What is the ICD 10 code for chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure?
ICD-10 code I50.32 for Chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What are the Medicare accepted ICD-10 codes for heart failure?
Listed below are all Medicare Accepted ICD-10 codes under I50.3 for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure. These codes can be used for all HIPAA-covered transactions. Billable - I50.33 Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure
What is the ICD 10 code for hypertensive heart disease?
Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure. I11.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I11.0 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the ICD 10 code for diagnosis?
I11.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I11.0 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I11.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 I11.0 may differ.
What is the ICD-10 code for diastolic dysfunction?
There is no code within the ICD-10-CM code set for diastolic dysfunction. When you look up dysfunction, heart in the alphabetic index it leads to I51. 89 Other ill-defined heart disease and likely the use of the diastolic heart failure code applied to documentation of the term dysfunction would be denied.
What is diastolic heart disease?
Diastolic heart failure, technically referred to as "heart failure with preserved ejection fraction" (HFpEF), is a condition where the lower left chamber of the heart (left ventricle) is not able to fill properly with blood during the diastolic phase, reducing the amount of blood pumped out to the body.
Is diastolic dysfunction the same as diastolic heart failure?
When heart failure is accompanied by a predominant or isolated abnormality in diastolic function, this clinical syndrome is called diastolic heart failure. Diastolic dysfunction refers to a condition in which abnormalities in mechanical function are present during diastole.
Is grade 1 diastolic dysfunction the same as heart failure?
Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction is sometimes referred to as diastolic failure or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). People with Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction have evidence of abnormal diastolic function and may or may not have symptoms.
Is diastolic heart failure a heart condition?
Diastolic heart failure, also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), is a condition in which your heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) becomes stiff and unable to fill properly. Diastolic heart failure is one of two kinds of left-sided heart failure.
Is diastolic heart failure left or right?
Diastolic heart failure occurs when the left ventricle cannot relax properly between heartbeats. The left ventricle fills with oxygenated blood between heartbeats, then pumps the blood around the body during a heartbeat, also known as systole.
Is grade 2 diastolic dysfunction considered heart failure?
Clinical manifestations of congestive heart failure may start to occur once grade II diastolic dysfunction is present, but not in the presence of grade I diastolic dysfunction (impaired relaxation).
What are the four grades of diastolic dysfunction?
According to the current guidelines (DD2016) and for patients with preserved ejection fraction, one should evaluate four variables to assess diastolic dysfunction: e′, E/e′ ratio, LAVI, and TRpV.
What are the 4 stages of diastolic heart failure?
There are four heart failure stages (Stage A, B, C and D). The stages range from "high risk of developing heart failure" to "advanced heart failure."...Stage CShortness of breath.Feeling tired (fatigue).Less able to exercise.Weak legs.Waking up to urinate.Swollen feet, ankles, lower legs and abdomen (edema).
What is Type 2 diastolic dysfunction?
Grade II – This diastolic dysfunction is characterized by increased filling pressure in the atrium and is considered to be moderate stage disease. The left atrium may also increase in size due to the increased pressure.
What is the treatment for grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
The first-line approach to diastolic dysfunction is currently beta blocker therapy, which slows the heart rate and allows the ventricles time to fill with blood properly.
What are the stages of diastolic dysfunction?
