What is the best treatment for a diabetic ulcer?
The Best Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatments
- Assess Wound With a Full Exam. The best treatments begin with a comprehensive exam with a full evaluation. ...
- Proper Dressing, Infection Control, and Offloading. ...
- Hyperbaric Wound Care for Diabetic Ulcers. ...
Can a diabetic ulcer heal by itself?
While diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) can be difficult to heal, if left untreated they can become infected and lead to further complications. The good news is that these foot ulcers can be healed with advanced treatments and can be further avoided when patients take preventative actions.
What is the prognosis of diabetic ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers can take several weeks to heal. Ulcers may take longer to heal if your blood sugar is high and if constant pressure is applied to the ulcer. Remaining on a strict diet and off-loading pressure from your feet is the most effective way to allow your foot ulcers to heal.
Which is the most common type of diabetic ulcer?
Wagner Grades 0 through 5 are as follows:
- No diabetic foot ulcer is present, but there is a high risk of developing one.
- A surface ulcer involves full skin thickness, but does not yet involve the underlying tissues.
- A deep ulcer penetrates past the surface, down to the ligaments and muscle. ...
- A deep ulcer occurs with inflammation of subcutaneous connective tissue or an abscess. ...

What is the ICD-10 code for ulcer of right heel?
ICD-10 code L97. 41 for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of right heel and midfoot is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot wound?
622).” Of these options, the most commonly used codes for diabetic foot ulcer are E10. 621 (Type 1 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer) and E11. 621 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer).
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic leg ulcer?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer- E11. 621- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes with foot ulcer?
621 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer.
What is the ICD-10 code for foot ulcer?
ICD-10 code L97. 509 for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is diabetic foot ulcer?
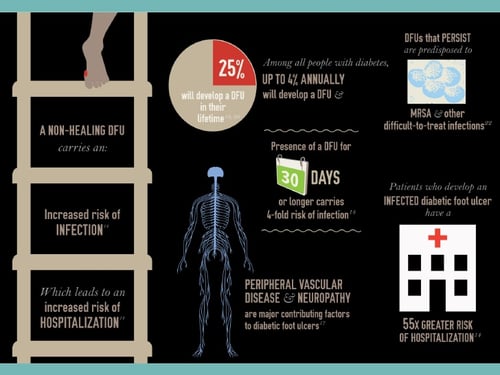
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
How do you code a diabetic foot ulcer?
Of these options, the most commonly used codes for diabetic foot ulcers are E10. 621 (Type 1 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer) and E11. 621 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer).
Are diabetic foot ulcers pressure ulcers?
Skin necrosis and gangrene are also included in the current system as ulcers.” This definition is similar to that of the EPUAP, all-inclusive and, as such, any pressure ulcer on the foot of a person with diabetes is a diabetic foot ulcer — as is any traumatic wound, including a thermal or chemical injury.
Are diabetic ulcers considered pressure ulcers?
Diabetic ulcers may look similar to pressure ulcers; however, it is important to note that they are not the same thing. As the name may imply, diabetic ulcers arise on individuals who have diabetes, and the foot is one of the most common areas affected by these skin sores.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for left diabetic foot infection?
E11. 621 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer | ICD-10-CM.
What is an ulcer on the foot?
Foot ulcers are open sores or lesions that will not heal or that return over a long period of time. These sores result from the breakdown of the skin and tissues of the feet and ankles and can get infected. Symptoms of foot ulcers can include swelling, burning, and pain.
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Regarded as the most common reason for hospital stays among people with diabetes, a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is an open sore caused by neuropathic (nerve) and vascular (blood vessel) complications of the disease. Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot, these complex, ...
How many people with diabetes have foot ulcers?
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA), approximately 15 percent of people with diabetes suffer from foot ulcers. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, about 6 percent will be hospitalized due to serious infections or other ulcer-related complications.
What is a L97.91 ulcer?
