidemiology. Gastrointestinal bleeding from the upper tract occurs in 50 to 150 per 100,000 adults per year. It is more common than lower gastrointestinal bleeding which is estimated to occur at the rate of 20 to 30 per 100,000 per year. Risk of bleeding is more common in males and increases with age.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for flu shot 2015
- 2. icd 10 cm code for cyst on scrotum
- 3. icd 10 code for repair of ruptured globe with uveal prolapse
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for fall from a tree
- 5. icd 10 code for bronchiectiasis
- 6. icd 10 cm code for claravis
- 7. icd 10 code for tinea capitis with kerion
- 8. icd 10 code for history of oophorectomy
- 9. icd 10 code for abnormal nerve conduction study
- 10. icd 10 code for possible drug put in dring