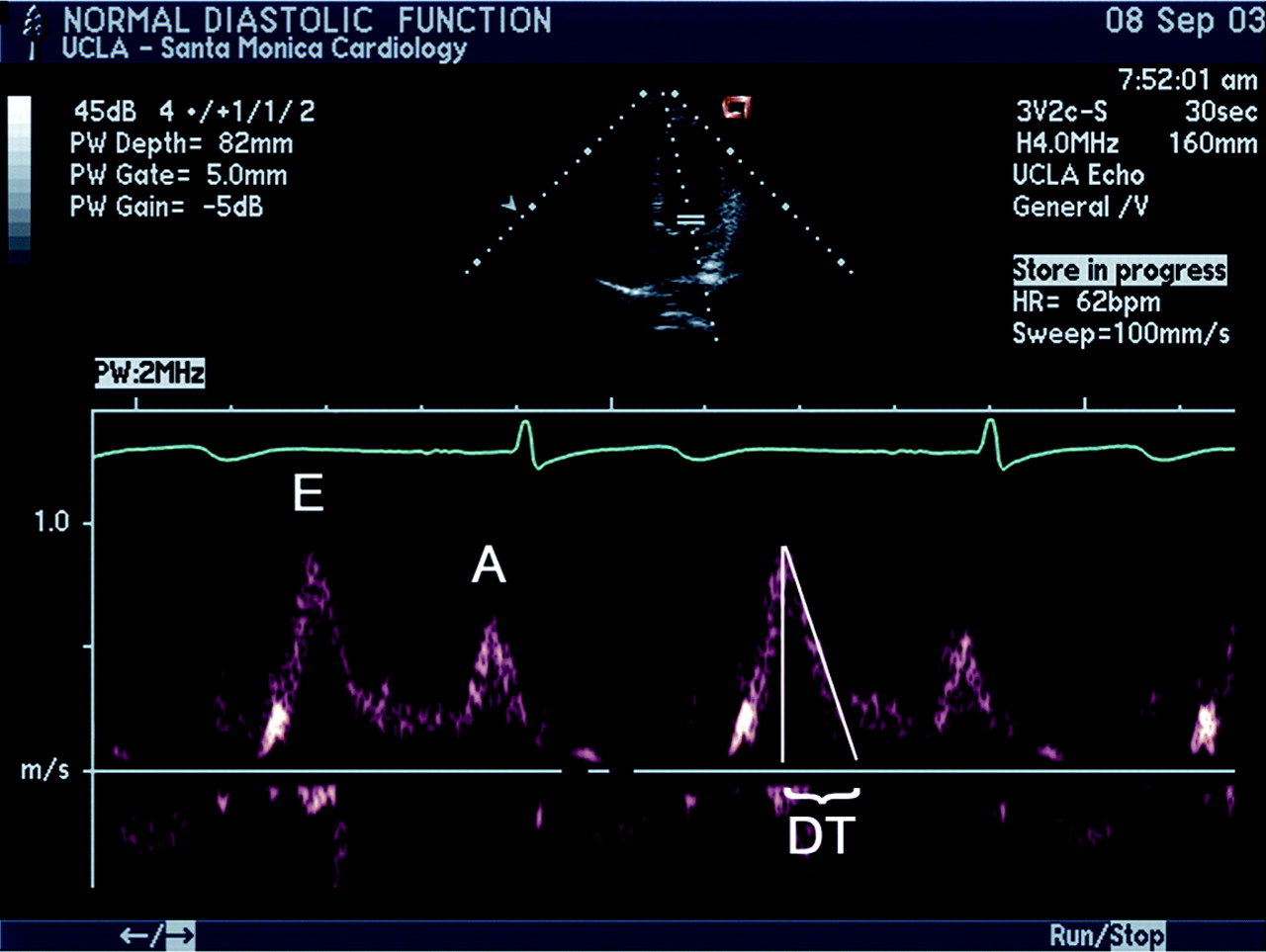
Diastolic dysfunction was graded on a four-point ordinal scale: 1) normal; 2) mild diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation without increased LV end-diastolic filling pressure (decreased E/A ratio <0.75); 3) moderate or “pseudonormal” diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation with increased LV end-diastolic ...
Is diastolic dysfunction serious?
When your heart isn't able to relax fast enough, it's called diastolic dysfunction (DD). DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure symptoms in patients who have what's called preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, according to cardiologist Wael Jaber, MD.
What is life expectancy with diastolic dysfunction?
Conclusions: Our study results indicate that diastolic dysfunction with a normal EF, in the absence of CAD and systolic dysfunction, has an excellent prognosis over a long period (5-6 years).
Can you live long with diastolic heart failure?
The life expectancy for congestive heart failure depends on the cause of heart failure, its severity, and other underlying medical conditions. In general, about half of all people diagnosed with congestive heart failure will survive five years. About 30% will survive for 10 years.
What is the treatment for diastolic dysfunction?
Medications — water pills can often help to alleviate the edema that is caused by diastolic dysfunction, and other medications can help to treat underlying medical problems like high blood pressure, diabetes or other heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
What is the condition called when the heart is decompensated?
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing (dyspnea), leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, infection, or thyroid disease.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code I50.3 is a non-billable code.
What is the ICD-10 code for heart failure?
I50.3 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hearing aid status
- 2. icd-10 code for blindness left eye, unspecified category
- 3. icd 10 cm code for type 2 diabetes uncontrolled
- 4. what is icd-10 pcs code for a breast biopsy with metallic localization clip and ultrasound guidance
- 5. icd 10 code for dysfunctional bladder
- 6. icd 10 code for traumatic rupture achilles tendonitis
- 7. icd 9 code for adenoma of the adrenal gland
- 8. icd 9 code for insomnia due to anxiety
- 9. 2016 icd 10 code for diabetic ulcer
- 10. icd 10 code for metastatic rectal cancer