What is mild to moderate left foraminal stenosis?
Moderate neural foraminal narrowing refers to the gradual constriction of the foramina, which are the nerve passageways in the spinal column that has caused nerve (neural) compression. As we age, these small passageways can slowly close around the nerves they are supposed to protect, resulting in neck and back pain.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for neural foraminal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis, cervical region
- M48.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M48.02 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M48.02 - other international versions of ICD-10 M48.02 may differ.
What is treatment for iliac artery stenosis?
- Hoffmann R, Mintz GS, Dussaillant GR, et al. ...
- Mehran R, Dangas G, Abizaid AS, et al. ...
- Kudo T, Chandra FA, Ahn SS. ...
- Koizumi A, Kumakura H, Kanai H, et al. ...
- Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Loewe C, et al. ...
- Laird JR, Katzen BT, Scheinert D, et al. ...
- Tosaka A, Soga Y, Iida O, et al. ...
- Davies MG, Bismuth J, Saad WE, et al. ...
- Kropman RH, Bemelman M, Vos JA, et al. ...
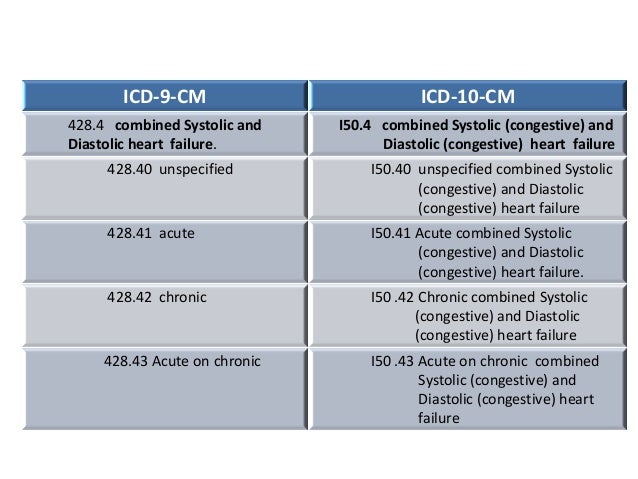
What is ICD-10 code for bilateral carotid stenosis?
ICD-10 Code for Occlusion and stenosis of bilateral carotid arteries- I65. 23- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for right carotid stenosis?
21.
What is the CPT code for right carotid stenosis?
2 - Occlusion and stenosis of carotid artery.
What is left carotid stenosis?
Carotid artery stenosis is a condition that happens when your carotid artery, the large artery on either side of your neck, becomes blocked. The blockage is made up of a substance called plaque (fatty cholesterol deposits).
How do you code a carotid artery stenosis?
With this update, as long as bilateral carotid artery disease is documented with occlusion and stenosis, code I65. 23 (Occlusion and stenosis of bilateral carotid arteries) should be used.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for LAD stenosis?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I25. 84 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the difference between 93880 and 93882?
Remember that a bilateral study which is not complete (i.e., limited) would be classified by CPT code 93882. For evaluation of carotid arteries, use CPT codes 93880, duplex scan of extracranial arteries, complete bilateral study or 93882, unilateral or limited study.
What ICD-10 DX code covers CPT 93880?
ICD-10 Codes That Support Medical Necessity and Covered by Medicare Program: Group 1 Paragraph: Extracranial Arteries Studies (93880-93882) Use a diagnosis code of R22. 1 (localized swelling, mass, and lump, neck) to report pulsatile neck mass.
What does CPT code 93880 mean?
DUPLEX SCAN OF EXTRACRANIAL ARTERIES93880. DUPLEX SCAN OF EXTRACRANIAL ARTERIES; COMPLETE BILATERAL STUDY.
What is common carotid artery?
Description. The Common Carotid artery is a large elastic artery which provides the main blood supply to the head and neck. The carotid arteries are the primary vessels supplying blood to the brain and face.
What is PSV and EDV?
PSV = peak systolic velocity. EDV = end diastolic velocity.
What is moderate carotid stenosis?
Moderate stenosis was defined as a peak systolic velocity of 125 to 230 cm/s at the site of maximal luminal narrowing.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left brachial vein thrombosis
- 2. icd 10 code for insect bite bilateral legs
- 3. icd-10 code for bariatric surgery clearance
- 4. icd 10 code for elevated wbc
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for wrist pain
- 6. icd 10 code for ordering std tests
- 7. icd 10 code for left buttock pain
- 8. icd 10 code for pedestrian hit by car
- 9. icd 10 code for bloated abdomen
- 10. icd 10 code for hyper k