What are the treatments for mild pulmonary vascular congestion?
- Alcohol abuse or cocaine and other illegal drug use
- HIV/AIDS
- Thyroid disorders (having either too much or too little thyroid hormone in the body)
- Too much vitamin E
- Treatments for cancer, such as radiation and chemotherapy
What are symptoms of pulmonary congestion?
The symptoms for long-term pulmonary edema include:
- shortness of breath when being physically active
- difficulty breathing when lying down
- wheezing
- waking up at night with a breathless feeling that goes away when you sit up
- rapid weight gain, especially in the legs
- swelling in the lower part of the body
- fatigue
What causes pulmonary artery constriction?
- The first group is idiopathic PH, likely related to inheritable and intrinsic pulmonary arterial pathology.
- The second group is PH due to left heart disease, causing a build-up of volume and pressure in the pulmonary vasculature.
- The third group is PH due to pathology within or related to the lungs. ...
What are the symptoms of pulmonary vascular disease?
The symptoms of pulmonary vascular disease vary according to several factors:
- The suddenness of the process affecting the pulmonary blood vessels
- Which pulmonary blood vessels are affected (where the pulmonary vascular disease is)
- How much of the pulmonary vascular system is affected
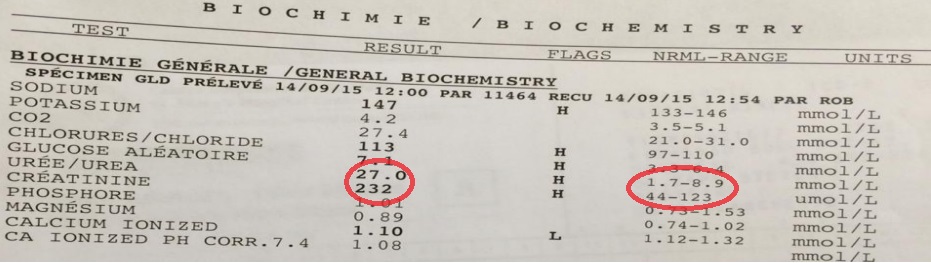
How do you code pulmonary vascular congestion?
514 - Pulmonary congestion and hypostasis. ICD-10-CM.
What is central pulmonary vascular congestion?
Pulmonary congestion is defined as accumulation of fluid in the lungs, resulting in impaired gas exchange and arterial hypoxemia. It occurs sequentially, first developing in the hilar region of the lungs, followed by filling of the interstitial space and finally, in its most severe form, by alveolar flooding.
What is the ICD-10 code for central vascular congestion?
If all you are given is pulmonary vascular congestion, you would could it to R09. 89.
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary edema?
ICD-10 code J81. 0 for Acute pulmonary edema is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is pulmonary vascular congestion and edema?
Overview. Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by too much fluid in the lungs. This fluid collects in the many air sacs in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. In most cases, heart problems cause pulmonary edema.
What causes pulmonary vascular congestion?
Pulmonary venous hypertension is most often caused by congestive heart failure. A damaged mitral valve in the heart (mitral stenosis or mitral regurgitation) may contribute to pulmonary venous hypertension.
What is pulmonary congestion and hypostasis?
n. Pulmonary congestion due to the stagnation of blood in the dependent portions of the lungs in old persons or in those who are ill and lie in the same position for long periods.
What is the ICD-10 code for cardiomegaly with pulmonary vascular congestion?
I51. 7 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I51. 7 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is diagnosis code R09 89?
ICD-10 code R09. 89 for Other specified symptoms and signs involving the circulatory and respiratory systems is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
How do you code acute pulmonary edema?
J81. 0, acute pulmonary edema.
What is acute pulmonary Oedema?
Acute pulmonary oedema is a medical emergency which requires immediate management. 1. It is characterised by dyspnoea and hypoxia secondary to fluid accumulation in the lungs which impairs gas exchange and lung compliance.
Is flash pulmonary edema acute?
Abstract. Flash pulmonary edema (FPE) is a general clinical term used to describe a particularly dramatic form of acute decompensated heart failure.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mild global hypokinesis
- 2. icd 9 code for encounter for rx refills
- 3. what icd-10-cm code is reported for elevated blood pressure
- 4. icd 10 code for jejunostomy tube fell out
- 5. icd-10 code for left pleural effusion
- 6. icd-10-pcs code for tooth extraction
- 7. icd 10 code for mass of left lung
- 8. icd 10 code for thumb injury, left
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral lower extremity ulceration
- 10. icd 10 code for blood pressure check in pregnancy