ICD-10-PCS Code 0CB70ZX
| 1: Section | 0 | Medical and Surgical |
| 2: Body System | C | Mouth and Throat |
| 3: Root Operation | B | Excision |
| 4: Body Part | 7 | Tongue |
| 5: Approach | 0 | Open |
How to look up incision and drainage in ICD 10?
Their corresponding character in ICD-10-CM is:
- Drainage: Character 9
- Extirpation: Character C
- Fragmentation: Character F
How many codes in ICD 10?
The following are USSD codes that I use with my Android OS Mobile:-
- *#06# - This USSD command displays the IMEI
- *#12580*369# - This USSD command displays the SW and HW information
- *#2222# - This USSD code displays the HW version
What does ICD 10 mean?
ICD-10. ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
What is the ICD 10 code for removal of stitches?
Suture Removal from Upper Extremity
- (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-PCS)
- (effective 10/1/2016): No change
- (effective 10/1/2017): No change
- (effective 10/1/2018): No change
- (effective 10/1/2019): No change
- (effective 10/1/2020): No change

What is the ICD-10 code for post surgery?
ICD-10 Code for Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems- Z48. 81- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10-PCS code for excision of skin lesion left lower arm?
0HBEXZXExcision of Left Lower Arm Skin, External Approach, Diagnostic. ICD-10-PCS 0HBEXZX is a specific/billable code that can be used to indicate a procedure.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin lesion?
ICD-10-CM Code for Disorder of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified L98. 9.
What is the ICD-10-PCS code for the excisional debridement?
If an excisional debridement the code would be 0HBMXZZ Excision of right foot skin, external approach. Example: Excisional debridement of skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle of buttocks. (Accounting for laterality), 0KBP3ZZ Excision of left hip muscle, percutaneous approach.
Is excision the same as resection?
Resection is similar to excision except it involves cutting out or off, without replacement, all of a body part. Resection includes all of a body part or any subdivision of a body part having its own body part value in ICD-10-PCS, while excision includes only a portion of a body part.
What is the CPT code for excisional biopsy?
No, CPT does not have a code for excisional biopsy. It is either a biopsy (11100 or 11101) or a benign or malignant excision code.
What is the ICD-10 code for benign skin lesion?
Other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified D23. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D23. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the medical code for disorder of the skin and subcutaneous tissue unspecified?
ICD-10 code: L98. 9 Disorder of skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified.
What is a skin lesion?
A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it. Two categories of skin lesions exist: primary and secondary. Primary skin lesions are abnormal skin conditions present at birth or acquired over a person's lifetime.
How do you code excisional debridement?
For excisional debridement of muscle or fascia, coders would report CPT code 11043 (debridement, muscle or fascia [includes epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, if performed]; first 20 sq. cm or less) for the first 20 sq. cm and add-on code 11046 (debridement, muscle or fascia; each additional 20 sq.
How do you code wound debridement?
Wound debridement codes (not associated with fractures) are reported with CPT codes 11042-11047. Wound debridements are reported by the depth of tissue that is removed and the surface area of the wound.
Is surgical debridement the same as excisional debridement?
One thing to keep in mind, is the difference between an excisional debridement and a non-excisional debridement. An excisional debridement: Is a surgical procedure that involves an excisional method of removal, or cutting away tissue, necrosis and/or slough. Groups to a surgical MS-DRG.
Convert 0DB80ZZ to ICD-9-PCS
The following crosswalk between ICD-10-PCS to ICD-9-PCS is based based on the General Equivalence Mappings (GEMS) information:
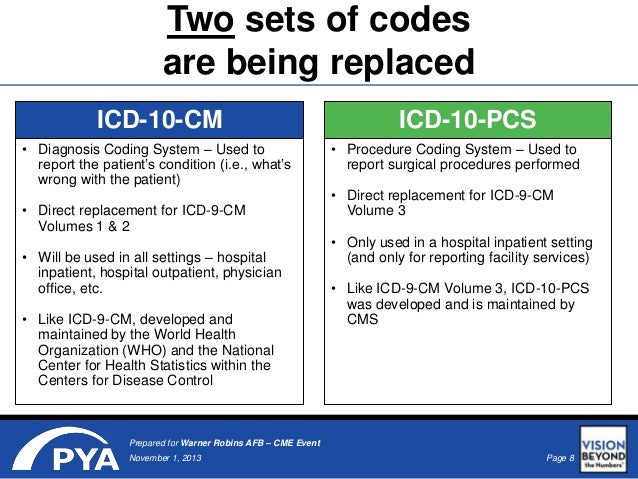
What is ICD-10-PCS?
The ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) is a catalog of procedural codes used by medical professionals for hospital inpatient healthcare settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is a Z00-Z99?
Categories Z00-Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury or external cause classifiable to categories A00 -Y89 are recorded as 'diagnoses' or 'problems'. This can arise in two main ways:
Why is Z53.09 not carried out?
Z53.09 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of other contraindication. Z53.1 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of patient's decision for reasons of belief and group pressure. Z53.2 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of patient's decision for other and unspecified reasons.
What is a Z00-Z99?
Categories Z00-Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury or external cause classifiable to categories A00 -Y89 are recorded as 'diagnoses' or 'problems'. This can arise in two main ways:
Why is Z53.09 not carried out?
Z53.09 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of other contraindication. Z53.1 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of patient's decision for reasons of belief and group pressure. Z53.2 Procedure and treatment not carried out because of patient's decision for other and unspecified reasons.
What is skin excision?
Excision involves the cutting and full-thickness removal of a lesion, with extension through the dermis into the subcutis. Skin lesion excisions include the surrounding tissue or margins. To accurately code lesion excisions, review the documentation for details regarding whether the lesion is benign or malignant, the location, and the excised diameter.
How to determine code selection?
Code selection is determined by the size of the excision , not the size of the lesion. Excision size includes the size of the lesion plus the width of the excised margins (the area surrounding the lesion that is also removed). To calculate the excision size, measure the diameter of the lesion at its longest point (greatest clinical diameter) plus two times the narrowest margin appropriate for removing the entire lesion (the margin on both sides of the lesion).#N#Note: The rule of thumb is to measure first; cut second. The provider should measure the lesion and margins preoperatively because the lesion tissue generally changes shape or shrinks once removed and placed in formalin.
What is the code for benign lesion excision?
Without a pathology report to confirm the diagnosis, you must assign an unspecified diagnosis and a benign lesion excision code (11400-11471).
What is the code for a malignant lesion?
If pathology confirms malignancy, assign a malignant lesion code (11600-11646). Malignancies can be further classified into: Carcinoma in-situ – precancerous cells that have not spread beyond the primary site; may evolve into an invasive malignancy.
What is the primary site of a tumor?
Primary site – the original, or first, tumor in the body growing at the anatomical site where tumor progression began. Secondary (metastatic) site – cancer cells that have spread from the primary site to other parts of the body and formed secondary tumors.
Who is Stacy Chaplain?
Stacy Chaplain, MD, CPC, is a development editor at AAPC. She has worked in medicine for more than 20 years, with an emphasis on education, writing, and editing since 2015. Prior to AAPC, she led a compliance team as director of clinical coding quality for a multispecialty group practice. Chaplain received her Bachelor of Arts in biology from the University of Texas at Austin and her Medical Doctorate from the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston. She is a member of the Beaverton, Oregon, local chapter.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for concussion after mva
- 2. icd 9 code for screening for hepatitis b immunity
- 3. icd 10 code for poor resting anal sphincter tone
- 4. icd 9 code for hoh
- 5. icd-10-cm code for removed basal cell carcinoma
- 6. icd 10 code for stabbed with knife
- 7. icd-10-cm code for left upper lobe thyroid neoplasm
- 8. icd-10-pcs code for placement of fetal monitoring device on scalp
- 9. icd 10 code for pediatric reflux
- 10. icd 10 code for fracture of the right distal metaphysis of the humerus