What is a central slip injury?
A central slip is a section of an extensor tendon which straightens the middle joint of your finger. Recovery. Your damaged tendon has been repaired. It will take about 12 weeks for it to heal fully. During this time, there is a risk that the tendon could rupture (break) and your fingers could become stiff.
What is the ICD 10 code for slipping and falling?
W01.0XXAICD-10-CM Code for Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling without subsequent striking against object, initial encounter W01. 0XXA.
What is an extensor tendon injury?
An extensor tendon injury is damage to the tissues on the back of the hand and fingers. It can make it hard for you to extend your wrist, open your hand, or straighten your fingers. The inability to perform these functions can severely limit hand and upper extremity function.
What is the ICD 10 code for a puncture wound?
239A for Puncture wound without foreign body of unspecified finger without damage to nail, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the diagnosis code for falling?
Z91.81Z91. 81 - History of falling. ICD-10-CM.
How do you code a Fall in ICD-10?
History of fallingZ91. 81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z91. 81 became effective on October 1, 2021.This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z91. 81 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z91. 81 may differ.
What is the tendon on the top of your foot called?
The extensor tendons, located in the top of the foot, are needed for flexing or pulling the foot upward. If they become inflamed due to overuse or wearing shoes without proper support, they may get torn or inflamed. This is known as extensor tendinitis, which can cause significant pain in the top of the foot.
What causes a ruptured tendon in hand?
bites – animal and human bites can cause tendon damage, and a person may damage their hand tendon after punching another person in the teeth. crushing injuries – jamming a finger in a door or crushing the hand in a car accident can divide or rupture a tendon.
What causes common extensor tendon tear?
Causes of Common Extensor Tendon Origin Rupture Common causes may include: Activity that requires repetitive motion of the forearm such as painting, typing, weaving, gardening, lifting heavy objects, and sports. Overuse of the forearm muscles. Direct trauma as with a fall, work injury, or motor vehicle accident.
What is the ICD 10 code for open wound?
The types of open wounds classified in ICD-10-CM are laceration without foreign body, laceration with foreign body, puncture wound without foreign body, puncture wound with foreign body, open bite, and unspecified open wound. For instance, S81. 812A Laceration without foreign body, right lower leg, initial encounter.
What are the classification of open wounds?
Burn Wound Burn wounds can be classified based on the extent of the injury: First-degree burns affect only the epidermis and may cause redness and pain. Second-degree burns affect the epidermis and the dermis and may cause blisters. Third-degree burns reach into the fatty layer under the skin and may destroy nerves.
Which of the following conditions would be reported with Code Q65 81?
Which of the following conditions would be reported with code Q65. 81? Imaging of the renal area reveals congenital left renal agenesis and right renal hypoplasia.
What is a ground level Fall?
A ground-level fall typically is defined as one that begins when a person has his or her feet on the ground. Of those patients who survived hospitalization, 51% were discharged to a skilled nursing facility, the researchers determined, and a third were sent home without assistance.
What is the ICD-10 code for generalized weakness?
ICD-10 code M62. 81 for Muscle weakness (generalized) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Soft tissue disorders .
What is the ICD-10 code for Fall down stairs?
W10.9XXA9XXA for Fall (on) (from) unspecified stairs and steps, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Other external causes of accidental injury .
What is the ICD-10 code for Fall from bed?
E88. 44 - Accidental fall from bed | ICD-10-CM.
When will the 2021 ICd-10-CM S66.303A be effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S66.303A became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.
What causes a central slip injury?
Central slip disruptions can occur as either open or closed injuries. Closed injuries are usually caused by forceful flexion induced by sports injuries or falls, while open injuries can arise from lacerations over the PIP joint (2,3). Failure to recognize this injury can have potentially devastating consequences due to the imbalance of flexor and extensor forces which will lead to a boutonniere deformity (Figure 1). More specifically, the volar migration of the lateral bands and subsequent attenuation of the triangular ligament causes this deformity (Figure 2). These injuries can also arise from fractures of the middle phalangeal base at the insertion of the central slip. Moreover, degenerative conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can also result in disruption of the central slip (3,4).
Where is the central slip of the extensor tendon located?
Arising from the extrinsic extensor tendon and lateral bands, the central slip is a tendinous attachment to the base of the middle phalanx. The transverse retinacular ligament stabilizes the extensor mechanism over the PIP joint and limits any dorso-palmar translation (1).
How to repair a central slip?
