How is a dilated aortic root repaired?
Your surgeon will remove the bulging weak area and sew a man-made substitute, called a graft, into place. If the aortic valve is not healthy, your surgeon may repair it or replace it with an artificial valve. After your surgeon does all of the repairs, normal blood flow through your heart and your aorta will resume.
What is the ICD 10 code for aortic root replacement?
The procedure code 02RX0KZ is in the medical and surgical section and is part of the heart and great vessels body system, classified under the replacement operation. The applicable bodypart is thoracic aorta, ascending/arch. 02RX0KZ replaces the following previously assigned ICD-10-PCS code (s):
What is the ICD 10 code for aortic stenosis?
Rheumatic aortic stenosis
- I06.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I06.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I06.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 I06.0 may differ.
What is aortic root abscess code?
Aortic root abscess is a complication of aortic valve infective endocarditis. Not uncommon, this is a devastating disease associated with high morbidity and mortality. It usually occurs in immune-compromised, debilitated patients with multiple co-morbidities or in I/V drug abusers either on native or on prosthetic valves.
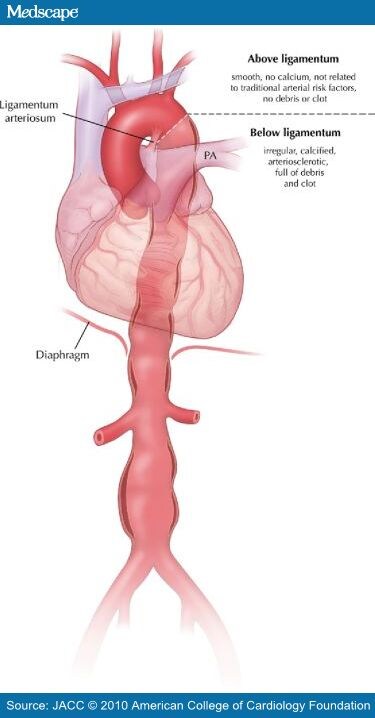
What is the ICD 10 code for aortic root dilatation?
Q25.44Q25. 44 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q25.
What is a mildly dilated aortic root?
Otherwise known as an aortic root aneurysm, a dilated aortic root is when the first section of the aorta, where the aortic valve resides, becomes enlarged. When this enlargement reaches a critical size, there is a risk of it rupturing or tearing, leading to a life-threatening situation.
Is a dilated aortic root an aneurysm?
An aortic root aneurysm occurs in the beginning, or root, of the aorta. The aorta is the body's largest blood vessel. It transports blood to the body from the heart. Doctors also call an aortic root aneurysm a dilated aortic root.
What is a mild dilated aorta?
A mild to moderately dilated ascending aorta was defined as having an aorta ascendens dimension between 40 mm to 45 mm on the computer tomography.
How common is a mildly dilated aortic root?
Aortic root aneurysms appear in less than 1% of open-heart surgery patients, but they can cause aortic regurgitation, dissection, and rupture with high morbidity and mortality.
What is considered aortic root dilation?
The risk of aortic dilation increases with age and the risk of dissection increases as the aortic diameter increases [25, 26]. When the aortic root diameter is above 4.5 cm, there is a family history of aortic dissection, or aortic diameter change is rapid it is recommended to perform echocardiogram annually [21].
Is a dilated aorta the same as an aneurysm?
Nevertheless, by common convention, aortic dilatation refers to a dimension that is greater than the 95th percentile for the normal person age, sex and body size. In contrast, an aneurysm is defined as a localized dilation of the aorta that is more than 50% of predicted (ratio of observed to expected diameter ≥ 1.5).
Is the aortic root part of the thoracic aorta?
The Thoracic Aorta has 4 distinct parts: Aortic Root – Lies in the front portion of the chest below the sternum. It starts at the level of the heart and includes the aortic valve and the portion where the coronary arteries arise called the Sinus of Valsalva.
Where is an aortic root aneurysm?
An aortic root aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of a specific part of the aorta, your largest artery that carries blood from your heart to the rest of the body. This type of thoracic aortic aneurysm occurs at the point the aorta exits the heart, which is where the aortic valve is located.
How do you fix a dilated aortic root?
In aortic valve and root replacement (composite aortic root replacement), your surgeon removes a section of the body's largest blood vessel (aorta) your aortic valve. The section of your aorta is replaced with an artificial tube (graft), and your aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
What causes a dilated aorta?
Causes of thoracic aortic aneurysms may include: Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis). Plaque buildup on the artery walls causes the arteries to become less flexible. Additional pressure can cause the arteries to weaken and widen (dilate).
What size is a dilated ascending aorta?
In adults, an ascending aortic diameter greater than 4 cm is considered to indicate dilatation 4. Aneurysmal dilatation is considered when the ascending aortic diameter reaches or exceeds 1.5 times the expected normal diameter (equal to or greater than 5 cm).
How serious is a mildly dilated ascending aorta?
An ascending aortic aneurysm is a weak spot in the top part of your aorta, which is the main artery in your body. The aneurysm bulges outward, and may cause your blood vessel wall to tear or break open. It's a life-threatening condition.
How is a dilated aortic root treated?
In aortic valve and root replacement (composite aortic root replacement), your surgeon removes a section of the body's largest blood vessel (aorta) your aortic valve. The section of your aorta is replaced with an artificial tube (graft), and your aortic valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
How is a dilated aorta treated?
Aortic root surgery. This type of open-chest surgery is done to treat an enlarged section of the aorta to prevent a rupture. Aortic aneurysms near the aortic root may be related to Marfan syndrome and other related condition. A surgeon removes part of the aorta and sometimes the aortic valve.
Can you live with a dilated aorta?
Yes, you can live with an aortic aneurysm, and there are many ways to prevent dissection (splitting of the blood vessel wall that causes blood to leak) or worse, a rupture (a burst aneurysm).
What is a dilated aorta?
Dilated aortas are prone to atherosclerotic plaque formation, which leads to an increased risk of stroke and mini-strokes, also called transient ischemic attacks. One of the simplest methods of screening for an enlarged aorta is with an ultrasound or echocardiogram. The first few inches of the aorta can be easily seen and measured ...
How many centimeters does an aorta dilate?
When the aorta reaches 4.5 centimeters in diameter, it is classified as an aneurysm. Once an aorta enlarges or dilates to 3.7 centimeters or greater, it may continue to dilate at an average rate of 2 millimeters per year, states HealthCentral. Therefore, dilated aortas should be monitored yearly.
What causes aorta to dilate?
Other issues leading to dilated aortas include trauma or infection.
How does a medical practitioner help a weakened aorta?
Medical practitioners work with the patient to mitigate the factors leading to a weakened aorta. These preventative measures help slow or prevent the formation of aneurysms, which can lead to ruptured aneurysms. Certain forces within the body contribute to aorta weakening and dilation.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sterla
- 2. icd-10 code for x ray right foot
- 3. icd 10 code for adverse effect of amphetamines
- 4. icd 10 code for pregnancy complications
- 5. physical exam for rehabilation icd 10 code
- 6. icd 10 code for splenic varices
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for mavyret
- 8. 2017 icd 10 code for surgical treatment for pathologic fracture to his right femur in the hospital
- 9. icd 10 code for fracture ankle
- 10. icd 10 code for bilateral leg myalgias