Will you have pericardial effusion with pneumonia?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. J96.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J96.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the complications of respiratory failure?
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J96.00 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. Acute respiratory failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia; Acute respiratory failure. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J96.00.
What is the criteria for respiratory failure?
ICD-10-CM/PCS MS-DRG v40.0 Definitions Manual > ... Acute eosinophilic pneumonia: J8283: Eosinophilic asthma: J8289: Other pulmonary eosinophilia, not elsewhere classified: J8401: Alveolar proteinosis: J8402: ... Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia: J9601:
What are symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
Oct 01, 2021 · J96.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute respiratory failure, unsp w hypoxia or hypercapnia. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
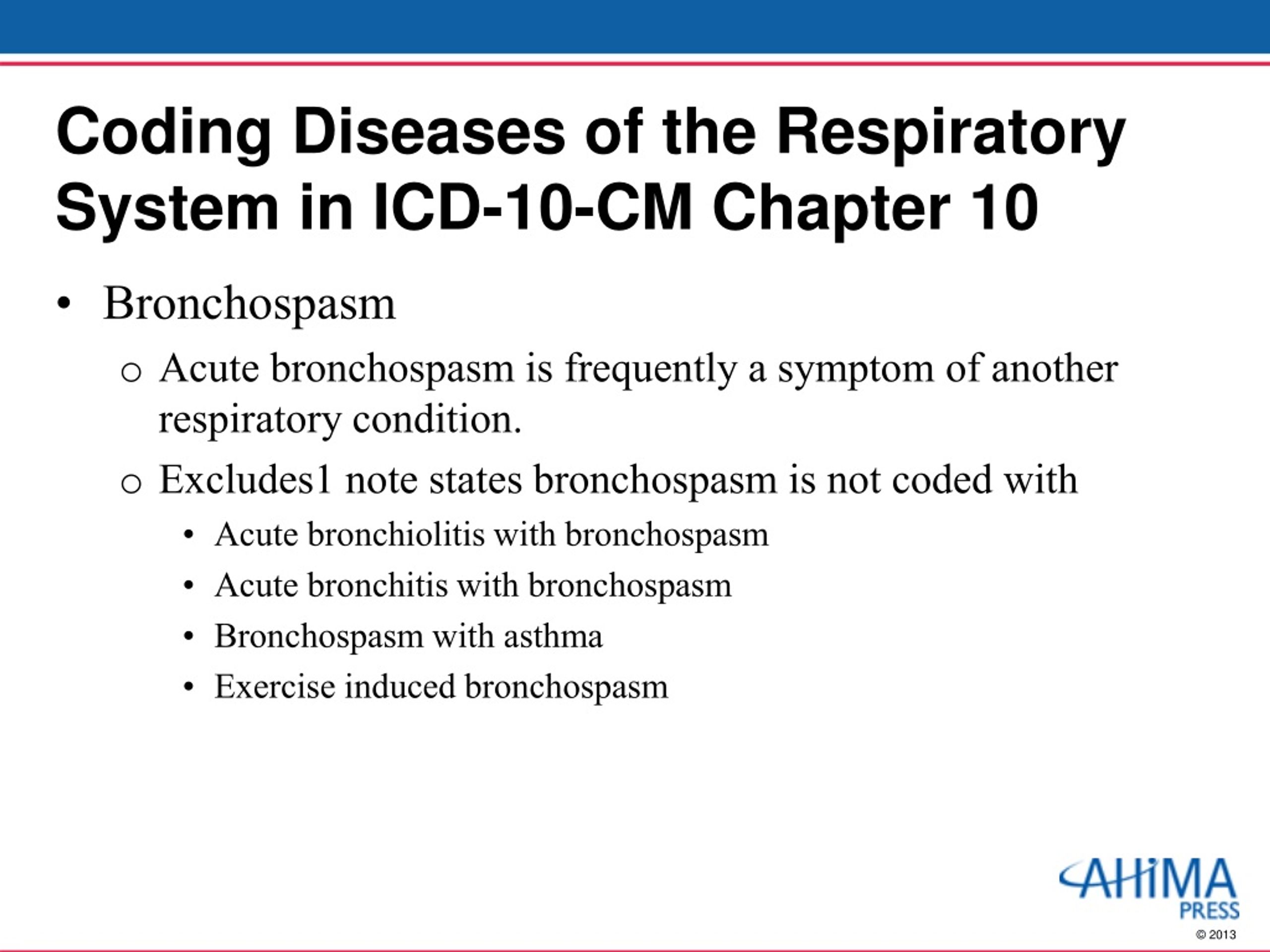
How do you code Acute respiratory failure?
