Superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, initial encounter. S43.431A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.431A became effective on October 1, 2018.
Could I have a labral tear in my shoulder?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M75.111 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Incomplete rotator cuff tear or rupture of right shoulder, not specified as traumatic. Incomplete rotatr-cuff tear/ruptr of r shoulder, not trauma; Non-traumatic partial right rotator cuff tear; Non-traumatic partial tear of right rotator cuff; Nontraumatic partial bilateral rotator cuff tear; Nontraumatic partial right rotator cuff tear.
What is intrasubstance tear to right shoulder?
Sep 13, 2017 · I wouldn't use the SLAP lesion code (S43.43__) unless the physician specifically states that lesion. I also use M24.11_ for degenerative labral tears or fraying type tears of the labrum. if not specified as degenerative or a SLAP i would use S43.49__ for labral tears. You must log in or register to reply here. Forums.
What is the amount for shoulder labral tear?
M75 M75.6 ICD-Code M75.6: Tear of labrum of degenerative shoulder joint The thin layer of cartilage on the edge of your glenoid cavity is damaged. The shoulder joint is the joint between the shoulder blade and the humerus. The surface of the joint at the shoulder blade is called the glenoid cavity. The glenoid cavity is a shallow depression.
What is a right shoulder SLAP tear?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. S43.431A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, init; The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.431A became effective on October 1, 2021.
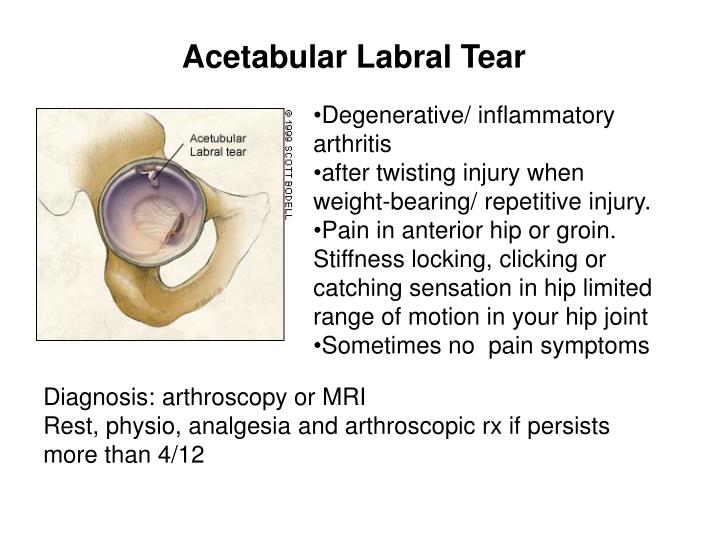
What is labral degeneration in shoulder?
What is the ICD 10 code for labral tear?
What is the ICD 10 code for left shoulder labral tear?
What is the ICD 10 code for anterior labral tear?
What is the ICD 10 code for right shoulder instability?
What is the ICD 10 code for posterior labral tear?
What is superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder?
What is ICD-10 code for left shoulder instability?
What can cause a labral tear in the shoulder?
Common causes of labral tears in the shoulder include: Trauma, such as a fracture or dislocated shoulder. Overuse. Repetitive motion.
What is the difference between CPT code 29806 and 29807?
What kind of code is M75 51?
What causes a slap tear in the shoulder?
The most common mechanisms for SLAP tears are forced traction on the shoulder and direct compression. Direct compression can occur in the acute traumatic setting or in the chronic setting typical in the overhead throwing athlete. Overhead throwers are predisposed to SLAP tears secondary to their adaptive anatomy.
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
Where is the glenoid labrum located?
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid bone [ 1] ( Fig. 15.1 ). As the outer labrum transitions from the periphery to its articulation with the glenoid, the histology changes from fibrous to a small fibrocartilaginous zone at the junction with the glenoid [ 2 ].
What is SLAP tear?
The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear. Anterior dislocations of the shoulder can be associated with a disruption of the anteroinferior labrum and anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, also known as a Bankart lesion.
What causes Bankart lesions?
