What is subclavian steal syndrome ICD 10?
Subclavian steal syndrome ICD-10-CM G45.8 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 061 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with mcc 062 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with cc
What is the new ICD 10 version for fistula?
Short description: Mech compl of surgically created arteriovenous fistula, init The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T82.590A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T82.590A - other international versions of ICD-10 T82.590A may differ.
What is the ICD-10 version of stroke?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G45.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 G45.8 may differ. 061 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with mcc
What causes subclavian steal syndrome?
Subclavian steal syndrome develops due to a blockage in or narrowing of a subclavian artery. The most common cause is atherosclerosis. Other risk factors include large artery vasculitis and congenital heart irregularities. Without treatment, some causes of subclavian steal syndrome can lead to serious complications.

What is the ICD-10 for subclavian steal syndrome?
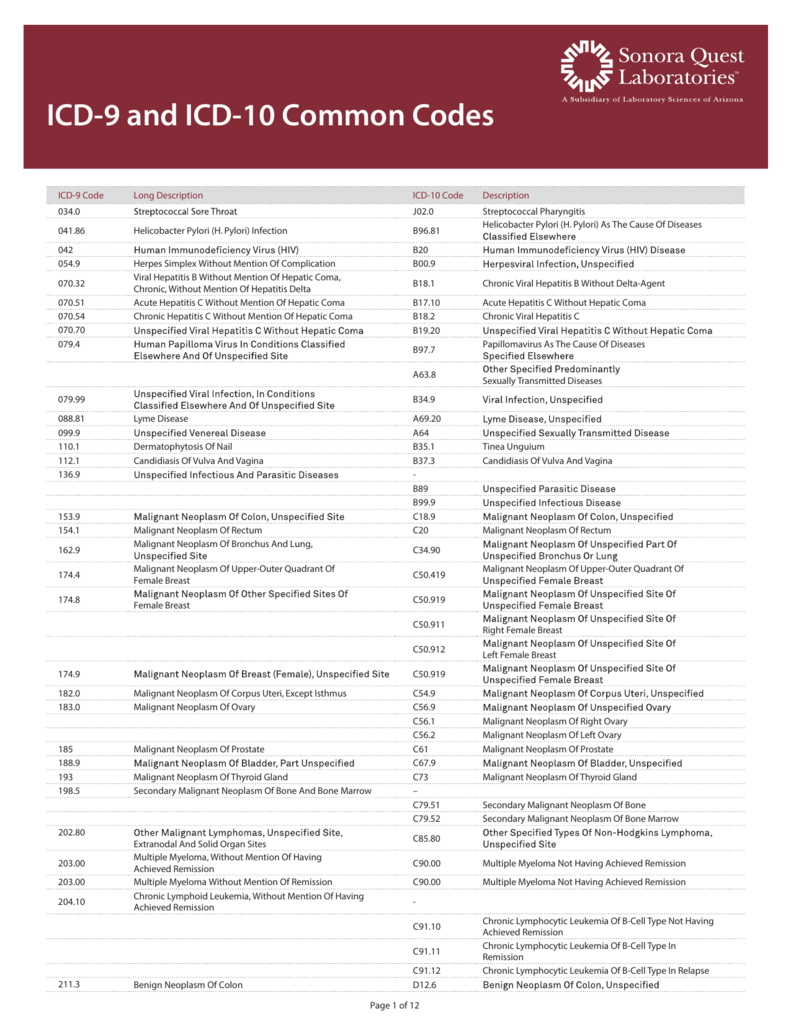
435.2 - Subclavian steal syndrome | ICD-10-CM.
What is arterial steal syndrome?
Arterial steal syndrome is a serious complication that can occur after upper extremity arteriovenous (AV) fistula creation for long-term hemodialysis (HD) access. Patients report hand and digit pain that results from hypoperfusion and ischemia distal to the AV fistula.
What is subclavian steal syndrome?
“Subclavian steal” refers to a syndrome of symptoms relating to arterial insufficiency in a branch of the subclavian artery stemming from flow reversal, attributable to occlusive disease in the subclavian artery proximal to that branch that is usually atherosclerotic in cause.
What is diagnosis code Z87 898?
Personal history of other specified conditionsICD-10 code Z87. 898 for Personal history of other specified conditions is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
How is steal syndrome diagnosed?
The diagnosis of steal is based on an accurate history and physical examination and confirmed with tests including an arteriogram, duplex Doppler ultrasound (DDU) evaluation with finger pressures and waveform analysis. Treatment of steal includes observation of developing symptoms in mild cases.
How do you get steal syndrome?
Ischemic steal syndrome (ISS) is a complication that can occur after the construction of a vascular access for hemodialysis. It is characterized by ischemia of the hand caused by marked reduction or reversal of flow through the arterial segment distal to the arteriovenous fistula (AVF).
How do you diagnose subclavian steal syndrome?
Confirmation of a steal syndrome is usually made by imaging studies. All imaging tools can be used to detect subclavian stenosis and to observe reversal of flow from the vertebral artery. Carotid duplex ultrasound(US) is the most used and usually the first diagnostic test.
What are the signs of steal syndrome?
Hemodialysis access-related hand ischemia or 'steal syndrome' causes problems such as hand numbness, pain, coldness and weakness, as well as significantly reduced blood flow/pressure to affected tissues. In extreme cases, it can cause tissue death (gangrene), which may lead to the loss of fingers.
What is the cause of subclavian steal syndrome?
Subclavian steal syndrome develops due to a blockage in or narrowing of a subclavian artery. The most common cause is atherosclerosis. Other risk factors include large artery vasculitis and congenital heart irregularities. Without treatment, some causes of subclavian steal syndrome can lead to serious complications.
What is the ICD-10 code for substance abuse?
Other psychoactive substance abuse, uncomplicated F19. 10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F19. 10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of substance abuse?
The ICD-10 code Z86. 4 applies to cases where there is "a personal history of psychoactive substance abuse" (drugs or alcohol or tobacco) but specifically excludes current dependence (F10 - F19 codes with the fourth digit of 2).
What is the ICD-10 code for alcohol use disorder?
ICD-10 code F10. 9 for Alcohol use, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What are the signs of steal syndrome?
Hemodialysis access-related hand ischemia or 'steal syndrome' causes problems such as hand numbness, pain, coldness and weakness, as well as significantly reduced blood flow/pressure to affected tissues. In extreme cases, it can cause tissue death (gangrene), which may lead to the loss of fingers.
How do you fix steal syndrome?
Discussion. Currently described therapies for steal syndrome include access ligation, banding, proximalization of the arterial inflow, and distal revascularization with interval ligation procedure. Distal radial artery ligation has also been used for patients with distal radiocephalic AVFs.
How do you deal with steal syndrome?
Mild cases can be observed closely, most of them will reverse in a few weeks. In order to prevent permanent sequela, severe cases require immediate intervention. Several surgical treatments have been used: access ligation, banding, elongation, distal arterial ligation, and distal revascularization-interval ligation.
Which drugs cause coronary steal syndrome?
Vasodilators. Adenosine or dipyridamole can cause ischemia by producing coronary steal that could be collateral dependent or transmural.
What is the code for adverse effect?
code for adverse effect, if applicable, to identify drug (T36-T50with fifth or sixth character 5)
What is E86-E87?
disorders of fluid and electrolyte imbalance (E86-E87)
What chapter in the T section is the external cause code?
Use secondary code(s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.
Can you use T82.898 for reimbursement?
T82.898should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
When will ICD-10-CM I97.89 be effective?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I97.89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is I97 in medical terms?
I97- Intraoperative and postprocedural complications and disorders of circulatory system, not elsewhere classified
steal syndrome
Hi Dr. Z, What is the correct icd-9 code for: steal syndrome not for subclavian artery. Thank you.
Need to ask Dr.Z?
Don't see the answer you're looking for in the knowledge base? No problem. You can ask Dr. Z directly!
What are the risk factors for subclavian steal?
Other possible risk factors for subclavian steal syndrome include: large artery vasculitis, which is the medical term for inflammation of the large arteries. thoracic outlet syndrome, which is a group of conditions that occur when the blood vessels or nerves between the collarbone and first rib become compressed.
What is the cause of subclavian steal?
Subclavian steal syndrome occurs when the heart has difficulty pumping oxygenated blood through the subclavian artery. This can cause some degree of retrograde blood flow within the subclavian artery and the arteries that branch off from it.
How many people have subclavian steal?
According to a 2019 report, experts estimate that subclavian steal syndrome affects between 0.6% and 6.4% of the general population.
Why is subclavian steal not a cause of lifestyle changes?
This is because in most cases, the cause is atherosclerosis.
Can a duplex ultrasound confirm subclavian steal?
Sometimes, however, duplex ultrasounds are not precise enough to give a doctor all the information they need to confirm a diagnosis of subclavian steal syndrome. In such cases, the doctor may recommend a magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). An MRA uses an MRI scanner to visualize blood flow in a person’s body.
Can subclavian steal syndrome be a symptom?
People with subclavian steal syndrome often do not experience any symptoms. If symptoms do develop, they will vary according to the arteries it affects.
Can subclavian steal be serious?
The condition has many potential causes, some of which can be serious without proper treatment. Subclavian steal syndrome affects the artery that supplies blood to the neck and head or the arteries that supply blood to the arms. Because of this, people may experience symptoms in these areas. However, many people with the condition do not experience ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is ros for sore throat icd 10 code
- 2. icd 10 code for tenosynovitis left great toe
- 3. the correct icd-10 code for acetaminophen toxicity is quizlet
- 4. icd 10 code for sortness of breath
- 5. icd 9 code for diabetic decubtis ulcer
- 6. icd 10 code for honk
- 7. icd 10 code for thigh riash
- 8. icd 10 code for check up school
- 9. icd 10 code for removal and reinsertion of nexplanon
- 10. icd 10 code for post term birth in hospital of twin, mate stillborn