ICD-10 code J96. 00 for Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
Is Acute respiratory failure always coded first?
Currently, the direction states that either the acute respiratory failure or the established etiology can be sequenced first; however, we must take the circumstances of the encounter into account. Many cite the coding convention related to etiology/manifestation as dictating that the etiology must be sequenced first.Apr 18, 2019
What code is J96 01?
Acute respiratory failureICD-10 code: J96. 01 Acute respiratory failure, not elsewhere classified Type 2 [with hypercapnia] - gesund.bund.de.
What are the two types of Acute respiratory failure?
The two types of acute and chronic respiratory failure are hypoxemic and hypercapnic. Both conditions can trigger serious complications and the conditions often coexist. Hypoxemic respiratory failure means that you don't have enough oxygen in your blood, but your levels of carbon dioxide are close to normal.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute respiratory failure?
J96.00Acute respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. J96. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
When may you assign acute respiratory failure as a secondary diagnosis?
If it occurs after admission or it is present on admission but does not meet the definition of principal diagnosis, respiratory failure may be listed as a secondary diagnosis.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10-CM Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris I25. 10.
What does AHRF stand for in medical terms?
Acute hypercapnic respiratory failure (AHRF): looking at long-term mortality, prescription of long-term oxygen therapy and chronic non-invasive ventilation (NIV) - PMC. An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know. The . gov means it's official.
What is acute respiratory failure with hypoxia ICD-10?
J96.0101.
What is the difference between acute and chronic respiratory failure?
Acute respiratory failure is a short-term condition. It occurs suddenly and is typically treated as a medical emergency. Chronic respiratory failure, however, is an ongoing condition. It gradually develops over time and requires long-term treatment.
What is type 1 and type 2 respiratory failure?
Type I respiratory failure involves low oxygen, and normal or low carbon dioxide levels. Type II respiratory failure involves low oxygen, with high carbon dioxide.May 25, 2003
What's acute respiratory failure?
When a person has acute respiratory failure, the usual exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs does not occur. As a result, enough oxygen cannot reach the heart, brain, or the rest of the body. This can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, a bluish tint in the face and lips, and confusion.Feb 22, 2019
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
What causes pneumonia in the lung?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection. Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
What is pneumonia due to solids and liquids?
pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) aspiration pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) neonatal aspiration pneumonia ( P24.-) (noo-mone-ya) an inflammatory infection that occurs in the lung. A disorder characterized by inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma.
What causes a decrease in oxygen in the lungs?
This may cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that blood can absorb from air breathed into the lung. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection but may also be caused by radiation therapy, allergy, or irritation of lung tissue by inhaled substances. It may involve part or all of the lungs.
What causes inflammation of the lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.
What are some examples of respiratory failure?
Examples include. lung diseases such as copd (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and cystic fibrosis.
What happens when your lungs are not able to remove carbon dioxide?
Respiratory failure happens when not enough oxygen passes from your lungs into your blood. Your body's organs, such as your heart and brain, need oxygen-rich blood to work well. Respiratory failure also can happen if your lungs can't remove carbon dioxide (a waste gas) from your blood.
