What is the latest ICD 10 for sepsis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Severe sepsis. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. R65.2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the combination code for sepsis and pneumonia?
Oct 19, 2017 · The code for septic shock cannot be assigned as a principal diagnosis. For septic shock, the code for the underlying infection should be sequenced first, followed by code R65.21, Severe sepsis with septic shock or code T81.12, Postprocedural septic shock. Additional codes are also required to report other acute organ dysfunctions.
What is the CPT code for sepsis in newborns?
Oct 01, 2021 · Severe sepsis with septic shock. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R65.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the CPT code for sepsis and shock?
Aug 01, 2015 · “Multi-organ dysfunction” is not coded. The patient may have many concurrent organ dysfunctions, but they must be specifically named to code them. Coding tips: When severe sepsis is documented, there will be a minimum of two codes when using ICD-10-CM: a code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code for Severe sepsis, R65.2-. If organ …
How do you code severe sepsis?
What is the 2021 ICD-10 code for septic shock?
What ICD-10 codes change in 2021?
What is diagnosis code R65 21?
What is ICD 10 code for severe sepsis?
R65. 21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R65. 21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is severe sepsis with septic shock?
How many 2021 ICD-10 codes are there?
The updated ICD-10 code set includes 490 new codes, 58 deleted codes and 47 revised codes. This takes the total number of ICD-10 codes in FY 2020 from 72,184 to 72,616 in FY 2021.Aug 17, 2021
IS 99211 being deleted in 2021?
When do you use Z20 822?
Can R65 21 be a primary diagnosis?
What constitutes severe sepsis?
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
What is septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to?
Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to group a streptococcus. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to group b streptococcus. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to meningococcal septicemia.
What is septic shock?
Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to anaerobic septicemia. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to chromobacterium. Septic shock with acute organ dysfunction due to coagulate-negative staphylococcu.
What is the obstetrical code for sepsis?
If the patient has severe sepsis, add R65.2- with the codes for specific organ dysfunctions.
Can you code for sepsis?
Documentation issues: You can code for sepsis when the physician documents the term “sepsis.”. Documentation should be consistent throughout the chart. Occasionally, during an extended length of stay, sepsis may resolve quickly and the discharging doctor may not include the diagnosis of sepsis on the discharge summary.
What are the symptoms of a localized infection?
Documentation issues: Often, a patient with a localized infection may exhibit tachycardia, leukocytosis, tachypnea, and fever, but not truly have SIRS or sepsis. These are typical symptoms of any infection.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if severe sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
Is septic shock documented without sepsis?
Documentation issues: The term “septic shock” is occasionally documented without the term “sepsis.”. According to the guidelines, for all cases of septic shock the code for the underlying systemic infection is sequenced first, followed by R65.21 Severe sepsis with septic shock or T81.12- Postprocedural septic shock.
What is post-procedural sepsis?
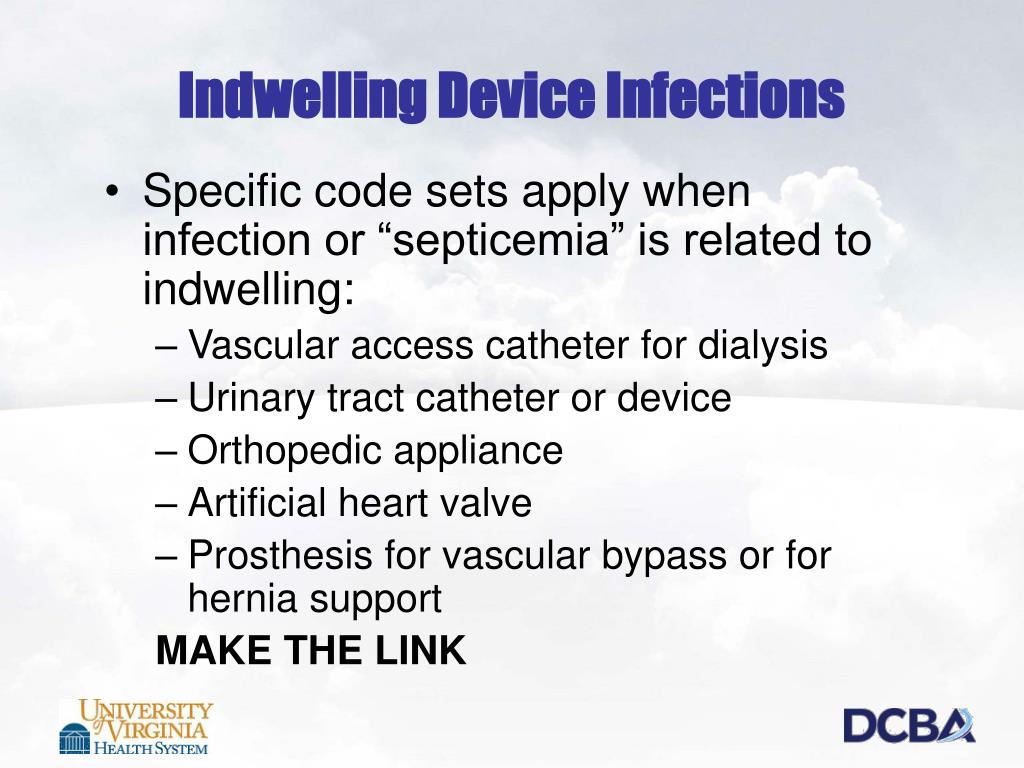
Post-procedural Sepsis and Sepsis Due to a Device, Implant, or Graft. A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to wound infection, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
How many times should you query for sepsis?
