What is the ICD 10 code for subluxation of the wrist?
Other subluxation of left wrist and hand, initial encounter 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code S63.092A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.092A became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is peroneal subluxation?
Subluxation or dislocation of the peroneal tendons is a disorder involving an elongation, a tear or an avulsion of the superior peroneal retinaculum. There can be also subluxation of the tendons with an intact SPR (intrasheath subluxation). Peroneus brevis and peroneus longus are contained in the retromalleolar sulcus on the fibula.
What is the ICD 10 code for dislocation of the shoulder?
S43. 086A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. What is the ICD-10 code for anterior inferior shoulder dislocation?
When is chirurgical treatment necessary for tendon subluxation?
If the conservative treatment failed or if there’s a chronic subluxation, chirurgical treatment is probably necessary. Early treatment is critical, since a tendon that continues to sublux (move out of position) is more likely to tear or rupture.
What is the ICD-10 code for subluxation of biceps tendon?
211A for Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon of other parts of biceps, right arm, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is R46 89?
ICD-10 code R46. 89 for Other symptoms and signs involving appearance and behavior is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is Z76 89 a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
What is the ICD-10 code for patella subluxation?
Subluxation and dislocation of patella The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S83. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S83. 0 - other international versions of ICD-10 S83.
What is r41 89?
89 for Other symptoms and signs involving cognitive functions and awareness is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for adjustment disorder?
Code F43. 23 is the diagnosis code used for Adjustment Disorder (AD) with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood. It is sometimes known as situational depression. It occurs when an individual is unable to adjust to or cope with a particular stress or a major life event.
Is Z76 89 a billable code?
Z76. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for encountering care?
Encounter for other specified special examinations The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z01. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z01.
What is the ICD 10 code for new patient?
Code the initial visit as a new visit, and subsequent treatment visits as established with the E/M code 99211.
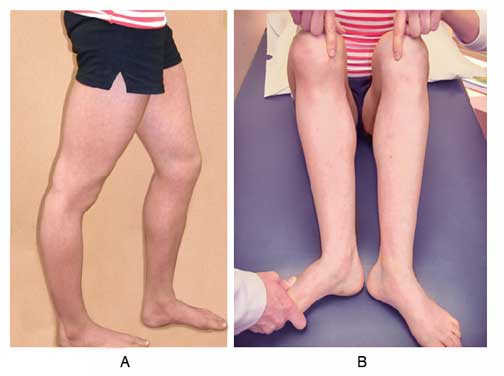
What is patellar subluxation?
The patella (kneecap) normally sits in a groove at the center of the bottom end of the thigh bone. A patellar subluxation means that the kneecap has briefly slid out of its normal place in that groove. In most cases the kneecap moves towards the outside of the body when it slides out of place.
What is ICD-10 code for left knee instability?
ICD-10 Code for Other instability, left knee- M25. 362- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for right knee instability?
ICD-10 Code for Other instability, right knee- M25. 361- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD 10 code for ADHD?
F90. 1, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, predominantly hyperactive type. F90. 2, Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, combined type.
What is the ICD 10 code for aggressive behavior?
R45.6ICD-10-CM Code for Violent behavior R45. 6.
What is subluxation of the peroneal tendons?
Subluxation or dislocation of the peroneal tendons is a disorder involving an elongation, a tear, or an avulsion of the superior peroneal retinaculum. There can be also subluxation of the tendons with an intact SPR (intrasheath subluxation).
How many grades of acute peroneal subluxation are there?
There are three grades to classify the acute peroneal subluxation
Where do tendons slip out of place?
Tendons slip out of place along the lower tip of the fibula
Can a peroneal tendon snap around the malleolus?
In most cases, a peroneal tendon snapping around the posterior margin of the lateral malleolus can be palpated and even visualized by the examinator. These clinical findings can be enhanced by applying a slight resistance to the dorsiflexion-eversion.
Is peroneal subluxation a sprained ankle?
Acute peroneal subluxation is often difficult to appreciate clinically. There is usually edema, ecchymosis and point tenderness in the same distribution than in case of a sprained ankle, therefore making diagnosis difficult.
Is a subluxing peroneal tendon operative?
In adults the treatment can be divided into non-operative and operative when considering acute or chronic injuries. When an acute subluxation is diagnosed, the patient may be consider non-operative treatment. If the conservative treatment failed or if there’s a chronic subluxation, chirurgical treatment is probably necessary. Early treatment is critical, since a tendon that continues to sublux (move out of position) is more likely to tear or rupture.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for scratched legs
- 2. icd 10 code for lymphedema lll
- 3. icd 10 code for personal history of ascites
- 4. icd 10 cm code for betamethsone injection
- 5. icd 10 code for history diverticulitis
- 6. icd 9 code for complicated prostatotomy of prostate cyst
- 7. icd 9 code for residual knee swelling
- 8. icd 10 code for insect bite left knee
- 9. icd 10 code for thiazide induced siadh
- 10. icd 10 code for s/p kneecap fx right