L97.91 -Non-pressure chronic ulcer of unspecified part of right lower leg. L97.92 – Non-pressure chronic ulcer of unspecified part of left lower leg. According to the American Podiatric Medical Association, about 14 to 24 percent of Americans with diabetic foot ulcers have amputations.
What are the risk factors for ulcers?
The most common risk factors for ulcer formation include – diabetic neuropathy, structural foot deformity, kidney disease, obesity and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. The condition can be effectively prevented if the underlying conditions causing it are diagnosed early and treated correctly.
How many amputations are there for diabetics?
The risk of foot ulceration and limb amputations increases with age and duration of diabetes. In the United States, about 82,000 amputations are performed each year on persons with diabetes; half of those ages 65 years or older. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers varies depending on their causes.
Where does neuropathic ulcer occur?
Neuropathic ulcers– occur where there is peripheral diabetic neuropathy, but no ischemia caused by peripheral artery disease. This type of foot infection generally occurs on the plantar aspect of the foot under the metatarsal heads or on the plantar aspects of the toes.
Where are diabetic ulcers located?
Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot , these complex, chronic wounds can affect people with both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If left untreated, diabetic foot ulcers can have a permanent, long-term impact on the morbidity, mortality and quality of a patients’ life.
What causes diabetic foot ulcers?
A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury.
Why do diabetics get ulcers?
The American Podiatric Medical Association adds that “ (diabetic foot) ulcers form due to a combination of factors , such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation (such as friction or pressure), and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes .”. They go on to note that “vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, ...
What percentage of diabetics have neuropathy?
After 10 years, ~90 percent of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics have some degree of neuropathy, most commonly affecting the feet and legs, and 90 percent of diabetic foot ulcers have diabetic neuropathy as a contributing factor. If the diabetic doesn’t recognize discomfort due to nerve impairment, they may not adjust their shoes ...
What is the L89 code for a pressure ulcer?
Pressure injuries with skin breakdown are considered pressure ulcers. An additional L89 code specifies the stage (depth of tissue injury) and the anatomical site. Pressure ulcers form in sites that experience shear or pressure, typically in tissue overlying bony prominences such as elbows, the sacrum, hips, or heels.
Why are pressure ulcers considered a patient safety indicator?
Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
Can diabetes cause heel ulcers?
Heel ulcers, however, are usually a consequence of a pressure injury, although it is also possible to have another mechanism cause a non-pressure injury involving the heel. Diabetes may accelerate or complicate the injury. Neuropathy results in malum perforans pedis (a.k.a. bad perforating foot) ulcers.
Is diabetes mellitus a secondary condition?
There are medical diagnoses that predispose patients to develop secondary conditions. Diabetes mellitus is a pervasive endocrinopathy whereby hyperglycemia affects every organ and system in the body, including the nerves and blood vessels. It makes a patient more prone to infection and poor healing.
Why was gangrenous pressure ulcer admitted?
The primary reason for the admission was for treatment of the gangrenous pressure ulcer. This was not a diabetic ulcer. Diabetic ulcers typically involve the foot and toes. Pressure ulcers develop in tissue near bony prominences, such as the elbows, tailbone, greater trochanters, or heels.
Does diabetes mellitus cause pressure ulcers?
Although diabetes mellitus may increase the risk of pressure ulcers because of its association with neuropathy and angiopathy, ICD- 10-CM doesn’t classify pressure ulcers the same way as diabetic ulcers.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for metabolic acidosis with lactic acidosis
- 2. icd 10 code for acut resp failure
- 3. icd-10 code for hymen remnant
- 4. icd 10 code for fever and malaise due to viral syndrome
- 5. icd 9 code for history of myocardial infarction
- 6. icd 9 code for i48.0
- 7. icd 10 code for choroidal neovascular membrane right eye
- 8. icd 10 dx code for ventilator dependent respiratory failure
- 9. icd 9 code for overweight
- 10. icd 10 code for long-term (current) use of anticoagulants