What can cause inverted T waves?
Strain on ventricles can cause T wave inversion. Pre-excitation syndrome is a condition in which the ventricles partially contract prematurely. T wave inversion is often present in this condition.
What does T wave inversion indicate?
To clarify, isolated T-wave inversions indicate that there has been ischemia. Ischemic T-wave inversions are symmetric (the normal T-wave is asymmetric) and maybe, but rarely are, deeper than 10 mm. ECG leads with the opposite angles of observation (opposite to leads with T-wave inversions) usually display positive T-waves.
What do inverted T waves indicate?
What Causes T-Wave Inversion?
- Hypokalaemia
- Pulmonary embolisms
- Some medications e.g. Digoxin
- Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
- Hypothyroidism
- Acute Myocarditis
- Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Ischemic Heart Condition
Which leads is T wave inversion normal?
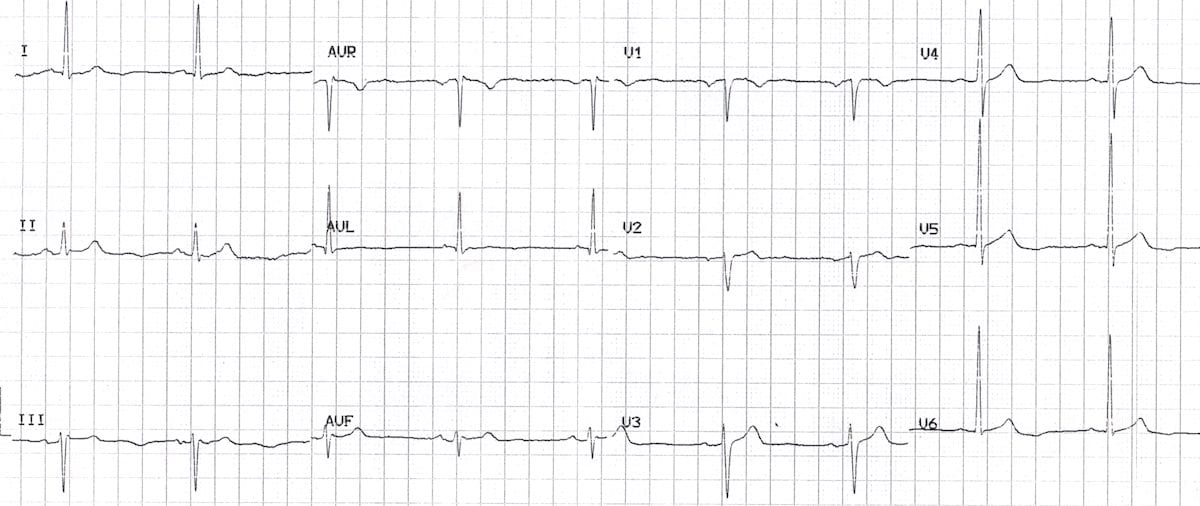
The T wave is the ECG manifestation of ventricular repolarization of the cardiac electrical cycle. The T wave is normally upright in leads I, II, and V3 to V6; inverted in lead aVR; and variable in leads III, aVL, aVF, V1, and V2. Thus, T-wave inversions in leads V1 and V2 may be fully normal.
How to prevent T wave inversion?
What does inverted T wave mean?
What is an active ECG?
What causes inverted T waves?
What is the amplitude of a T wave?
What is the T wave?
What is the T wave in a heart?
See 2 more
What does R94 31 on an EKG mean?
Abnormal electrocardiogramICD-10 code R94. 31 for Abnormal electrocardiogram [ECG] [EKG] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for EKG changes?
R94. 31 - Abnormal electrocardiogram [ECG] [EKG] | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for nonspecific ST abnormality?
Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction I21. 4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I21. 4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are T codes ICD-10?
It is important to note that in ICD-10-CM, a handful of “T” codes actually function as both a diagnosis and external cause of injury code. This applies to overdose codes (T36-T50) and toxic effects codes (T51-T65), where information about the drug or substance involved and the intent are captured a single code.
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal echocardiogram?
ICD-10-CM Code for Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging of heart and coronary circulation R93. 1.
What is the difference between 93005 and 93010?
93000 is the complete procedure and includes ECG tracing with physician review, interpretation and report. Use 93005 to report the tracing only, and 93010 to report physician interpretation and written report only.
What is code i21 4?
4: Acute subendocardial myocardial infarction.
What is the ICD 10 code for non stemi Type 2?
Subsequent non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction I22. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I22. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for nonspecific intraventricular conduction delay?
I45. 4 - Nonspecific intraventricular block | ICD-10-CM.
Can T codes be used as primary diagnosis?
Manifestation codes cannot be reported as first-listed or principal diagnoses. In most cases the manifestation codes will include the verbiage, “in diseases classified elsewhere.” “Code first” notes occur with certain codes that are not specifically manifestation codes but may be due to an underlying cause.
Can M54 50 be a primary diagnosis code?
M54. 50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do I find ICD codes?
If you need to look up the ICD code for a particular diagnosis or confirm what an ICD code stands for, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website to use their free searchable database of current ICD-10 codes.
How to prevent T wave inversion?
A healthy diet with balanced meals and adequate exercise are the best ways to prevent T-wave inversion. Other ways of preventing inversion of your heart’s T-wave are; Reduce stress. Having ample rest and sleep. Drinking lots of clean water.
What does inverted T wave mean?
Inverted T waves mean on an ECG that you should go for further testing. This is because T waves are very non-specific. Inverted T waves may occur for a variety of reasons. Some of these reasons may be life threatening or some may be just normal and not life threatening.
