Diastolic (congestive) heart failure. I50.3 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for CHF?
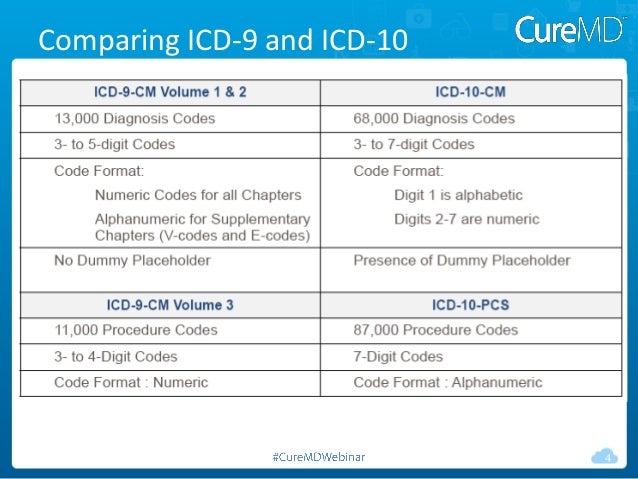
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.3 Diastolic (congestive) heart failure 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code I50.3 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · Chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I50.32 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.32 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Diastolic (congestive) heart failure (I50.3) I50.23 I50.3 I50.30 ICD-10-CM Code for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50.3 ICD-10 code I50.3 for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for diastolic dysfunction?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure. I50.33 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.33 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code I50.3 is a non-billable code.
What is the condition called when you have difficulty breathing?
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing (dyspnea), leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion ...
What causes a decompensation attack?
An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, infection, or thyroid disease. Acute interstitial pulmonary edema.
What is the ICD 10 code for exacerbation of CHF?
Acute systolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the pathophysiology of congestive heart failure?
Congestive heart failure is a syndrome that can be caused by a variety of abnormalities, including pressure and volume overload, loss of muscle, primary muscle disease or excessive peripheral demands such as high output failure. In the usual form of heart failure, the heart muscle has reduced contractility.
What is a CHF exacerbation?
CHF exacerbation occurs when there is an increase in or worsening of heart failure symptoms. Heart failure happens when your heart is unable to pump enough blood throughout your body.
How do you code acute on chronic congestive heart failure?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 23.
How do you code a CHF exacerbation?
Coding Guidance Assign code I50. 9, heart failure NOS for a diagnosis of congestive heart failure. “Exacerbated” or “Decompensated” heart failure – Coding guidelines advise that “exacerbation” and “decompensation” indicate an acute flare-up of a chronic condition.
What is CHF anatomy and physiology?
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Defined CHF as a condition in which cardiac function is reduced so that the heart inadequately pumps blood at a rate to meet the need of the body’s tissues and/or allows it to do so only from an abnormally elevated ventricular diastolic pressure.
What is the pathophysiology of heart failure that results in impaired cardiac output?
Cardiac and Vascular Changes Overall, the changes in cardiac function associated with heart failure result in a decrease in cardiac output. This results from a decline in stroke volume that is due to systolic dysfunction, diastolic dysfunction, or a combination of the two.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 diagnosis code for nausea and vomiting
- 2. icd 10 code for decreased appetite
- 3. icd 10 code for z01.419
- 4. icd 10 code for fibrocystic disease of breast bilateral
- 5. icd-10 code for chronic pancreatitis
- 6. icd 10 cm code for abdominal pain in epigastrium due to bilateral hepatic and renal cyst
- 7. icd 10 code for cms hcc
- 8. icd 9 code for medical procedrue
- 9. icd 10 code for dehydration complicating pregnancy
- 10. icd 10 code for lung mass rul