Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for optic papillitis?
Optic papillitis, unspecified eye. H46.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H46.00 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for diseases of tongue?
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K14 - Diseases of tongue'. The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K14. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index. Scrotal tongue. Riga (-Fede) disease.
What are the different types of lingual papillitis?
Types and Symptoms 1 Classic or Localized Type. This type of transient lingual papillitis refers to inflammation of one or several fungiform papillae within one area of the tongue, often the tip. 2 Eruptive Lingual Papillitis Type. This type usually affects children and causes a sudden whole-body illness. ... 3 Papulokeratotic Type. ...
What is the best treatment for transient lingual papillitis?
Treatment of transient lingual papillitis Usually no treatment is required for the classic form of transient lingual papillitis as the condition resolves within hours or days. Treatments reported by some patients to give relief have included: salt water mouth rinses
What is the ICD-10 code for sore tongue?
K14. 6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for tongue swelling?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R22. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R22.
What code is Z98 890?
Other specified postprocedural statesICD-10 code Z98. 890 for Other specified postprocedural states is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is it called when your tongue swells?
The medical term for a swollen tongue is glossitis. It's a condition in which the tongue becomes red and inflamed, and the surface of the tongue appears smooth.
What is angioedema of the tongue?
Angioedema is acute, self-limited localized swelling of subcutaneous or mucosal tissue. It often affects the lips, eyelids, face, tongue, larynx or bowel, and often causes large, well-demarcated lesions that typically resolve in 2–3 days but may last 5–7 days.
What does Postprocedural state mean?
Definition. the condition of a patient in the period following a surgical operation. [
What is the ICD 10 code for other specified Postprocedural States?
Z98.890Z98. 890 Other specified postprocedural states - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for post op?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems Z48. 81.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R06 2?
ICD-10 code R06. 2 for Wheezing is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is diagnosis code j06 9?
9 Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
How is transient lingual papillitis diagnosed?
Transient lingual papillitis and eruptive lingual papillitis are usually diagnosed clinically based on typical presentation.
When is lingual papillitis most common?
Eruptive (familial) lingual papillitis affects young children, and their families. It appears to be most common in Spring, although it can occur all year round. Children in contact with many other children, such as school, kindergarten or day care, appear to be most likely to develop this condition.
What is fungiform papillary glossitis?
Fungiform papillary glossitis has been described in patients with a history of eczema, asthma, or hayfever. It may be another name for transient lingual papillitis. These authors suggested the condition is due to increased environmental sensitivity of the tongue, similar to the increased sensitivity of the skin, lungs or nose resulting in eczema, asthma or hayfever respectively.
What causes transient lingual papillitis?
The most likely cause of transient lingual papillitis is local irritation or trauma to a fungiform papilla.
How long does lingual papillitis last?
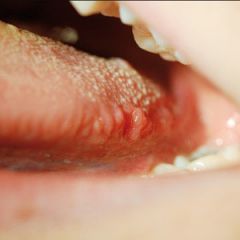
The classic form of transient lingual papillitis presents as a single painful raised red or white bump on the tongue, usually towards the tip. It lasts 1-2 days then disappears, often recurring weeks, months or years later. There is no associated illness or lymph gland enlargement. Less commonly the lesions are more numerous, may disappear within hours or last several days, or may be associated with a burning or tingling sensation. Uncommonly the lesion (s) may not cause any symptoms. Some reports suggest an association with geographic tongue or scalloped markings on the side of the tongue.
What is a transient papillitis?
Transient lingual papillitis is a common painful inflammatory condition affecting one or several fungiform papillae on the tongue. It is also known as ‘lie bumps’ and may be related to or the same as eruptive ( familial) lingual papillitis and fungiform papillary glossitis. A nonpainful papulokeratotic variant has been reported.
What are the bumps on the surface of the tongue called?
Fungiform papillae are one of the special types of bumps found on the surface of the tongue. Fungiform papillae contain taste buds (especially for bitter taste), temperature receptors and have a good blood supply.
The ICD code K14 is used to code Oral and maxillofacial pathology
Oral and maxillofacial pathology (also termed oral pathology, stomatognathic disease, dental disease, or mouth disease) refers to the diseases of the mouth ("oral cavity" or "stoma"), jaws ("maxillae" or "gnath") and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin (the skin around the mouth).
Coding Notes for K14 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Use Additional Code note means a second code must be used in conjunction with this code. Codes with this note are Etiology codes and must be followed by a Manifestation code or codes.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K14 - Diseases of tongue'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K14. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What is the infection that is commonly associated with eruptive lingual papillitis?
Underlying infection, either viral or bacterial (this is commonly associated with eruptive lingual papillitis)
How to diagnose transient lingual papillitis?
When diagnosing transient lingual papillitis, your healthcare provider will perform a medical history that explores potential triggers (e.g., trauma). Your healthcare provider will also perform a physical examination that focuses on the mouth, tongue, lips, and neck area (to look for lymph node swelling).
What is the name of the disease that causes bumps on the side of the tongue?
Eruptive Lingual Papillitis Type. This type usually affects children and causes a sudden whole-body illness. A child often has a fever and lymph node enlargement in the neck ("swollen glands"), in addition to painful bumps on the tip and sides of the tongue.
What is a transient papillitis?
This type of transient lingual papillitis refers to inflammation of one or several fungiform papillae within one area of the tongue, often the tip. It manifests as single or multiple raised red or white/yellow painful bumps.
What is the condition called when you have a lump on your tongue?
Symptoms. Causes. Diagnosis. Treatment. Transient lingual papillitis, also called "lie bumps," is a common inflammatory condition that affects the tongue, specifically the fungiform papillae. Fungiform papillae are flat, pink bumps located on the top and sides of the tongue, especially towards the tip.
What is the best treatment for lingual papillitis?
The treatment of transient lingual papillitis is supportive, meaning a healthcare provider may recommend therapies—saltwater rinses, cold foods, or topical corticosteroids— that can soothe any tongue discomfort.
How long does lingual papillitis last?
The illness lasts about one week on average but then may recur a couple of months later. Besides pain, fever, and swollen glands, a child may produce excess saliva and have difficulty eating. 2 . Household transmission may occur with eruptive type lingual papillitis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for muscle atrophy of the thumb
- 2. icd 10 code for finger amputation follow up after
- 3. icd 9 code for aftercare following surgery
- 4. what is the icd 10 code for alcoholism
- 5. icd 10 code for repaired cleft palate
- 6. icd 10 cm code for post op back
- 7. icd 10 code for enthesitis
- 8. icd 10 code for e coli septicemia
- 9. icd 10 code for clona
- 10. icd 10 cm code for pre term newborn gestational age 33 weeks