What is the ICD 10 code for portal thrombosis?
Portal vein thrombosis. I81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I81 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I81 - other international versions of ICD-10 I81 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for portal vein?
ICD-10-CM Codes › I00-I99 Diseases of the circulatory system › I80-I89 Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, not elsewhere classified › Portal vein thrombosis I81 Portal vein thrombosis I81-
What is deep vein thrombosis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I81 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Portal vein thrombosis. Thrombosis of portal vein; hepatic vein thrombosis (I82.0); phlebitis of portal vein (K75.1); Portal (vein) obstruction. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I81. I81 Portal vein thrombosis.
What is thrombosis (thrombus)?
ICD-10 code I81 for Portal vein thrombosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymp Select Code Sets
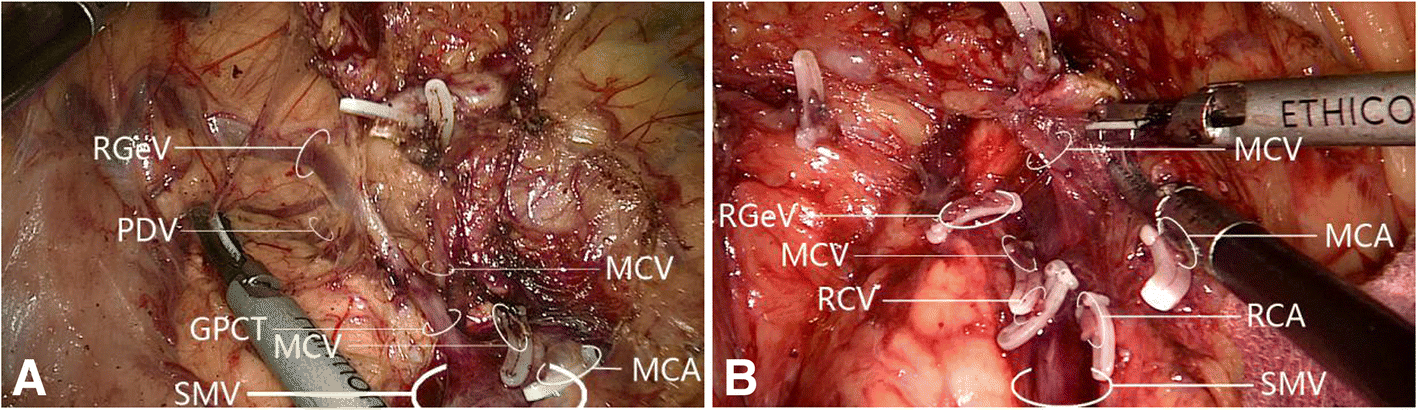
What is portal venous thrombus?
Is portal vein thrombosis the same as DVT?
...
| Portal vein thrombosis | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Angiology |
What is the ICD-10 code for portal hypertension?
Is portal vein thrombosis the same as portal hypertension?
What is portal artery?
How do you rule out portal vein thrombosis?
What is the meaning of portal hypertension?
What causes portal vein hypertension?
What are the signs of portal hypertension?
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
- Enlarged veins (varices) of the esophagus and stomach. ...
- Internal hemorrhoids.
- Weight loss from malnutrition.
- Fluid buildup in the belly (ascites)
- Kidney malfunction.
- Low platelets.
- Fluid on the lungs.
What is portal vein in liver?
How common is portal vein thrombosis?
Does portal vein thrombosis cause high blood pressure?
Where does DVT occur?
Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, is a blood clot that forms in a vein deep in the body. Most deep vein clots occur in the lower leg or thigh. If the vein swells, the condition is called thrombophlebitis. A deep vein thrombosis can break loose and cause a serious problem in the lung, called a pulmonary embolism.
What is the ICd 10 list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I81:
What is the I81 code?
I81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis. The code I81 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
Can you get a DVT from sitting still?
A deep vein thrombosis can break loose and cause a serious problem in the lung, called a pulmonary embolism. Sitting still for a long time can make you more likely to get a DVT. Some medicines and disorders that increase your risk for blood clots can also lead to DVTs. Common symptoms are.
What is the ICD code for portal vein thrombosis?
I81 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICd 9 code for embolus?
Specialty: Vascular Surgery. MeSH Codes: D013927, D013927, D013927, D013927. ICD 9 Codes: 437.6 , 453 , 671.5 , 671.9.
What is the process of forming a blood clot?
Thrombosis (Greek: θρόμβωσις) is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus; Greek: θρόμβος) inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for labile
- 2. icd 10 cm code for hyzaar
- 3. icd 10 code for overdose on drug nsp
- 4. icd 10 code for left knee chondromalacia medial femoral condyle
- 5. icd 10 code for metastatic bone cancer chest
- 6. icd 10 code for old retinal hole
- 7. icd 10 code for hx of marijuana abuse
- 8. icd 10 code for incarcerated epigastric hernia
- 9. what is the icd 10 code for lumbar compression fracture
- 10. icd 10 code for annular tear of lumbar disc