Compared to other extensor tendons, the central slip is thinner and may be more challenging to repair in the ED. Often, the best setting to manage these injuries is the operating room. Remember that for all extensor tendon injuries, extension splinting with referral to a hand surgeon within 1 week is an acceptable strategy. In a central slip injury, splinting and referral is generally the preferred management after general wound care and skin closure is performed. This is because specialized procedures such as suturing together of portions of the lateral bands to recreate the central slip may be required. 6
What is a central clip injury?
For injuries of overlying or near the PIP joint, suspect a central clip injury. These extensor tendons run superficially! In the acute setting, a central slip injury will often not result in an anatomically evident abnormality, unlike in a chronic injury which results in a Boutonnière deformity [Figure 2B]. 1 There is often some level of preservation of active PIP extension due to the intact lateral bands. 2
What are the 3 bands of the PIP joint?
As the extensor mechanism of the hand crosses over the PIP joint, it branches into 3 bands: the central slip and 2 lateral bands (Figure 2). 1 The central slip attaches to the middle phalanx and the lateral bands attach to the distal phalanx. When it comes to our case, the 3 bands have significant implications on how we should proceed with examination.
What is a slipped disc?
Spinal disc herniation, also known as a slipped disc, is a medical condition affecting the spine in which a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings. Disc herniation is usually due to age-related degeneration of the anulus fibrosus, although trauma, lifting injuries, or straining have been implicated. Tears are almost always postero-lateral in nature owing to the presence of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the spinal canal. This tear in the disc ring may result in the release of inflammatory chemical mediators, which may directly cause severe pain, even in the absence of nerve root compression.
What is the ICD code for lumbar disc displacement?
Code is only used for patients 15 years old or older. M51.26 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of other intervertebral disc displacement, lumbar region.
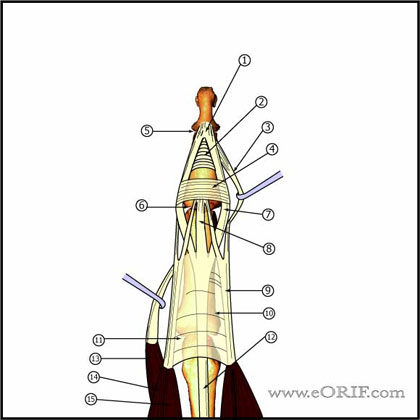
Anatomy
Mechanism and Types of Injury
- Central slip disruptions can occur as either open or closed injuries. Closed injuries are usually caused by forceful flexion induced by sports injuries or falls, while open injuries can arise from lacerations over the PIP joint (2,3). Failure to recognize this injury can have potentially devastating consequences due to the imbalance of flexor and extensor forces which will lead to a boutonnie…
Symptoms
- Patients usually present with pain and swelling over the dorsal PIP joint of the affected finger or a laceration. Digital block is often helpful to further assess extent of injury.
Physical Examination
- After a thorough neurovascular examination, attention can be turned to the digit with a suspected central slip injury. This digit will often be held in flexion at the PIP joint, and exhibit a positive Elson Test (5). Following adequate digital blockade, one can assess the integrity of the central slip by having the patient flex his or her fingers over a table at the PIP joint. As a brief reminder, finger e…
Treatment
- Nonoperative: 6 weeks of PIP joint splinting in full extension, indicated for acute injuries usually <4 weeks old. Full active flexion of the DIP joint is encouraged to avoid stiffness distally and contraction of the oblique retinacular ligament. Part-time splinting then recommended for an additional 4-6 weeks (2,3). Operative: Various operative strategies have been described, includin…
Example Case
- 30 y.o. right handed male who had a motor vehicle accident; was a restrained lone driver when he struck another vehicle and rolled over x2 in his vehicle. Open laceration over the PIPJ of the left middle finger. Left small finger with nail plate injury and radial sided laceration. Left middle finger held in flexion, unable to extend actively or passively. Elson test not possible due to pain. Sensat…
References
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for wrong medication given
- 2. icd 10 code for radiation keratitis to eye welders flash
- 3. icd 9 code for peripheral neuropathy with evidence of callus formation
- 4. icd 10 dx code for change of suprapubic cath
- 5. icd 10 code for pco
- 6. icd 10 code for healed right bimalleolar ankle fracture with pain from retained metal hardware
- 7. icd 10 code for dexa scan medicare
- 8. icd 10 code for mensical tear
- 9. icd 10 code for pancreatitis nos
- 10. icd 9 code for fem pop bypass