The guidelines for sepsis refer to querying five times, demonstrating the complexity of these cases and the need to ask for clarification.
What is sequela code?
sequela is the residual effect (condition produced) after the acute phase of an illness or injury has terminated. There is no time limit on when a sequela code can be used. The residual may be apparent early, such as in cerebral infarction, or it may occur months or years later, such as that due to a previous injury. Examples of sequela include: scar formation resulting from a burn, deviated septum due to a nasal fracture, and infertility due to tubal occlusion from old tuberculosis. Coding of sequela generally requires two codes sequenced in the following order: the condition or nature of the sequela is sequenced first. The sequela code is sequenced second.
What is the code for infection of obstetric surgical wound?
For infections following a procedure, a code from T81.40, to T81.43 Infection following a procedure, or a code from O86.00 to O86.03, Infection of obstetric surgical wound, that identifies the site of the infection should be coded first, if known. Assign an additional code for sepsis following a procedure (T81.44) or sepsis following an obstetrical procedure (O86.04). Use an additional code to identify the infectious agent.If the patient has severe sepsis, the appropriate code from subcategory R65.2 should also be assigned with the additional code(s) for any acute organ dysfunction.
What is the convention of ICd 10?
The conventions for the ICD-10-CM are the general rules for use of the classification independent of the guidelines. These conventions are incorporated within the Alphabetic Index and Tabular List of the ICD-10-CM as instructional notes.
What does NEC mean in coding?
NEC “Not elsewhere classifiable” This abbreviation in the Alphabetic Index represents “other specified.”When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Alphabetic Index directs the coder to the “other specified” code in the Tabular List.
What is the ICD-10-CM?
The ICD-10-CM has two types of excludes notes. Each type of note has a different definition for use but they are all similar in that they indicate that codes excluded from each other are independent of each other.
What is the assignment of a diagnosis code?
The assignment of a diagnosis code is based on the provider’s diagnostic statement that the condition exists. The provider’s statement that the patient has a particular condition is sufficient. Code assignment is not based on clinical criteria used by the provider to establish the diagnosis.
What is the external cause of morbidity code?
An external cause of morbidity code should be assigned to identify the cause of the injury(ies) incurred as a result of the hurricane. The use of external cause of morbidity codes is supplemental to the application of ICD-10-CM codes. External cause of morbidity codes are never to be recorded as a principal diagnosis (first-listed in non-inpatient settings). The appropriate injury code should be sequenced before any external cause codes. The external cause of morbidity codes capture how the injury or health condition happened (cause), the intent (unintentional or accidental; or intentional, such as suicide or assault), the place where the event occurred, the activity of the patient at the time of the event, and the person’s status (e.g., civilian, military). They should not be assigned for encounters to treat hurricane victims’ medical conditions when no injury, adverse effect or poisoning is involved. External cause of morbidity codes should be assigned for each encounter for care and treatment of the injury. External cause of morbidity codes may be assigned in all health care settings. For the purpose of capturing complete and accurate ICD-10-CM data in the aftermath of the hurricane, a healthcare setting should be considered as any location where medical care is provided by licensed healthcare professionals.
What is the response to sepsis?
Sepsis is an extreme response to infection that develops when the chemicals the immune system releases into the bloodstream to fight infection cause widespread inflammation. This inflammation can lead to blood clots and leaky blood vessels, and without timely treatment, may result in organ dysfunction and then death. Severe cases of sepsis often result from a body-wide infection that spreads through the bloodstream, but sepsis can also be triggered by an infection in the lungs, stomach, kidneys, or bladder. Thus, it is not necessary for blood cultures to be positive to code sepsis (guideline I.C.1.d.1.a.i).
Can sepsis be treated with antibiotics?
Almost any type of infection can lead to sepsis. Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract. When localized infections are contained, they tend to be self-limiting and resolve with antibiotics. It’s important to identify and treat localized infections promptly, otherwise, sepsis may develop. Occasionally, the source of sepsis cannot be determined during the inpatient stay, but sepsis should be coded when it is adequately documented.
What is systemic infection?
A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to postoperative wound infections, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
Is septicemia difficult to code?
Sepsis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and septicemia have historically been difficult to code. Changing terminology, evolving definitions, and guideline updates over the past 20 years have created confusion with coding sepsis.
Where does sepsis start?
Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract. When localized infections are contained, they tend to be self-limiting and resolve with antibiotics. It’s important to identify and treat localized infections promptly, otherwise, sepsis may develop.
What are the symptoms of a localized infection?
Documentation issues: A patient with a localized infection usually presents with tachycardia, leukocytosis, tachypnea, and/or fever. These are typical symptoms of any infection. It is up to the clinical judgment of the physician to decide whether the patient has sepsis.
When is a localized infection coded?
If the patient is admitted with a localized infection and the patient does not develop sepsis or severe sepsis until after the admission, the localized infection is coded first, followed by the appropriate codes for sepsis or severe sepsis, if applicable .
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for unsafe at home
- 2. icd 9 code for reflex sympathetic dystrophy
- 3. icd 10 code for long term use of hydrocortisone
- 4. icd 10 code for head trauma without loss of consciousness
- 5. icd 10 code for mass in colon
- 6. 2015 icd 10 code for degenerative hand
- 7. icd 10 code for ranula of floor of mouth
- 8. icd 10 code for blue keratosis pilaris
- 9. icd-10 code for school adjustment
- 10. icd 10 code for sick thyroid syndrome