What is cardiac hypokinesia ICD 10 code?
Other specified diseases of gallbladder
- K82.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K82.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K82.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 K82.8 may differ.
What is the difference between pneumonia and pulmonary edema?
- Elevated hydrostatic pressure of pulmonary veins (cardiac failure, constrictive pericarditis, pericardial effusion and fluid overload),
- Low serum proteins (chronic liver disease, protein losing enteropathy, nephrotic syndrome, widespread skin lesions, hypothyroidism and burns),
- Infections (pneumonia, lung abscess, tuberculosis),
What is ICD 10 for pulmonary nodules?
- lung, solitary (subsegmental branch of the bronchial tree) R91.1
- pulmonary, solitary (subsegmental branch of the bronchial tree) R91.1
- solitary, lung (subsegmental branch of the bronchial tree) R91.1
What is ICD for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with (acute) lower respiratory infection
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with mcc
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with cc
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease without cc/mcc

How do you code acute pulmonary edema?
J81. 0, acute pulmonary edema.
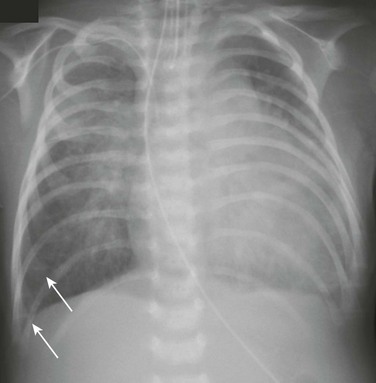
What is pulmonary edema also known as?
Pulmonary edema is a condition in which the lungs fill with fluid. It's also known as lung congestion, lung water, and pulmonary congestion. When pulmonary edema occurs, the body struggles to get enough oxygen and you start to have shortness of breath.
Is pulmonary edema inherent to CHF?
By way of your question, you understand that pulmonary edema is considered integral to heart failure and the two would not be reported together in normal circumstances. But if the etiology of the pulmonary edema is identified as not related to heart failure then it could be reported.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for pulmonary congestion?
514 - Pulmonary congestion and hypostasis. ICD-10-CM.
Is pulmonary edema the same as pulmonary congestion?
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure.
What is an acute pulmonary edema?
Acute pulmonary oedema is a medical emergency which requires immediate management. 1. It is characterised by dyspnoea and hypoxia secondary to fluid accumulation in the lungs which impairs gas exchange and lung compliance. 2.
What heart conditions cause pulmonary edema?
Medical conditions that can cause heart failure and lead to pulmonary edema include:Coronary artery disease. ... Cardiomyopathy. ... Heart valve problems. ... High blood pressure (hypertension). ... Other heart problems. ... Kidney disease. ... Chronic health conditions.
Which side of heart failure causes pulmonary edema?
Left-side heart failure When the left side of the heart is failing, it can't handle the blood it gets from the lungs. Pressure then builds up in the veins of the lungs, causing fluid to leak into the lung tissues. This may cause CHF and pulmonary edema. This causes you to feel short of breath, weak, or dizzy.
Which is most likely to cause pulmonary edema?
The most common cause of pulmonary edema is congestive heart failure, where the heart cannot keep up with the demands of the body.
Is flash pulmonary edema acute?
Abstract. Flash pulmonary edema (FPE) is a general clinical term used to describe a particularly dramatic form of acute decompensated heart failure.
What is the ICD-10 code for chest congestion?
R09. 89 - Other specified symptoms and signs involving the circulatory and respiratory systems | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for fluid overload?
ICD-10 code E87. 70 for Fluid overload, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is Pulmonale?
Definition. Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the arteries of the lung and right ventricle of the heart can lead to cor pulmonale.
What Orthopnea means?
Orthopnea is the sensation of breathlessness in the recumbent position, relieved by sitting or standing. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) is a sensation of shortness of breath that awakens the patient, often after 1 or 2 hours of sleep, and is usually relieved in the upright position.
What is dyspnoea?
Dyspnoea (also is known as dyspnea, shortness of breath or breathlessness). The sensation of uneasy breathing and indicates a medical emergency, Dyspnoea represents one of the most frequent cardinal symptoms globaly. It is a sensation of lacking of the air and of not being able to breathe normally.
What causes emphysema?
The main cause of emphysema is long-term exposure to airborne irritants, including: Tobacco smoke. Marijuana smoke. Air pollution.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as J81. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together , such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. chemical (acute) pulmonary edema (.
What causes pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary edema is usually caused by heart problems, but it can also be caused by high blood pressure, pneumonia, certain toxins and medicines, or living at a high altitude. Symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, and trouble exercising.
What is the disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that
A disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure. Accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues causing disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What causes pulmonary edema?
Pulmonary edema is usually caused by heart problems, but it can also be caused by high blood pressure, pneumonia, certain toxins and medicines, or living at a high altitude. Symptoms include coughing, shortness of breath, and trouble exercising.
What is excessive accumulation of fluid in the lung?
Excessive accumulation of extravascular fluid in the lung, an indication of a serious underlying disease or disorder. Pulmonary edema prevents efficient pulmonary gas exchange in the pulmonary alveoli, and can be life-threatening. Extravascular accumulation of fluid in the pulmonary tissue and air spaces.
What is the disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that
A disorder characterized by accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues that causes a disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure. Accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues causing disturbance of the gas exchange that may lead to respiratory failure.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right sided tinnitus
- 2. icd 10 code for l lumbar paraspinal nodule
- 3. icd 10 code for parainfluenza 4
- 4. icd 20 code for complication of a leg brace
- 5. icd 10 code for lump of skin of lower extremity, right
- 6. icd 10 code for amniotic bronchitis
- 7. icd 10 code for ear infection unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for failed hearing test
- 9. icd 10 code for coma
- 10. icd 9 code for epigastric pain