What is the ICD 10 code for venous sinus thrombosis?
The ICD code I676 is used to code Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is the presence of acute thrombosis (a blood clot) in the dural venous sinuses, which drain blood from the brain.
What is sigmoid sinus thrombosis?
Lateral sinus thrombosis, also known as sigmoid sinus thrombosis, forms when infection from the adjacent mastoid contacts and penetrates the venous wall and forms a thrombus. Embolization of the thrombus can cause distal disease.
What is the ICD 10 code for intracranial thrombosis?
I67.6 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of nonpyogenic thrombosis of intracranial venous system. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the ICD 10 code for embolism and thrombosis?
Embolism (multiple) (paradoxical) I74.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I74.9. Embolism and thrombosis of unspecified artery 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. intracranial - see also Occlusion, artery, cerebral venous sinus (any) G08. intraspinal venous sinuses or veins G08.
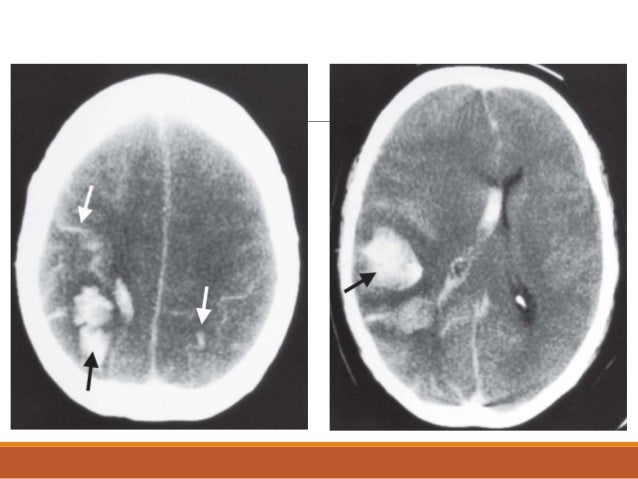
What is sigmoid sinus thrombosis?
Lateral sinus thrombosis, also known as sigmoid sinus thrombosis, forms when infection from the adjacent mastoid contacts and penetrates the venous wall and forms a thrombus. Embolization of the thrombus can cause distal disease.
Is sigmoid sinus thrombosis a stroke?
CVST is a rare form of stroke. It affects about 5 people in 1 million each year. The risk for this kind of stroke in newborns is greatest during the first month. Overall, about 3 out of 300,000 children and teens up to age 18 will have a stroke.
What does sinus thrombosis mean?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a blood clot in the cavernous sinuses. It can be life-threatening. The cavernous sinuses are hollow spaces located under the brain, behind each eye socket. A major blood vessel called the jugular vein carries blood through the cavernous sinuses away from the brain.
What causes sinus venous thrombosis?
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) occurs when a blood clot forms in the brain's venous sinuses. The clot keeps blood from draining out of the brain. As a result, pressure builds up in the blood vessels.
Is sinus venous thrombosis fatal?
In the past, 50% of people with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis survived. Now, the condition has a fatality percentage of fewer than 5% to 10% of people who have it. This is because of better imaging and treatments.
Which sinus is the most common site for thrombosis?
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis is a challenging condition because of its variability of clinical symptoms and signs. It is very often unrecognised at initial presentation. All age groups can be affected. Large sinuses such as the superior sagittal sinus are most frequently involved.
What is the treatment for sinus thrombosis?
Sinus Thrombosis Treatment Clot removal using catheters and other specialized equipment, antibiotics, and anticoagulation drugs are the main methods used for the treatment of venous sinus thrombosis. Your physician may recommend one or a combination of these treatments.
Can you get a blood clot behind your ear?
Cauliflower ear, also known as perichondrial hematoma, is a swelling of the ear caused by a blood clot. This blood clot causes tissue damage that leads to a lumpy appearance that is said to resemble a cauliflower.
Can you get a blood clot in your sinuses?
In cavernous sinus thrombosis, a blood clot develops in the sinuses behind your eyes or at the bottom of your skull after an infection. The clot is meant to prevent the infection from spreading, but it often blocks the blood flow out of your brain.
Can blood thinners cause sinus problems?
Nosebleeds are very common and occur when the fragile blood vessels in the nose are irritated. Blood thinners can cause or worsen nosebleeds. The blood thinners make clotting more difficult; therefore, it may take longer to stop nosebleeds when someone is on blood thinners.
