What is the incidence of peroneus quartus?
Peroneus quartus and functional ankle instability In the literature the incidence of a supernumerary peroneus quartus muscle varies from 0 to 21.7%. Most times this muscle is asymptomatic and is only fortuitously discovered. However some cases of chronic ankle pain or instability have been reported in the literature.
What is the CPT code for peroneal debridement?
1. Right foot resection of prominent peroneal tubercle, calcaneus (CPT 28120) 2. Right Peroneal longus tendon debridement, removal of low lying muscle belly, distal to tip of the fibula (CPT 28200) 3. Right foot debridement of peroneal brevis tendon (CPT 28200)
What is the CPT code for peroneal tubercle removal?
Right foot resection of prominent peroneal tubercle, calcaneus (CPT 28120) 2. Right Peroneal longus tendon debridement, removal of low lying muscle belly, distal to tip of the fibula (CPT 28200) 3. Right foot debridement of peroneal brevis tendon (CPT 28200)
What is the CPT code for repair of peroneus tendon and groove deepening?
However, I have CPT 27676 for the Repair of peroneus tendon and groove deepening in the fibula. Since the provider includes cutting fibular bone "fibular grooving" (fibular osteotomy) I believe CPT 27676 is the correct code. This is where I am pulling it from the OP report you posted:
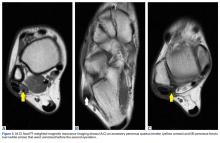
What is the ICD-10 code for split tear of peroneus brevis tendon?
S86. 312A - Strain of muscle(s) and tendon(s) of peroneal muscle group at lower leg level, left leg [initial encounter] | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for peroneal tendonitis?
ICD-10 Code for Peroneal tendinitis, right leg- M76. 71- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for left peroneal tendonitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Peroneal tendinitis, left leg M76. 72.
What is other specified disorders of Muscle?
M62.8 - Other specified disorders of muscle. M62.81 - Muscle weakness (generalized) M62.82 - Rhabdomyolysis. M62.83 - Muscle spasm. M62.84 - Sarcopenia.
What is peroneus?
The peroneus longus muscle is a major mover and stabilizer of your ankle. The muscle, along with the peroneus brevis and tertius, courses down the lateral side of your lower leg and attaches to your foot. It serves to move your foot and ankle in various directions.
What is peroneal tendonitis?
Peroneal tendonitis (also known as peroneal tendinopathy) is a form of tendonitis that affects the foot and ankle. Peroneal tendonitis is a condition that causes pain on the outside of the foot and up the outside of your lower leg when walking or running.
Where are the peroneal tendons?
The peroneal tendons are two tendons in the foot that run side-by-side behind the outer ankle bone. One peroneal tendon attaches to the outer part of the midfoot, while the other runs under the foot and attaches near the inside of the arch.
Where is the peroneus brevis tendon?
The peroneus brevis tendon is located directly behind the fibula bone and in general is more prone to injury. It serves to evert the foot, meaning to move it outwardly away from the rest of the leg.
Is peroneus brevis flexor or extensor?
Answer-peroneals are considered "flexors" or evertors, the AMA recently confimed to her, after consulting with a CPT advisor from the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society.
What are the 7 most common diseases of the muscular system?
Types of neuromuscular disorders include:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.Multiple sclerosis.Muscular dystrophy.Myasthenia gravis.Myopathy.Myositis, including polymyositis and dermatomyositis.Peripheral neuropathy.More items...
What is the ICD-10 code for musculoskeletal pain?
ICD-10-CM Code for Myalgia M79. 1.
What is the most common muscle disease?
The most well known of the muscular dystrophies is Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), followed by Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD).
What muscle is the peroneal compartment?
Peroneus quartus muscle. Originally, several accessory muscles were distinguished in the peroneal compartment: This terminology has been simplified by summarizing all peroneal compartment variants under the definition of a peroneus quartus muscle as a muscle arising from the lower leg and inserting onto the lateral hind and midfoot.
Where is the PQ muscle located?
The origin of the PQ muscle is the distal lateral portion of the fibula. It typically descends medial and posterior to the peroneal tendons.
What is accessory peroneal muscle?
Accessory peroneal muscles. Accessory peroneal muscles are a group of accessory muscles that can occur in the foot region as a normal variant in some individuals. The peroneal compartment is known as the lateral compartment of the leg.
What is the origin of the PQ muscle?
the peroneal tendons. the lateral retinaculum of the ankle. the cuboid bone. The origin of the PQ muscle is the distal lateral portion of the fibula. It typically descends medial and posterior to the peroneal tendons.
Is the Peroneus Tertius lateral or lateral?
The peroneus tertius muscle is not a lateral (peroneal) compartment muscle, as it runs in the same compartment as the extensor digitorum longus, that is the anterior compartment of the leg. It arises from the lower third of the anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane and from an intermuscular septum connecting it with the peroneus brevis muscle (septum of Otto). Its tendon passes under the superior and inferior extensor retinacula of the ankle and inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for pro-air inhaler
- 2. icd 10 cm code for albuterol.
- 3. icd 10 code for right arm ecchymosis
- 4. icd 9 code for lipoma on neck
- 5. icd 10 code for e d
- 6. icd 10 code for struck against stationary object
- 7. icd 10 code for presence of cataract
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for pleural effusion
- 9. icd 10 code for idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy
- 10. icd 10 code for type 2 diabetes with ketoacidosis without coma