What is the ICD 10 code for azotemia?
| ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 R79.89 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code R798 is used to code Azotemia
What is the ICD 10 code for prerenal uremia?
Pre renal uremia syndrome; Prerenal uremia syndrome; uremia NOS (N19); Prerenal uremia ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N17.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute kidney failure, unspecified
What is prerenal azotemia and postrenal azotemia?
Azotemia may be further described as prerenal, postrenal, or renal azotemia states. Prerenal azotemia, 788.9, postrenal azotemia, 788.9, and azotemia (renal), 790.6, refer to marked elevation of urea nitrogen (and creatine).
What is the pathophysiology of azotemia?
It involves an elevated serum concentration of nonprotein nitrogenous compounds, primarily urea nitrogen, but also creatinine, amino acids, uric acids, creatine, and ammonia. Azotemia is produced by diminished glomerular filtration of these compounds by the kidney.
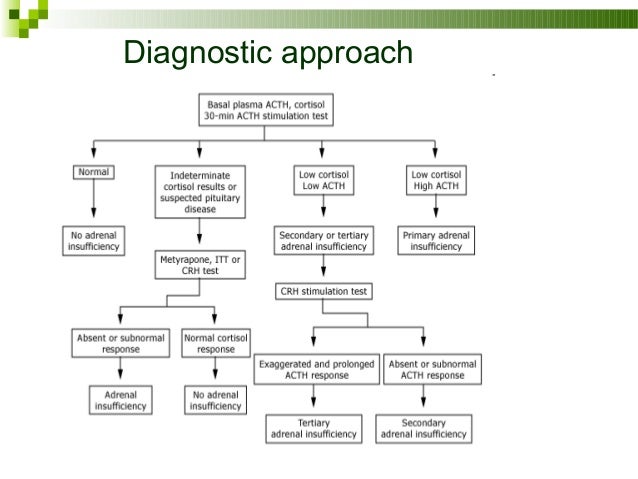
What is Prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia is an abnormally high level of nitrogen waste products in the blood.
How do you code Prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia is assigned to code 788.9, Other symptoms involving urinary system.
Is Prerenal azotemia the same as AKI?
The concept of prerenal azotemia is ingrained in the clinical practice of nephrology. AKI, which is defined by sudden increases in serum creatinine levels, can be classified into three categories: AKI caused by prerenal azotemia, AKI induced by intrarenal causes and AKI induced by postrenal obstruction.
What is the ICD-10 code for azotemia?
89.
What is diagnosis code N28 9?
N28. 9, disorder of kidney and ureter, unspecified.
What is Prerenal AKI?
Prerenal acute kidney injury (AKI) , (which used to be called acute renal failure), occurs when a sudden reduction in blood flow to the kidney (renal hypoperfusion) causes a loss of kidney function. In prerenal acute kidney injury, there is nothing wrong with the kidney itself.
How can you tell the difference between renal and prerenal azotemia?
Prerenal azotemia can usually be distinguished from renal azotemia by clinical signs (evidence of dehydration or hypovolemia), urinalysis (urine should be “adequately” concentrated i.e. > 1.030 in the dog, > 1.040 in the cat, > 1.025 in large animals; usually with no evidence of renal tubule dysfunction such as ...
Is azotemia the same as renal failure?
The primary cause of azotemia is a loss of kidney function. However, the different types of azotemia, which may arise from or be a part of renal failure, have different causes: when fluid flowing through the kidneys isn't enough to remove the nitrogen (prerenal azotemia)
How can you tell the difference between renal and Prerenal?
Response to fluid repletion is still regarded as the gold standard in the differentiation between prerenal and intrinsic AKI. Return of renal function to baseline within 24 to 72 hours is considered to indicate prerenal AKI, whereas persistent renal failure indicates intrinsic disease.
What is R79 89 diagnosis?
R79. 89 - Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry. ICD-10-CM.
What does diagnosis code R79 89 mean?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is ICD-10 code N19?
ICD-10 code N19 for Unspecified kidney failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is azotemia in medical terms?
Azotemia (azot, "nitrogen" + -emia, "blood condition") is a medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds (such as urea, creatinine, various body waste compounds, and other nitrogen-rich compounds) in the blood.
What is the ICD10 code for R79.89?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code R79.89 and a single ICD9 code, 790.99 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICD code for blood chemistry?
R79.89 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
When will the 2022 ICd-10-CM N19 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N19 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is acute renal failure?
Acute renal failure is usually associated with oliguria or anuria, hyperkalemia, and pulmonary edema.
What is renal uremic toxins?
A clinical syndrome associated with the retention of renal waste products or uremic toxins in the blood. It is usually the result of renal insufficiency. Most uremic toxins are end products of protein or nitrogen catabolism, such as urea or creatinine. Severe uremia can lead to multiple organ dysfunctions with a constellation of symptoms.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for allergy panel reg 1
- 2. icd 10 code for depression recurrent mild
- 3. icd code for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
- 4. icd-10 code for intractable back pain
- 5. what is the smartip for icd 10 code l89.222
- 6. icd 10 code for depression situational prolonged
- 7. icd-10 code for breast lump left
- 8. icd 9 code for morbidly obese
- 9. icd 10 code for laceration, tongue, approximately 1 inch in length. (initial encounter.)
- 10. icd 10 code for disc space narrowing at c5-c6