Abnormal electroencephalogram [EEG] R94.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R94.01 became effective on October 1, 2018.
How many codes in ICD 10?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What are the common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
How ICD 10 is different from ICD 9 codes?
- Similar to the diagnosis code set, the alpha characters in ICD 10 code sets are not case-sensitive.
- The letters “O” and “I” are not in the code set. ...
- The 7 characters in the procedure code set help in providing very precise details. ...
- The fourth character identifies the part of the body. ...
What does ICD - 10 stand for?
The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
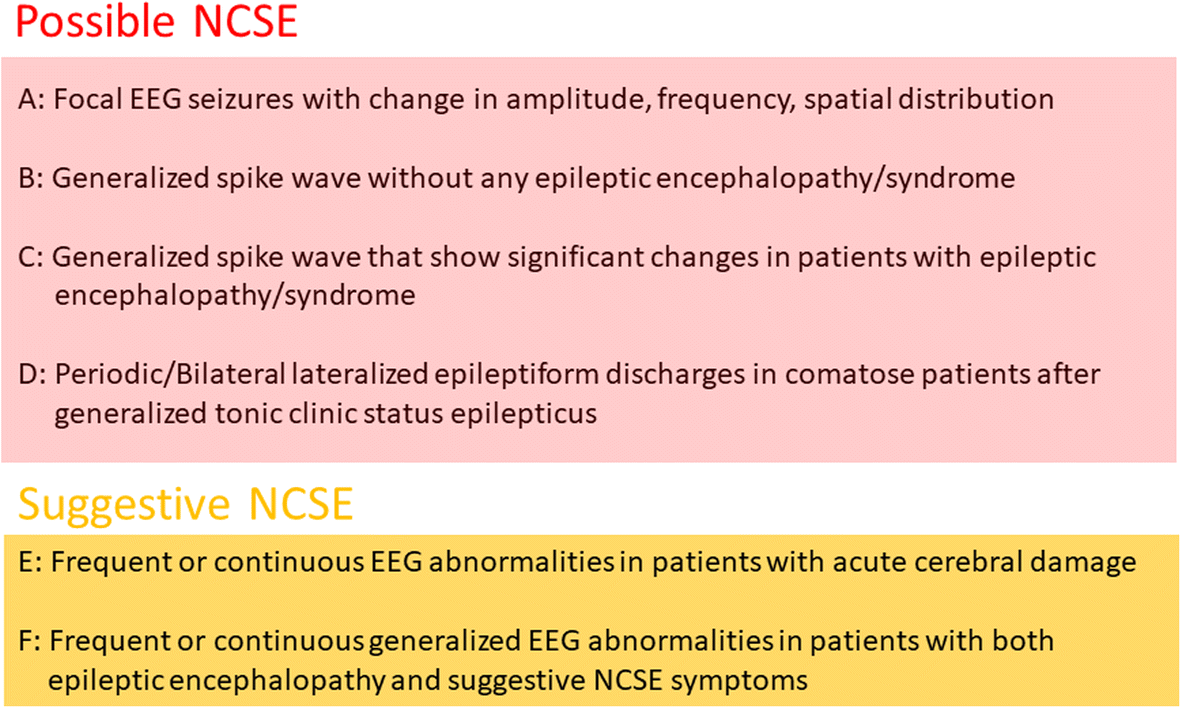
What is the ICD 10 code for EEG?
R94.01ICD-10 code R94. 01 for Abnormal electroencephalogram [EEG] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the CPT code for EEG?
A routine EEG is described by Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) codes 95812, 95813, 95816, 95819 or 95822 and refers to a routine EEG recording of less than a 24 hour continuous duration.
What is diagnosis code Z03 89?
ICD-10 code Z03. 89 for Encounter for observation for other suspected diseases and conditions ruled out is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD 10 code for rule out diagnosis?
Second solution – Use Z03.89 ICD 10 In such case, if the rule/condition is confirmed in the final impression we can code it as Primary dx, but if the rule/out condition is not confirmed then we have to report suspected or rule/out diagnosis ICD 10 code Z03. 89 as primary dx.
What is the CPT code for a 24 hour EEG?
