What is the ICD 10 code for dislocation of left elbow?
“Pathological dislocation of left elbow, NEC” for short. M24.322 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Pathological dislocation of left elbow, not elsewhere classified. It is found in the 2019 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2018 - Sep 30, 2019.
What is the ICD 10 code for dislocation and sprain?
2021 ICD-10-CM Codes S53*: Dislocation and sprain of joints and ligaments of elbow. ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. S00-T88 Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes. ›.
How do you code open dislocation in ICD 10?
In ICD-10-CM open or closed is no longer a combination code when coding for dislocations. Instead, ICD-10-CM includes an instructional note at the beginning of each category of dislocation (S03, S13. S23, S33, S43, S53, S63, S73, S83, S93) that informs the user to code separately any associated open wound. About.
What is the ICD 10 code for dislocation of ulnohumeral joint?
S53.104A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Unsp dislocation of right ulnohumeral joint, init encntr The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S53.104A became effective on October 1, 2020.
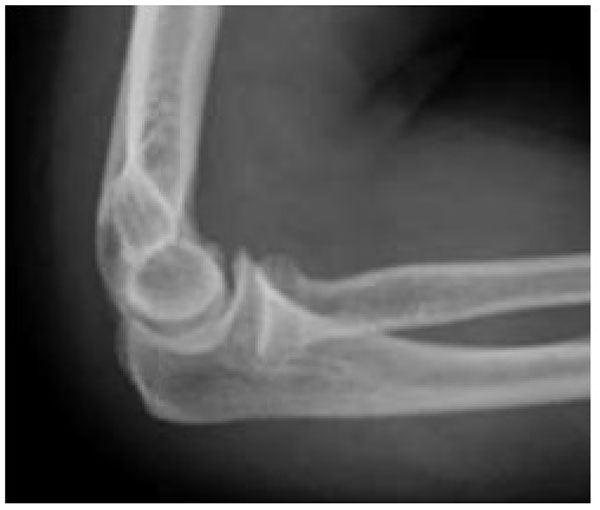
What is the ICD 9 code for elbow dislocation?
Table 1ICD-9 codeDefinition832.09Closed dislocation of elbow, other832.10Open dislocation of elbow, unspecified832.11Open anterior dislocation of elbow832.12Open posterior dislocation of elbow8 more rows•Aug 16, 2018
What is posterior dislocation of elbow?
Posterior elbow dislocation (PED) occurs when the radius and ulna are forcefully driven posteriorly to the humerus. Specifically, the olecranon process of the ulna moves into the olecranon fossa of the humerus and the trochlea of the humerus is displaced over the coronoid process of the ulna.
What is the most common elbow dislocation?
A small avulsion fracture of the olecranon is present. Posterior elbow dislocations comprise over 90% of elbow injuries. Early recognition of this injury is required due to the need for early reduction, given a higher likelihood for poor function and possible neurovascular compromise with delays in reduction.
What is an anterior elbow dislocation?
Anterior elbow dislocation is an infrequent lesion, produced by direct trauma to the proximal ulna after a fall on the elbow in flexion and injury to the neurovascular bundle is not infrequent. Authors report a case of acute anterior dislocation of the elbow joint with neurovascular injury.
How do you describe an elbow dislocation?
Elbow dislocation occurs when the humerus, ulna and radius (the elbow bones) move out of place where they meet at the elbow joint. This usually occurs when an individual breaks a fall with an outstretched hand while the arm is held straight.
What types of elbow dislocations are common?
The two general types of elbow dislocation are:Simple elbow dislocation: The radius and ulna articulate with the humerus at the elbow. ... Complex elbow dislocation: This injury is a simple dislocation combined with a fracture of the humerus, radius, ulna or a combination of all three bones.
Is a pulled elbow a dislocation?
A 'pulled elbow' is a common injury amongst young children under the age of five years. It is not a dislocation. It is the result of a ligament that has slightly slipped over the head of one of the arm bones (radius) making it difficult and painful for a child to move their arm.