Bankart lesions are created by episodes of anterior instability. As the humeral head moves out anteriorly and inferiorly, anterior damage can occur to the anterior-inferior labrum, glenohumeral ligaments, joint capsule, rotator cuff, and possibly neurovascular structures.
How many people have tears in their rotator cuff?
Dislocations later in life increase the risk of rotator cuff injury, with tears occurring in nearly 30% of patients older than 40 years and in up to 80% of patients older than 60 years.
How to tell if a slap tear is a slap?
A patient with a SLAP tear will most commonly present with symptoms of deep-seated pain, which can be sharp or dull [ 11 ]. It is usually located deep within the center of the shoulder and can be made worse with overhead activities, pushing heavy objects, lifting, or reaching behind the back. Patients may have mechanical symptoms, such as catching, popping, or grinding with rotation of the shoulder. Many patients with a SLAP tear will also have other shoulder disease, making clinical diagnosis challenging [ 11 ].
What is the ICd 10 code for hip articular cartilage?
M24.159 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other articular cartilage disorders, unspecified hip. The code M24.159 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code M24.159 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acetabular labrum tear, articular cartilage disorder of hip, articular cartilage disorder of the pelvic region and thigh, fibrocartilage lesion of joint or tear of fibrocartilage of joint.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like M24.159 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What causes cartilage to be damaged?
Injured, inflamed, or damaged cartilage can cause symptoms such as pain and limited movement. It can also lead to joint damage and deformity. Causes of cartilage problems include. Tears and injuries, such as sports injuries. Genetic factors. Other disorders, such as some types of arthritis.
What is cartilage in the body?
Information for Patients. Cartilage is the tough but flexible tissue that covers the ends of your bones at a joint. It also gives shape and support to other parts of your body, such as your ears, nose and windpipe. Healthy cartilage helps you move by allowing your bones to glide over each other.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code M24.159 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Where is the ball in the hip?
Your hip is the joint where your femur (thigh bone) meets your pelvis (hip bone). There are two main parts: a ball at the end of the femur, which fits in a socket in the pelvis. Your hip is known as a ball-and-socket joint.
What is the joint between the femur and the pelvis called?
Hip Injuries and Disorders. Your hip is the joint where your femur (thigh bone) meets your pelvis (hip bone). There are two main parts: a ball at the end of the femur, which fits in a socket in the pelvis. Your hip is known as a ball-and-socket joint.
What is the joint between the femur and the hip?
There are two main parts: a ball at the end of the femur, which fits in a socket in the pelvis. Your hip is known as a ball-and-socket joint.
What is the ICd 10 code for glenoid labrum tear?
S43.432D is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder, subsequent encounter. The code S43.432D is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code S43.432D might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of left shoulder or glenoid labrum tear. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#S43.432D is a subsequent encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used after the patient has completed active treatment for a condition like superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines a "subsequent encounter" occurs when the patient is receiving routine care for the condition during the healing or recovery phase of treatment. Subsequent diagnosis codes are appropriate during the recovery phase, no matter how many times the patient has seen the provider for this condition. If the provider needs to adjust the patient's care plan due to a setback or other complication, the encounter becomes active again.
How to diagnose shoulder pain?
Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
Is S43.432D a POA?
S43.432D is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG). CMS publishes a listing of specific diagnosis codes that are exempt from the POA reporting requirement. Review other POA exempt codes here.
What are the bones of the shoulder?
Your shoulder joint is composed of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone). Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it.
What is the best treatment for shoulder pain?
Arthritis. Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code S43.432D its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for esophageal foreign body
- 2. icd 10 code for mets to axillary lymph nodes
- 3. icd 10 code for excerise sweating
- 4. icd-10 code for aftercare following surgery of reproductive system
- 5. icd-10 code for giant cell tumor of tendon sheath finger
- 6. icd-10-cm code for trigeminal neuropathy
- 7. icd 1o code for hgb a1c
- 8. icd 10 code for presence of artificial right knee joint
- 9. icd 10 cm code for senile dementia
- 10. icd-10 code for findings in csf