New Technical Component CodesRecording TypeDuration of LTEEGContinuous Monitoring up to 4 pts monitoredEEG alone12 to 26 hours recording Typically 24 hours95710EEG w/ video2 to 12 hours recording Typically 8 hours95713EEG w/ video12 to 26 hours recording Typically 24 hours957161 more row
How do you bill a 72 hour EEG?
Using the New Codes in Practice Technical Component codes are used daily. For example, a 72-hour unmonitored ambulatory video-EEG would be coded as 95724 for the physician's work, 95700 for the electrode set-up, and 3 technical units of 95708—1 unit coded for each day of monitoring.
Can Z03 89 be a primary DX?
Here, you cannot use the Z03. 89 as primary diagnoses. The observation codes are not used if an injury or illness, or any signs or symptoms related to the suspected condition, are present.
What is diagnosis code Z20 828?
Z20. 828, Contact with and (suspected) exposure to other viral communicable diseases. Use this code when you think a patient has been exposed to the novel coronavirus, but you're uncertain about whether to diagnose COVID-19 (i.e., test results are not available).
When should you use the code v71 09?
09 for Observation of other suspected mental condition is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -PERSONS WITHOUT REPORTED DIAGNOSIS ENCOUNTERED DURING EXAMINATION AND INVESTIGATION.
Can I code for possible diagnosis?
Under ICD-10 coding rules, in the outpatient setting, if you note your patient's diagnosis as “probable” or use any other term that means you haven't established a diagnosis, you are not allowed to report the code for the suspected condition. However, you may report codes for symptoms, signs, or test results.
How do you code a suspected diagnosis?
If the diagnosis documented at the time of discharge is qualified as “probable,” “suspected,” “likely,” “questionable,” “possible,” or “still to be ruled out,” or other similar terms indicating uncertainty, code the condition as if it existed or was established.
Can you code rule out diagnosis?
In the guidelines, CMS states the following: “Do not code diagnosis documented probable, suspected, questionable, rule out, compatible with, consistent with, or working diagnosis or similar terms indicating uncertainty.
How long is an EEG?
Electroencephalogram (EEG), continuous recording, physician or other qualified health care professional review of recorded events, analysis of spike and seizure detection, interpretation, and summary report, complete study greater than 36 hours, up to 60 hours of EEG recording, with video (VEEG)
How does video electroencephalographic monitoring improve patient outcomes?
The Agency for Health Care Policy and Research has stated that information provided by video electroencephalographic (EEG) monitoring has improved patient outcome by permitting accurate diagnoses and modified therapy.
Does Aetna require EEG?
Aetna considers attended electroencephalographic (EEG) video monitoring performed in a healthcare facility medically necessary for the following indications, where the diagnosis remains uncertain after recent (within the past 90 days) neurological examinations and standard EEG studies#N#Footnote 1#N#*, and non-neurological causes of symptoms (e.g., syncope, cardiac arrhythmias) have been ruled out:
How long does a patient have to be monitored for Medicare?
Documentation supporting medical necessity should be legible, maintained in the patient’s medical record and made available to Medicare upon request. Monitoring beyond 72 hours must be supported by written documentation for each additional 24 hours of monitoring and be made available to Medicare upon request.
How long does it take for an ambulance to monitor?
Ambulatory monitoring beyond 48 hours frequently produces poor data in the period after 48 hours as electrode contact may no longer be optimal after 48 hours. Occasionally patients may require an additional 48 hour monitoring period to establish a diagnosis which is usually performed at a later date.
How long is a daytime EEG?
Two codes for daytime monitoring (typically eight hours) with physician access to data throughout the recording period and a report written at the end of the two- to 12-hour period: 2-12 hours of EEG continuous recording; without video (95717) 2-12 hours of EEG continuous recording; with video (95718)
How long is a multi day EEG?
Six new codes for multi-day testing, typically for patients tested in their homes, physician access to data at conclusion of study when the summary report is written (formerly 95953): 36-60 hours (2-day) EEG continuous recording, without video (95721) 36-60 hours (2-day) EEG continuous recording, with video (95722)
What is TC code?
