What are symptoms of chronic respiratory failure?
What are the signs and symptoms of Respiratory Failure?
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid breathing
- Bluish colored skin, lips and fingernails (called cyanosis)
- Confusion
What are the criteria for chronic respiratory failure?
- Life-threatening condition that may be caused by a respiratory condition as well as a non-respiratory condition.
- Look for documented signs / symptoms of:
- SOB (shortness of breath)
- Delirium and/or anxiety
- Syncope
- Use of accessory muscles / poor air movement
- Distended neck veins / peripheral edema
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- Confusion
Is progressive respiratory failure acute or chronic?
Acute Respiratory Failure in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a progressive, irreversible lung disorder characterized by airway inflammation and impaired breathing. Although it usually takes years for COPD to cause significant symptoms, the condition is typically ...
What are the complications of respiratory failure?
What are the risk factors for respiratory failure?
- Aspiration of stomach contents
- Combination of drug and alcohol use
- Multiple blood transfusions
- Severe obesity
- Shock
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
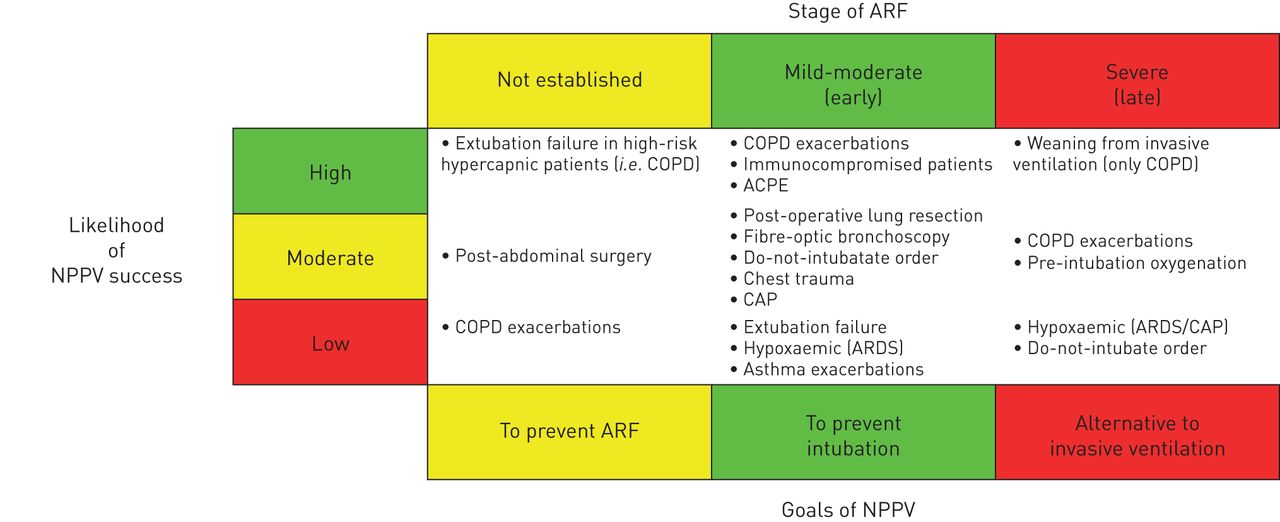
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia?
ICD-10 code J96. 12 for Chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the ICD-10 code for hypercapnia?
J96. 12 - Chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia. ICD-10-CM.
What is chronic respiratory failure with hypercapnia?
Chronic respiratory failure can also be classified as hypoxemic or hypercapnic respiratory failure. Low blood oxygen levels cause hypoxemic respiratory failure. High carbon dioxide levels cause hypercapnic respiratory failure.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia and hypercapnia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia J96. 10.
How do you code Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia and hypercapnia?
J96.00 – Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia.J96.01 – Acute respiratory failure, with hypoxia.J96.02 – Acute respiratory failure, with hypercapnia.
Is hypercarbia and hypercapnia the same thing?
Hypercapnia, or hypercarbia, is when you have too much carbon dioxide (CO2) in your bloodstream. It usually happens as a result of hypoventilation, or not being able to breathe properly and get oxygen into your lungs.
What is chronic hypercapnia?
Chronic hypercapnia allows for renal compensation to the elevated CO2 levels within the blood. As a result, PaCO2 will be elevated above the normal reference range of 45 mm Hg and the HCO3 level will also be elevated proportionally resulting in a less severe pH imbalance in the low-normal range.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute and chronic respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure J96. 2.
Is COPD hypercapnic respiratory failure?
Hypercapnia is a buildup of carbon dioxide in your bloodstream. It affects people who have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). If you have COPD, you can't breathe as easily as other people do.
What is chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia ICD-10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia J96. 11.
What causes hypercapnia?
What Causes Hypercapnia? Hypercapnia occurs when the blood's CO2 level rises above normal due to respiratory problems, excessive metabolism, or more rarely, from breathing in too much CO2. The body produces CO2 as a byproduct of metabolism.
When do you code Acute respiratory failure?
A code from subcategory J96. 0, Acute respiratory failure, or subcategory J96. 2, Acute and chronic respiratory failure, may be assigned as a principal diagnosis when it is the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for the hospital admission.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for etoh abuse
- 2. icd 10 code for bilateral external otitis media
- 3. icd 10 code for right knee surgery
- 4. icd 10 code for encounter for antibiotic therapy
- 5. icd-10 code for neck injury
- 6. icd 10 code for right wirst pain
- 7. what is the correct icd 10 code for open trimalleolar
- 8. icd 10 code for tear of lateral meniscus left knee
- 9. icd 10 cm code for hydrosalpinx
- 10. icd-9-cm code for behavioral disturbance