How is sigmoid sinus treated?
Sigmoid Sinus Dehiscence/Diverticulum – Treatment Surgery involves localizing the dehiscence or diverticulum through the mastoid bone and covering the area with either bone and/or bone substitute. In many cases after resurfacing the pulsatile tinnitus greatly reduces or resolves.
Can venous thrombosis cause stroke?
Did you know? DVT does not cause heart attack or stroke. There are two main types of blood clots.
Can sinus issues cause a stroke?
Sinus inflammation, located close to your brain, may also put pressure on its arteries, which could disrupt normal blood flow and lead to a stroke.
Can a stroke affect your sinuses?
Dural sinus thrombosis is not common, and if you or a loved one has had a dural sinus thrombosis, it is likely that you have been diagnosed with a stroke.
How is cerebral venous thrombosis treated?
Treatment, which is started as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed, consists of reversing the underlying cause when known, control of seizures and intracranial hypertension, and antithrombotic therapy. Anticoagulation is the mainstay of acute and subacute treatment for CVT.
What is the left sigmoid sinus?
The sigmoid sinus is actually a pair of two sinuses (right and left) that enable veins to spread from the middle of the head downwards. This dual structure is considered an extension of the transverse sinus, which lies in the hind portion of the brain.
What is a septic embolism?
Septic embolism of intracranial or intraspinal venous sinuses and veins. Septic endophlebitis of intracranial or intraspinal venous sinuses and veins. Septic phlebitis of intracranial or intraspinal venous sinuses and veins. Septic thrombophlebitis of intracranial or intraspinal venous sinuses and veins.
When will ICD-10-CM I67.6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I67.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as I67.6. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
The ICD code I676 is used to code Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is the presence of acute thrombosis (a blood clot) in the dural venous sinuses, which drain blood from the brain. Symptoms may include headache, abnormal vision, any of the symptoms of stroke such as weakness of the face and limbs on one side of the body, and seizures.
Coding Notes for I67.6 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I67.6 - Nonpyogenic thrombosis of intracranial venous system'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I67.6. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 437.6 was previously used, I67.6 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
How to treat sigmoid sinus thrombophlebitis?
Since the introduction of antibiotics, conservative medical treatment has evolved as the mainstay in the management of sigmoid sinus thrombophlebitis. Initiation of broad-spectrum antibiotics is the most important first step. In the presence of clinical and radiologic indications of underlying middle ear and mastoid involvement, a mastoidectomy is warranted, taking care to decompress the bone overlying the sigmoid sinus. Management of the thrombosis within the sinus by surgical manipulation or anticoagulation is controversial. In general, there is resolution of the thrombosis, with complete recanalization of the sigmoid sinus, within 4 to 6 weeks. 77 Thus, a more conservative approach may minimize the risk of surgical manipulation of the sigmoid sinus and anticoagulation. 78–80
What causes a septic thrombus in the middle ear?
Although the exact mechanism is unknown, the likely cause is by direct extension and thrombosis or by cerebral infarction, leading to tissue congestion and obstruction, and secondarily propagating to thrombosis.
What is the superior sagittal sinus?
The superior sagittal sinus is the largest of the venous sinuses ( Fig. 39-6), and it receives blood from the frontal, parietal, and occipital superior cerebral veins and the diploic veins, which communicate with the meningeal veins. Infection can spread from the meninges to the superior sagittal sinus via the diploic veins, especially in cases with purulent exudate near the superior sagittal sinus. The cerebral veins and venous sinuses have no valves; therefore, blood within them can flow in either direction. The superior sagittal sinus drains into the transverse sinus. The transverse sinuses also receive venous drainage from small veins from both the middle ear and the mastoid cells. The transverse sinus becomes the sigmoid sinus before draining into the internal jugular vein. Septic transverse or sigmoid sinus thrombosis can be a complication of acute and chronic otitis media or mastoiditis. Infection spreads from the mastoid air cells to the transverse sinus via the emissary veins or by direct invasion.
What is intracranial thrombophlebitis?
Septic intracranial thrombophlebitis is a bacterial infection of the cortical veins and sinuses with resultant venous thrombosis. It is a complication of bacterial meningitis, subdural empyema, epidural abscess, or infection in the skin of the face, paranasal sinuses, middle ear, or mastoid.
