The table below includes the most commonly used ICD-10 codes for CVA:
| ICD-10 Chapter | Codes | Code Description |
| 9 | I63.00 | Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of ... |
| 9 | I63.01 | Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of ... |
| 9 | I63.011 | Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of ... |
| 9 | I63.012 | Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of ... |
How many codes in ICD 10?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is ICD 10 used for?
Used for medical claim reporting in all healthcare settings, ICD-10-CM is a standardized classification system of diagnosis codes that represent conditions and diseases, related health problems, abnormal findings, signs and symptoms, injuries, external causes of injuries and diseases, and social circumstances.
What is a combination code for ICD 10?
ICD-10-CM features combination codes for poisonings and their associated external cause. These codes identify both the substance that was taken and the intent. No additional external cause code is required for poisonings, toxic effects, adverse effects, and underdosing codes. This chart gives an example of a combination code for poisonings.

How do you code a CVA in ICD-10?
When a patient has a history of cerebrovascular disease without any sequelae or late effects, ICD-10 code Z86. 73 should be assigned.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA unspecified?
ICD-10 Code for Cerebral infarction, unspecified- I63. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute CVA?
Acute cerebrovascular insufficiency I67. 81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I67. 81 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 for history of CVA?
Z86. 73 - Personal history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), and cerebral infarction without residual deficits | ICD-10-CM.
What does CVA stand for?
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is the medical term for a stroke. A stroke is when blood flow to a part of your brain is stopped either by a blockage or the rupture of a blood vessel.
What is a CVA in medical terms?
In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. CVAs are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
Is a CVA a stroke?
Stroke Center. A stroke, also referred to as a cerebral vascular accident (CVA) or a brain attack, is an interruption in the flow of blood to cells in the brain. When the cells in the brain are deprived of oxygen, they die.
Is CVA the same as cerebral infarction?
Obstruction in blood flow (ischemia) to the brain can lead to permanent damage. This is called a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). It is also known as cerebral infarction or stroke. Rupture of an artery with bleeding into the brain (hemorrhage) is called a CVA, too.
When do you code history of stroke?
In ICD-10 CM, code category I63 should be utilized when the medical documentation indicates that an infarction or stroke has occurred.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of CVA with right sided weakness?
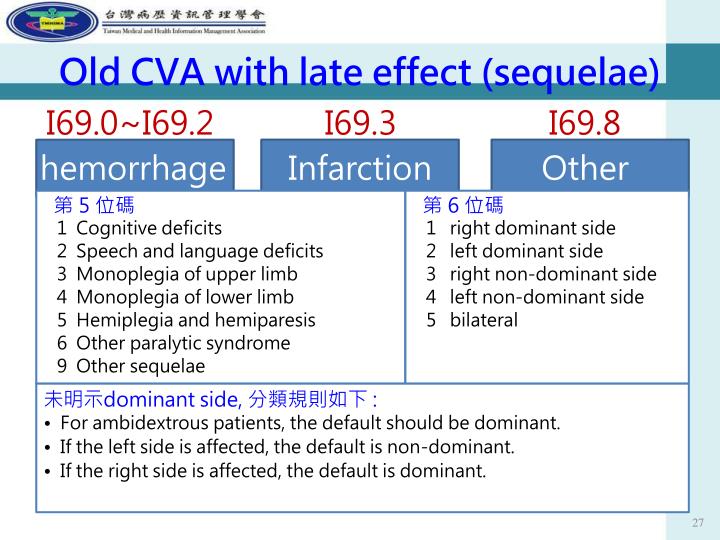
ICD-10 code I69. 351 for Hemiplegia and hemiparesis following cerebral infarction affecting right dominant side is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
How long can you code an acute CVA?
Acute stroke: 24 hours to one week. Subacute stroke: One to three weeks. Chronic stroke: Greater than three weeks.
What is cerebral infarction?
A disorder resulting from inadequate blood flow in the vessels that supply the brain. Representative examples include cerebrovascular ischemia, cerebral embolism, and cerebral infarction. A spectrum of pathological conditions of impaired blood flow in the brain.
What is the broad category of disorders of blood flow in the arteries and veins which supply the brain?
Broad category of disorders of blood flow in the arteries and veins which supply the brain; includes cerebral infarction, brain ischemia, brain hypoxia, intracranial embolism and thrombosis, intracranial arteriovenous malformations, etc; not limited to conditions that affect the cerebrum, but refers to vascular disorders of the entire brain. ...
What is the F10?
alcohol abuse and dependence ( F10.-) tobacco dependence ( F17.-) A disorder resulting from inadequate blood flow in the vessels that supply the brain. Representative examples include cerebrovascular ischemia, cerebral embolism, and cerebral infarction.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ileitis
- 2. icd 9 code for ige syndrome
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic ear infection
- 4. icd 10 code for cerebral atrophy
- 5. icd 10 code for v13.89
- 6. icd 10 code for family history of melanoma
- 7. icd 10 code for injury of right hand
- 8. icd 10 code for laceration right index finger with damage to nail
- 9. icd 10 code for history of patent ovale
- 10. icd 10 code for hemodynamically stable