How uniform is ICD-10 diagnosis and coding for uveitis?
McKay et al. set out to assess the degree of uniformity in uveitis diagnosis and ICD-10 coding among institutions that used the same electronic health record (EHR) system. They found that although uveitis-related ICD-10 code mapping was highly uniform among the institutions, some discrepancies did exist.
What is the ICD 10 code for panuveitis?
There are no specific ICD-10 codes for panuveitis secondary to a systemic disease. For these conditions, use the secondary anterior uveitis code in addition to the panuveitis code. By definition, panuveitis includes anterior uveitis, so this coding is anatomically correct. Figure 1.
What is the ICD 10 for uveitis ra Syndrome?
Chronic iritis, both eyes Uveitis ra syndrome, both eyes ICD-10-CM H20.13 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 124 Other disorders of the eye with mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for uveitis secondary to tuberculosis?
Confirmed diagnosis: Infectious chronic anterior uveitis, secondary to tuberculosis, OU. ICD-10 codes: H20.033, A18.54. A 24-year-old man presented to the clinic with the complaint of bilateral floaters for the past 6 months. He noted no redness, irritation, or blurriness in either eye.
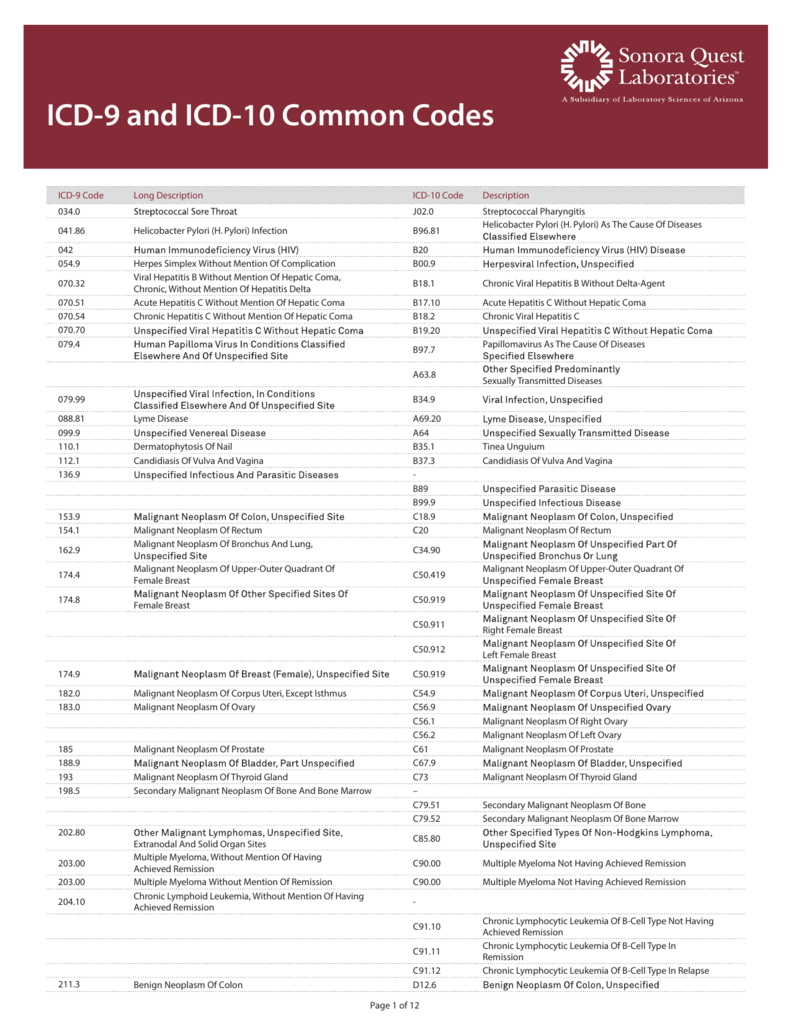
What is the ICD-10-CM code for uveitis?
Sympathetic uveitis, unspecified eye H44. 139 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H44. 139 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for anterior uveitis left eye?
012.
What is chronic anterior uveitis?
Anterior uveitis encompasses inflammation of the iris and/or ciliary body and is one of the most common types of ocular inflammation that primary eye care practitioners will encounter. Anterior uveitis may be caused by a variety of etiologies, including infectious, non-infectious, and masquerade diseases.
What is diagnosis code H20 9?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H20. 9: Unspecified iridocyclitis.
What is acute anterior uveitis?
Acute anterior uveitis is characterised by an extremely painful red eye, often associated with photophobia, and occasionally with decreased visual acuity. Chronic anterior uveitis is defined as inflammation lasting over 6 weeks. It is usually asymptomatic, but many people have mild symptoms during exacerbations.
What is traumatic uveitis?
Inflammation of the Iris Caused by an Eye Injury.
What causes chronic uveitis?
Possible causes of uveitis are infection, injury, or an autoimmune or inflammatory disease. Many times a cause can't be identified. Uveitis can be serious, leading to permanent vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications and preserve your vision.
Is anterior uveitis the same as iritis?
Iritis (i-RYE-tis) is swelling and irritation (inflammation) in the colored ring around your eye's pupil (iris). Another name for iritis is anterior uveitis.
What are the types of uveitis?
What are the types of uveitis?Anterior uveitis affects the iris at the front of the eye. ... Intermediate uveitis affects the ciliary body and the vitreous (gel-like fluid that fills the eye).Posterior uveitis affects the retina and the choroid at the back of the eye.More items...•
What is intermediate uveitis?
Intermediate uveitis (IU) is a chronic, relapsing disease of insidious onset. According to the Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) working group criteria, IU is defined as an intraocular inflammation mainly focused on the vitreous and peripheral retina.
How common is posterior uveitis?
This condition affects males and females in equal numbers. It can strike at almost any age, but usually begins between the ages of 30 and 40. According to one estimate, posterior uveitis occurs in 18/100,000 people (2020).
What is ICD-10 code for eye pain?
ICD-10 code H57. 10 for Ocular pain, unspecified eye is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
When will the ICD-10-CM H20.13 be effective?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H20.13became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for cataracts?
code for any associated cataract (H26.21-)
When will the ICd 10-CM H44.11 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H44.11 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the term for the injury of the eye and orbit?
injury (trauma ) of eye and orbit ( S05.-) A disorder characterized by inflammation of the entire uvea which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Causes include systemic infections, sarcoidosis, and cancers.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cyst of nipple
- 2. icd-10-cm code for diagnosis of reactive airway disease exacerbation
- 3. nys icd code for occupational therapy
- 4. icd 10 code for alzheimer dementia
- 5. icd 10 code for wide spread rhinitis
- 6. icd 10 code for history of primary neoplasm of ovary
- 7. icd 10 code for diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy
- 8. icd 10 code for clotting disorder
- 9. icd-9 code for varus deformity
- 10. icd 10 code for pright elbow pain