What is the Dense Triangle of Thrombus?
Dense triangle of thrombus, δ sign, if sinus seen in cross section#N#–#N#Phrase used mainly to describe sagittal sinus thrombosis#N#–#N#Sagittal CT reconstruction of TS or coronal reconstruction of SS could show δ sign
Is CSF negative for sigmoid sinus thrombosis?
CSF for culture should be obtained to aid in directing therapy; however, culture may be negative depending on the location and loculation of the abscess. Lateral sinus thrombosis, also known as sigmoid sinus thro mbosis, forms when infection from the adjacent mastoid contacts and penetrates the venous wall and forms a thrombus.
Can septic thrombosis cause nausea?
Patients with septic thrombosis of the superior sagittal sinus have headache, nausea and vomiting, weakness of the lower extremities with bilateral Babinski signs, focal or generalized seizures, and an alteration in the level of consciousness. There may be a rapid development of stupor and coma.
Stroke and Cerebrovascular Center
Sigmoid sinus diverticulum is a rare vascular finding due to an opening in the bone at the area of the sigmoid sinus creating a pouch, or diverticulum. Sometimes, there may be associated stenosis. The diverticulum may present as pulsatile tinnitus.
Diagnosis
Sigmoid sinus diverticulum can be diagnosed either by CT, CTA, MRI or MRV. Cerebral angiography provides definitive diagnosis
Treatment
If no other source is found for the patient's symptoms of pulsatile tinnitus, treatment of the diverticulum via endovascular coiling, if found on the same side of the patient's symptoms, can provide relief in reducing or eliminating this sound.
What are the abnormalities of the sigmoid sinus?
In some cases abnormalities may exist that increase irregular flow in the sigmoid sinus allowing the patients to her their heartbeat. Two different abnormalities may exist. One is a simple absence of bone over the sigmoid sinus known as a dehiscence. The second is both and absence of bone and an outpouching of the sigmoid sinus known as ...
Where is the sigmoid sinus?
The sinus exists on both sides. The sinus is covered normally in bone through the temporal bone near the middle and inner ear.
What are the symptoms of sinus thrombosis?
Pain in the sinus area. Pain or pressure in the ear. Loss of vision, double vision, or blurred vision. Swelling around the eyes. Tests for diagnosing sinus thrombosis. Your doctor also may want you to have imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis. These tests will include: CT scan.
How to tell if you have venous sinus thrombosis?
Diagnosing Sinus Thrombosis. Symptoms of sinus thrombosis. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask you about any symptoms you are experiencing. Symptoms of venous sinus thrombosis may include: Weakness. Headaches. Pain in the sinus area. Pain or pressure in the ear.
What is the most centrally located sinus?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) — The cavernous sinuses are the most centrally located of the dural sinuses. Their irregular shape and location at the base of the skull make them a primary target for infection. CST is often the result of: Bacterial infection. Trauma.
What causes a cavernous sinus thrombosis?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) — The cavernous sinuses are the most centrally located of the dural sinuses. Their irregular shape and location at the base of the skull make them a primary target for infection. CST is often the result of: 1 Bacterial infection 2 Trauma 3 Ear infection 4 Infection of the maxillary teeth
What is a venous clot?
Sinus thrombosis, or venous sinus thrombosis, is a rare type of blood clot found within the dural venous sinuses. The condition is often difficult to diagnose because symptoms vary from person to person depending on the location of the clot.
What is the best treatment for sinus thrombosis?
Removing clots. Clot removal using catheters and other specialized equipment, antibiotics, and anticoagulation drugs are the main methods used for the treatment of venous sinus thrombosis. Your physician may recommend one or a combination of these treatments.
Which sinus has the largest venous channel?
Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis— Multiple veins empty into the sagittal sinus, making it the largest venous channel in the brain. Because of its size, clots here are rare.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mild sinusitis
- 2. icd 10 code for djd of shoulder
- 3. icd-10-pcs code for circumcision revision, urethral meatoplasty
- 4. icd-10 code for osteomyelitis of rt foot
- 5. icd-10 code for advair hfa
- 6. icd 10 code for cva without residual effects
- 7. icd 10 code for stenosis of celiac artery
- 8. icd 10 code for hypodermic needle stick
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic moderate persistent asthma
- 10. icd-10 code for delirium tremens unspecified