What are the signs of a ruptured eardrum?
The nine signs you may have a perforated eardrum include:
- Hearing loss
- A spinning sensation (vertigo)
- Nausea or vomiting from vertigo
- Ear pain that may subside
- Mucus-like, pus-filled, or bloody drainage from your ear
- A ringing in your ear (tinnitus)
- Episodic ear infections
- Facial weakness
- Dizziness
Does a ruptured eardrum smell bad?
Why Does My Ear Smell Inside. Ear infection. Ear infections usually occur in your middle ear. They can be either bacterial or viral. The infections are most often painful due to inflammation and buildup. An ear infection can cause drainage and you might notice a bad smell. You May Like: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode. The Causes Of A Ruptured Eardrum Are:
How can a ruptured eardrum be prevented?
These tests include:
- Laboratory tests. If there's discharge from your ear, your doctor may order a laboratory test or culture to detect a bacterial infection of your middle ear.
- Tuning fork evaluation. Tuning forks are two-pronged, metal instruments that produce sounds when struck. ...
- Tympanometry. ...
- Audiology exam. ...
Does a ruptured eardrum Always Hurt?
Perforations or ruptures of the eardrum may or may not cause pain depending upon the underlying cause of the rupture or hole. Moreover, the size of the hole, and where it is located on the eardrum surface may play a role in eardrum pain or its absence. Infections are the primary cause of a ruptured eardrum.

What is a rupture ear?
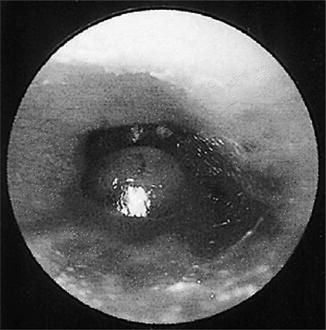
A ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole or tear in the thin tissue that separates the ear canal from the middle ear (eardrum). A ruptured eardrum can result in hearing loss. It can also make the middle ear vulnerable to infections.
What is the medical term for ruptured eardrums?
Middle ear infections may cause pain, hearing loss and spontaneous rupture (tear) of the eardrum, resulting in a perforation. In this circumstance, there may be infected or bloody drainage from the ear. In medical terms, this is called otitis media with perforation.
What is central perforation of tympanic membrane?
Information: A central perforation is a perforation in the pars tensa that leaves an intact portion of the tympanic membrane between the rim of the perforation and the bony canal. The fibrous annulus, the tickened portion of the TM near the bony canal, is also intact.
What is the ICD-10 code for tympanic membrane?
Unspecified disorder of tympanic membrane, bilateral The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H73. 93 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H73.
What causes a ruptured eardrum?
A ruptured eardrum is often caused by a middle ear infection. With an infection fluid develops behind the drum creating pain and discomfort. This fluid buildup can create a small rupture of the drum allowing fluid to drain from the ear, appearing as pus. Bleeding may also occur.
When do you refer to tympanic membrane perforation?
Symptoms include sudden ear pain, or sudden decrease in ear pain, discharge (which may be bloody) or hearing loss. The vast majority of ruptured eardrums will heal without treatment. A simple perforation of the ear drum as part of acute otitis media does NOT need referral unless it persists > 6 weeks.
What are the types of tympanic membrane perforation?
The type of perforation seen were central 57.6%, subtotal 33.3%, total 6.1%, marginal 3.0%. The sides affected were left ear 45.5%, right ear 15.2%, and both ears 39.4%. The causes found were chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) 90.9%, acute suppurative otitis media (ASOM) 6.1%, and trauma to the affected ear 3.0%.
How do you classify tympanic membrane perforation?
The classification was according to the size of perforation: small perforation, <1 quadrants or maximum diameter <3. mm; middle perforation, >1 quadrants and <2 quadrants or maximum diameter between 3 and 5 mm; and large perforation, >2 quadrants or maximum diameter >5 mm.
What is the most common type of tympanic membrane perforation?
The outcome may also be related to the cause, mechanism, treatment and complications associated with the injuries. Simple traumatic tympanic membrane perforation (TTMP) remains the most common type of trauma - induced otologic dysfunction.
What is the ICD-10 code for ear effusion?
ICD-10 code H92 for Otalgia and effusion of ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is the ICD-10 code for otitis externa?
Unspecified otitis externa, unspecified ear H60. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H60. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for ear infection?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What is the ICd 10 code for eardrum rupture?
Traumatic rupture of ear drum 1 S09.2 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S09.2 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S09.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 S09.2 may differ.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is a code title?
Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. "In diseases classified elsewhere" codes are never permitted to be used as first listed or principle diagnosis codes.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as H72. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for tripped and fell on tractor
- 2. icd 10 cm code for smoldering multiple myeloma
- 3. icd 10 code for pinned between objects
- 4. icd 10 code for allergy panel animals
- 5. icd 10 code for heterogeneous uterus
- 6. icd-10 code conversions for chiropractors
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for sprain lumbar spine
- 8. icd 10 code for incision check
- 9. icd 10 code for traumatic rhabdomyolysis initial encounter
- 10. icd 10 code for palpable mass of clavicle