What causes increased carbon dioxide levels in the respiratory system?
Causes include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, emphysema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, pneumothorax, ...
What is impaired gas exchange?
A disorder characterized by impaired gas exchange by the respiratory system resulting in hypoxemia and a decrease in oxygenation of the tissues that may be associated with an increase in arterial levels of carbon dioxide. Impaired gas exchange by the respiratory system resulting in hypoxemia and decreased oxygenation of the tissues ...
What is the ICD-10 code for emphysema?
For these conditions, ICD-10 uses two base code categories: J43 for emphysema and J44 for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). All codes require a fourth digit. However, without additional testing, it is unlikely that a primary care physician can clearly differentiate emphysema from chronic bronchitis. Per the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the National Institutes of Health, “Most people who have COPD have both emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Thus, the general term ‘COPD’ is more accurate.” 1 In that case, J44.9, “COPD, unspecified,” should be used. (See “ Emphysema/COPD codes .”)
What is the ICd 10 code for nasopharyngitis?
Ready for some good news? The common cold is still the common cold and has a simple, three-digit ICD-10 code: J00, “Acute nasopharyngitis.” ICD-10 even includes “common cold” in the description.
What is the code for a cold nose?
Infective rhinitis defaults to the “Acute nasopharyngitis” (common cold) J00 code, discussed earlier. However, chronic rhinitis gets its own code, J31.0. Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis also have their own code series (J30). (See “ Rhinitis and other codes related to the nose .”)
How many digits are in the sinus code?
Each of the acute sinusitis codes requires a fifth digit that differentiates “acute” from “acute recurrent.”. The chronic codes have only four digits. (See “ Sinusitis codes .”) If the cause of the sinusitis is known, add a code from B95-B97, “Bacterial and viral infectious agents,” to identify the infectious agent.
What is the classification of asthma?
Classification of asthma is based on the NHLBI's “Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma” published in 2007. Coding is based on the classification level and the presence of an acute exacerbation or status asthmaticus. (See “ Asthma codes .”)
When to use ICD-10 code J30.1?
It is being used per ICD-10 guidelines “ when the information in the medical record is insufficient to assign a more specific code. ”. However, if in your clinical judgment the condition is caused by pollen, you need to document that judgment in the record and then assign code J30.1, “Allergic rhinitis due to pollen.”.
Is there a recurrent code for larynx?
These codes include acute (with or without obstruction) and chronic codes, but there are no acute recurrent codes. The unspecified codes do not differentiate between the larynx and trachea but use the term “Supraglottitis.” (See “Larynx, trachea, and epiglottis codes .”)
What to do if documentation is not clear as to whether acute respiratory failure and another condition are equally responsible for occasioning
If the documentation is not clear as to whether acute respiratory failure and another condition are equally responsible for occasioning the admission, query the provider for clarification. So, long story short, the answer depends on the encounter.
What is the selection of the principal diagnosis?
Selection of the principal diagnosis will be dependent on the circumstances of the admission. If both the respiratory failure and the other acute condition are equally responsible for occasioning the admission to the hospital, and there are no chapter-specific sequencing rules, the guideline regarding two or more diagnoses ...
Do you sequence the definitive diagnosis code before the symptom code?
The definitive diagnosis code should be sequenced before the symptom code. Signs or symptoms that are associated routinely with a disease process should not be assigned as additional codes, unless otherwise instructed by the classification. The early Coding Clinics instructed coders to sequence the pneumonia first, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for s86.112a
- 2. icd code for virtual reality treatment
- 3. icd 10 code for aids
- 4. icd 10 code for r trochanteric bursitis
- 5. icd 9 code for turner syndrome
- 6. icd 10 cm code for orthopnea
- 7. icd 10 code for right hand dupuytren's contracture
- 8. icd 10 diagnosis code for pelvic pain
- 9. icd 10 code for encephalocele
- 10. icd 10 code for chronic migraine