What is an active ECG?
An active ECG test is done while you are exercising or involved in some activity. A treadmill walk or jog is often preferred for active ECG testing. With medical advances, you can have an ECG test to look at your T-wave done in the ambulatory method.
What causes inverted T waves?
Primary causes of inverted T-waves are caused by benign reasons. Secondary reasons are as a result of new ailments to the heart. Some of the conditions that are known to cause T-wave inversion include. Hypokalaemia. Pulmonary embolisms. Some medications e.g. Digoxin. Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome.
What is the amplitude of a T wave?
It normally has an amplitude of <5 millimetres. In normal ECG readings, the T-wave should be upward. It is usually an upward curve that is followed by a rapid dip. If the readings show different characteristics then you have inverted T-waves. Inverted T-waves are always noted in the aVR and V1 leads.
What is the T wave?
There are several factions of peaks, spaces between peaks and dips. These indents are usually called Waves and the T wave is one of them. The T wave causes ventricular repolarization of the heart in anticipation of the next contraction.
What is the T wave in a heart?
Electrical impulses are necessary for your heart to expand and contract antagonistically. One of the electrical impulses measures is called a T wave. T-wave inversion is sometimes detected in medical tests done using an electrocardiogram. This article gives you an in-depth understanding of the T wave in your Electrocardiogram results.
What are the two types of T waves in Wellens syndrome?
Two patterns of T waves can be seen in Wellens syndrome. Type-A T waves are biphasic, with initial positivity and terminal negativity. These T wave findings are present in approximately 25% of cases. Type-B T waves are deeply and symmetrically inverted. These findings are present in approximately 75% of cases. The 2 types of T waves found in Wellens syndrome exist on a spectrum of disease with type-A T waves evolving into type-B T waves. The T-wave abnormalities may be persistent, remaining in place for hours to weeks, even when the patient is pain-free.
How long do T waves last in Wellens syndrome?
The T-wave abnormalities may be persistent, remaining in place for hours to weeks, even when the patient is pain-free. Wellens syndrome is not always an acute process.
What is the ECG pattern of Wellens syndrome?
The ECG pattern of Wellens syndrome is relatively common in patients who exhibit symptoms consistent with unstable angina. In studies performed by Dr. Wellens and colleagues, the ECG pattern was present in 14% to 18% of patients admitted for unstable angina. Pathophysiology.
Is troponin a biomarker?
Cardiac biomarkers including troponin may be falsely reassuring in patients with Wellens syndrome as they frequently result within normal limits. In one prospective study, only 12% of patients with Wellens’ pattern on ECG had elevated cardiac enzymes, and these elevations were less than twice the upper limit of normal.
Known As
Abnormal EKG is also known as abnl finding on EKG, abnormal finding on ekg, electrocardiogram abnormal, inverted T wave, and T wave inversion in ekg. This excludes long QT syndrome (426.82).
Abnormal EKG Definition and Symptoms
An abnormal EKG is any abnormalities in an EKG test. An EKG test, electrocardiogram, is a test used to monitor the beats of the heart. Some of the common reasons for an abnormal EKG are heart defects, heart valve issues, blocked arteries, heart attack, or a previous heart attack.
How to prevent T wave inversion?
A healthy diet with balanced meals and adequate exercise are the best ways to prevent T-wave inversion. Other ways of preventing inversion of your heart’s T-wave are; Reduce stress. Having ample rest and sleep. Drinking lots of clean water.
What does inverted T wave mean?
Inverted T waves mean on an ECG that you should go for further testing. This is because T waves are very non-specific. Inverted T waves may occur for a variety of reasons. Some of these reasons may be life threatening or some may be just normal and not life threatening.
What is an active ECG?
An active ECG test is done while you are exercising or involved in some activity. A treadmill walk or jog is often preferred for active ECG testing. With medical advances, you can have an ECG test to look at your T-wave done in the ambulatory method.
What causes inverted T waves?
Primary causes of inverted T-waves are caused by benign reasons. Secondary reasons are as a result of new ailments to the heart. Some of the conditions that are known to cause T-wave inversion include. Hypokalaemia. Pulmonary embolisms. Some medications e.g. Digoxin. Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome.
What is the amplitude of a T wave?
It normally has an amplitude of <5 millimetres. In normal ECG readings, the T-wave should be upward. It is usually an upward curve that is followed by a rapid dip. If the readings show different characteristics then you have inverted T-waves. Inverted T-waves are always noted in the aVR and V1 leads.
What is the T wave?
There are several factions of peaks, spaces between peaks and dips. These indents are usually called Waves and the T wave is one of them. The T wave causes ventricular repolarization of the heart in anticipation of the next contraction.
What is the T wave in a heart?
Electrical impulses are necessary for your heart to expand and contract antagonistically. One of the electrical impulses measures is called a T wave. T-wave inversion is sometimes detected in medical tests done using an electrocardiogram. This article gives you an in-depth understanding of the T wave in your Electrocardiogram results.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for herniated nucleus pulposus cervical
- 2. icd 10 code for muscular calcification and ossification
- 3. icd code for radiation therapy
- 4. 2019 icd 10 code for post drainage ulcer right foot
- 5. icd 10 cm code for hypotension due to drugs
- 6. icd code 10 for scoliosis
- 7. 2019 icd 10 code for urinary incontinence
- 8. icd-10 dx code for trauma by hocky puck
- 9. icd 10 code for orenica
- 10. icd 9 code for orthostatic vertigo