What is the terrible triad of the elbow?
The terrible triad of the elbow consists of a combination of an elbow dislocation, a radial head fracture, and a coronoid process fracture. This situation almost always renders the elbow unstable, making surgical fixation necessary.
What is medial epicondylitis also known as?
Golfer's elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is caused by damage to the muscles and tendons that control your wrist and fingers. The damage is typically related to excess or repeated stress — especially forceful wrist and finger motions.
What is radial head dislocation?
Radial head dislocation occurs when the radial head is displaced from its normal articulation with the ulna and the humerus. The dislocation may be acquired or congenital (see the separate article on congenital radial head dislocation).
What type of joint is the elbow?
hinge jointNormal Anatomy of the Elbow. The arm in the human body is made up of three bones that join together to form a hinge joint called the elbow. The upper arm bone or humerus connects from the shoulder to the elbow forming the top of the hinge joint.
What is the pit of your elbow called?
antecubital fossaTechnically, you can refer to the area as the antecubital fossa. Antecubital is an adjective meaning "of or relating to the inner or front surface of the forearm" (in Latin ante means "before" and cubitum means "elbow"). Fossa is a Medieval Latin borrowing that is used for an anatomical pit, groove, or depression.
How do you fix a dislocated posterior elbow?
Prone Approach Grab the wrist of the injured arm. Apply traction and slight supination to the forearm. Attempt to distract and unlock the coronoid process from the olecranon fossa. Reduction of posterior elbow dislocation.
How is a posterior elbow dislocation treated?
Reduce the elbow—supine positionPlace the patient in the supine position and have an assistant stabilize the humerus with both hands.Grasp the patient's wrist, keep it supinated, apply steady axial traction, and slightly flex the elbow to keep the muscles of the triceps loose.More items...
What is the posterior elbow called?
olecranonStructure. The olecranon is situated at the proximal end of the ulna, one of the two bones in the forearm. When the hand faces forward (supination) the olecranon faces towards the back (posteriorly).
What is the treatment for an elbow dislocation?
Normal alignment after the elbow has been reduced. Simple elbow dislocations are treated by keeping the elbow immobile in a splint or sling for 1 to 3 weeks, followed by early motion exercises. If the elbow is kept immobile for a long time, the ability to move the elbow fully (range of motion) may be affected.
What is the ICD-10 code for dislocation?
Instead, ICD-10-CM includes an instructional note at the beginning of each category of dislocation (S03, S13. S23, S33, S43, S53, S63, S73, S83, S93) that informs the user to code separately any associated open wound.
What is a dislocated elbow in toddlers?
For example, nursemaid’s elbow is a partial dislocation common in toddlers. The main symptom is refusal to use the arm. Nursemaid’s elbow can be easily treated in a doctor’s office. A dislocated joint may be accompanied by numbness or tingling at the joint or beyond it. Additional signs and symptoms may include.
What are the complications of dislocation?
Complications of a joint dislocation may include: 1 Tearing of the muscles, ligaments and tendons that reinforce the injured joint 2 Nerve or blood vessel damage in or around your joint 3 Susceptibility to re-injury if you have a severe dislocation or repeated dislocations 4 Development of arthritis in the affected joint as you age
What is the difference between anterior and posterior dislocation?
Dislocations may further be defined by positioning: Anterior – The end of the bone is displaced to the anterior, medial, and slightly inferior to its normal anatomic position. Posterior – The end of the bone is displaced posterior to the joint and its normal anatomic position.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for persistent vomiting
- 2. icd 10 code for i95.9
- 3. icd 10 code for increased wob
- 4. icd 10 code for puncture wound left hand without foreign body
- 5. icd 10 code for tinea pedis infection
- 6. icd 10 code for well exam adult with abnormal finding
- 7. icd 10 diagnosis code for sacral decubitus ulcer
- 8. 2016 icd 10 code for vent dependent
- 9. what icd-10 code is reported for a patient that has rsv pneumonia
- 10. icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm