What is the prognosis for a ventricular septal defect?
The oxygen-rich blood then gets pumped back to the lungs instead of out to the body, causing the heart to work harder. A small ventricular septal defect may cause no problems, and many small VSDs close on their own. Medium or larger VSDs may need surgical repair early in life to prevent complications.
Does ventricular septal defect cause low blood pressure?
This helps preserve the function of the lungs, but causes yet another problem. Blood flow within the heart goes from areas where the pressure is high to areas where the pressure is low. If a ventricular septal defect is not repaired, and lung disease begins to occur, pressure in the right side of the heart will eventually exceed pressure in the left.
Should small ventricular septal defects be closed?
Treatments for a ventricular septal defect depend on the size of the hole and the problems it might cause. Many ventricular septal defects are small and close on their own; if the hole is small and not causing any symptoms, the doctor will check the infant regularly to ensure there are no signs of heart failure and that the hole closes on its own.
Who discovered ventricular septal defect?
While many VSDs close spontaneously, if they do not, large defects can lead to detrimental complications such as pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), ventricular dysfunction, and an increased risk of arrhythmias.[1][2][3] VSDs were first identified by Dalrymple in the year 1847.[4] Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is the most common congenital cardiac anomaly in children and is the second most common congenital abnormality in adults, second only to a bicuspid aortic valve.
What is the ICD-10 code for ventricular septal defects?
ICD-10 code Q21. 0 for Ventricular septal defect is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is large ventricular septal defect?
Click here to view a larger image. A ventricular septal defect (pronounced ven·tric·u·lar sep·tal de·fect) (VSD) is a birth defect of the heart in which there is a hole in the wall (septum) that separates the two lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart. This wall also is called the ventricular septum.
What are the 4 types of ventricular septal defect?
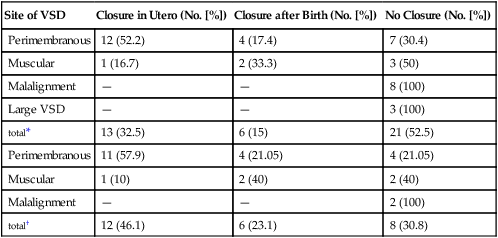
Ventricular septal defects are the most commonly occurring type of congenital heart defect, accounting for about half of congenital heart disease cases....There are four basic types of VSD:Membranous VSD. ... Muscular VSD. ... Atrioventricular canal type VSD. ... Conal septal VSD.
What is the ICD-10 code for septal hypertrophy?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy - Asymmetric Septal Hypertrophy (ASH) - Adult & Child (ICD-10: I42) - Indigomedconnect.
What is the difference between atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect?
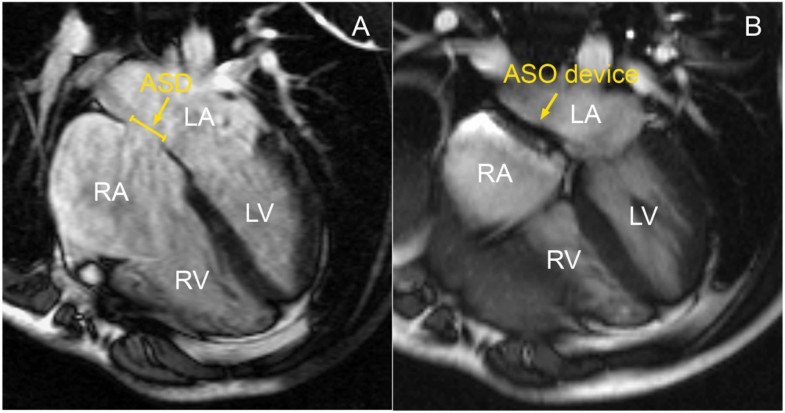
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the heart's two upper chambers. ASD is a congenital condition, which means it is present at birth. A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a hole in the wall between the two lower chambers.
Is a 4mm VSD large?
The VSDs were classified as: small (diameter less than or equal to 3 mm), medium (3 to 6 mm) and large (greater than 6 mm).
What causes VSD heart defect?
The most common cause of a VSD is a congenital heart defect, which is a defect from birth. Some people are born with holes already present in their heart. They may cause no symptoms and take years to diagnose. A rare cause of a VSD is severe blunt trauma to the chest.
What is AV septum?
The atrioventricular septum is a septum of the heart between the right atrium (RA) and the left ventricle (LV). Atrioventricular septum. Interior of heart. (AV septum not labeled, but region is visible.) Coronal cross section of heart.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for ventricular hypertrophy?
Other hypertrophic cardiomyopathy I42. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I42. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for right ventricular hypertrophy?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I42 I42.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for left ventricular hypertrophy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiomegaly I51. 7.
The ICD code Q210 is used to code Ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart.
Coding Notes for Q21.0 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #306-307 - Cardiac congenital and valvular disorders with MCC.
Related Concepts SNOMET-CT
Acquired subaortic stenosis due to restrictive ventricular septal defect associated with functionally univentricular heart (disorder)
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'Q21.0 - Ventricular septal defect'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code Q21.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 745.4 was previously used, Q21.0 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What are the different types of atrial septal defects?
They include ostium primum, ostium secundum, sinus venosus, and coronary sinus defects.
What is the term for a condition in which the foramen ovale in the atrial septum fails to
Sinus venosus atrial septal defect. Clinical Information. A condition in which the foramen ovale in the atrial septum fails to close shortly after birth. This results in abnormal communications between the two upper chambers of the heart.
What is patent ovale foramen?
An isolated patent ovale foramen without other structural heart defects is usually of no hemodynamic significance. Defect in the wall between the lower chambers of the heart. Developmental abnormalities in any portion of the atrial septum resulting in abnormal communications between the two upper chambers of the heart.
Is an ASD congenital?
The asd can be congenital or acquired. Present On Admission. POA Help. "Present On Admission" is defined as present at the time the order for inpatient admission occurs — conditions that develop during an outpatient encounter, including emergency department, observation, or outpatient surgery, are considered POA.
What is the ICd 10 code for ASD?
This is a rare type of ASD and accounts for less than 1 percent cases. Relevant ICD-10-CM codes for ASD are: Q21.1 Atrial septal defect – Alternative wording ...
What is the most commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomaly presenting in adulthood?
Print Post. Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the most commonly recognized congenital cardiac anomaly presenting in adulthood. An ASD is a defect in the interatrial septum that allows pulmonary venous return from the left atrium to pass directly to the right atrium.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sebaceous cyst perineal
- 2. icd 10 code for inhalant abuse
- 3. icd 10 code for ocd disorder
- 4. icd 10 code for r knee replacement
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone
- 6. icd 10 code for history of distal femurfracture
- 7. icd 10 code for left hip pain after fall
- 8. icd 10 code for dvt with pulmonary
- 9. icd 10 code for history of leukemia
- 10. icd 9 code for chemotherapy administration