The TC codes are reported for services provided in a physician office, independent diagnostic testing facility (IDTF), or for services provided in a patient’s home if ordered by a physician’s office or an IDTF.
Why is scalp EEG monitoring important?
An American Academy of Neurology Technology Assessment (Nuwer, et al., 1990) stated that intraoperative scalp EEG monitoring has long been carried out in an effort to safeguard the brain during carotid endarterectomy.
What is scalp electroencephalography?
Standard scalp electroencephalography measures and records the electrical activity of the brain by placing electrodes on the scalp/head; most commonly used when a physician is trying to establish the presence of a seizure disorder.
Why does Aetna use grid monitoring?
Aetna considers grid monitoring to determine the location of the epileptogenic focus for possible surgical resection medically necessary for members with intractable seizures when any of the following conditions is met:
How long do subdural grid electrodes stay in place?
These electrodes remain in place for several days to up to 1 to 2 weeks, as needed to record seizures and map brain.
Does EEG localize epileptogenic area?
Surface (scalp) electro encephalogrphy (EEG) recording did not adequately localize the epileptogenic area, or. There is a discordance between electrophysiological localization and that provided by other neurodiagnostic studies suggesting an abnormality in more than one region of the brain.
Is emergence agitation a predictor of sevoflurane?
Jang and colleagues (2018) noted that emergence agitation (EA) is common after sevoflurane anesthesia, but there are no definite predictors. In a prospective, predictive study, these researchers examined if intra-operative EEG can indicate the occurrence of EA in children. EEG-derived parameters (spectral edge frequency 95, beta, alpha, theta, and delta power) were measured at 1.0 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) and 0.3 MAC of end-tidal sevoflurane (EtSEVO) in 29 patients. EA was evaluated using an EA score (EAS) in the post-anesthetic care unit on arrival (EAS 0) and at 15 and 30 minutes after arrival (EAS 15 and EAS 30). The correlation between EEG-derived parameters and EAS was analyzed using Spearman correlation, and receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis was used to measure the predictability. EA occurred in 11 patients. The alpha power at 1.0 MAC of EtSEVO was correlated with EAS 15 and EAS 30. The theta/alpha ratio at 0.3 MAC of EtSEVO was correlated with EAS 30. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve of percentage of alpha bands at 0.3 MAC of EtSEVO and the occurrence of EA was 0.672. The authors concluded that children showing high-alpha powers and low theta powers (= low theta/alpha ratio) during emergence from sevoflurane anesthesia were at high risk of EA in the post-anesthetic care unit. These preliminary findings need to be validated by well-designed studies.
Is intraoperative EEG considered experimental?
In addition, this use of intraoperative EEG is considered experimental and investigational.
How long does an ambulatory EEG monitor last?
Ambulatory or 24-hour EEG monitoring is performed by a recorder that continuously records brain wave patterns during a patient's routine daily activities and sleep up to 72 hours. An ambulatory EEG can be done with or without video recording. The monitoring equipment includes an electrode set, preamplifiers, and a recorder. The electrodes attach to the scalp, and the leads are connected to a recorder, usually worn on a belt. Ambulatory EEG allows patients to be evaluated in their natural environments, with exposure to potential stressors and other seizure triggers.
What is the NICE guideline for epilepsy?
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline on the diagnosis and management of epilepsy stated “long-term video or ambulatory EEG may be used in the assessment of children, young people and adults who present diagnostic difficulties after clinical assessment and standard EEG” (NICE, 2012; 2020).
What is the CPT 95957?
Digital EEG spike analysis (CPT 95957) performed in conjunction with an EEG is considered medically necessary for topographic voltage and dipole analysis in presurgical candidates with intractable (e.g., medically refractory, drug-resistant) epilepsy.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for pain in right lower back
- 2. icd 10 code for disorder of bone and cartilage, left
- 3. icd 10 code for bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy
- 4. icd 10 code for crush injury right hand
- 5. icd 10 code for left thumb basal arthritis
- 6. icd-10-cm code for alcohol use disorder ??
- 7. icd code for couples therapy
- 8. icd 10 code for cva with left hemiplegia
- 9. icd 10 code for left shoulder parasthemia
- 10. icd 10 code for severe persistent asthma