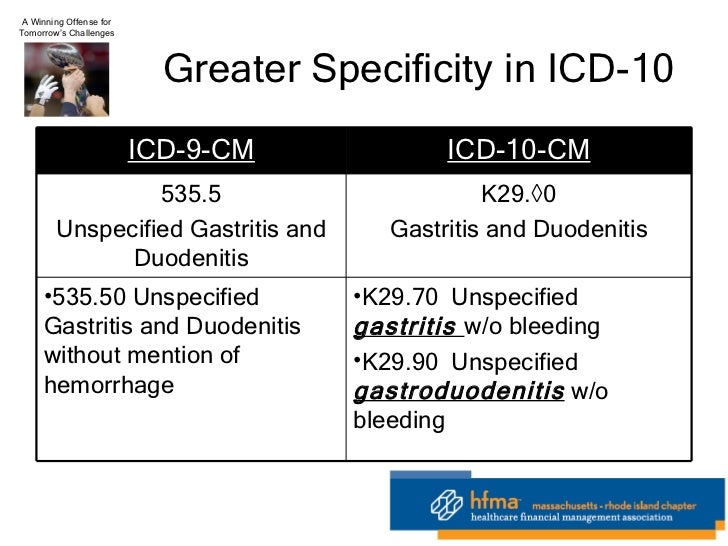
How to code diabetes correctly?
The appearance of an abnormally large amount of glucose in the urine, such as more than 500 mg/day in adults. It can be due to hyperglycemia or genetic defects in renal reabsorption (renal glycosuria). ICD-10-CM R81 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0): 637 Diabetes with mcc; 638 Diabetes with cc; 639 Diabetes without cc/mcc
What is ICD 10 code covers A1c?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O99.815 Abnormal glucose complicating the puerperium 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Maternity Dx (12-55 years)
What is diabetes insipidus ICD 10 code?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes R81*: Glycosuria ICD-10-CM Codes › R00-R99 Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified › R80-R82 Abnormal findings on examination of urine, without diagnosis › Glycosuria R81 Glycosuria R81- Type 1 Excludes renal glycosuria ( E74.818) Clinical Information
What is the diagnostic code for diabetes?
ICD-10-CM Code R81 Glycosuria BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 R81 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of glycosuria. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code R81 is used to code Glycosuria Glycosuria or glucosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine.
What is the difference between glycosuria and Glucosuria?
Glycosuria is a term that defines the presence of reducing sugars in the urine, such as glucose, galactose, lactose, fructose, etc. Glucosuria connotes the presence of glucose in the urine and is the most frequent type of glycosuria and is the focus of this review.Mar 24, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for glucose?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R73. 0: Abnormal glucose.
What is glycosuria?
Glycosuria happens when you have glucose, or other sugars like lactose, fructose, or galactose, in your urine. This is sometimes also called glucosuria. Normally, your body eliminates glucose in your urine when your blood sugar levels are too high.Jun 21, 2021
When do you use R73 09?
02 or R73. 09 would all be appropriate depending on which test is being used to justify the diagnosis of prediabetes. A diagnosis made based on abnormal A1c would fall into the R73. 09 code.Jun 16, 2015
What is the ICD 10 code for impaired fasting glucose?
R73.01R73. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is elevated glucose the same as hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia doesn't cause symptoms until glucose values are significantly elevated — usually above 180 to 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 10 to 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks.Jun 27, 2020
Why is glucose in urine?
In conditions when blood sugar is extremely high, the kidneys, in their effort to lower blood sugar levels, prevent the reabsorption of glucose back into the blood. This results in the presence of glucose in urine. Glucose in urine is not usually normal and is associated with conditions like diabetes.Apr 29, 2021
What is sugar in the urine called?
The presence of glucose in the urine is called glycosuria or glucosuria. Glucose level can also be measured using a blood test or a cerebrospinal fluid test.Jan 13, 2020
What is gestational sugar?
Overview. Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy (gestation). Like other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes affects how your cells use sugar (glucose). Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar that can affect your pregnancy and your baby's health.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.Nov 18, 2019
When do you code E11 8?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified complications 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
ICD-10 | Other fatigue (R53. 83)
The ICD code R81 is used to code Glycosuria
Glycosuria or glucosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine. Ordinarily, urine contains no glucose because the kidneys are able to reclaim all of the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. Glycosuria is nearly always caused by elevated blood glucose levels, most commonly due to untreated diabetes mellitus.
Coding Notes for R81 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Type-1 Excludes mean the conditions excluded are mutually exclusive and should never be coded together. Excludes 1 means "do not code here."
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'R81 - Glycosuria'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code R81. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 791.5 was previously used, R81 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What does it mean when you have a high blood glucose level?
This condition is seen frequently in diabetes mellitus, but also occurs with other diseases and malnutrition. Pre-diabetes means you have blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Glucose comes from the foods you eat.
What is the state of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are
State of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are not all satisfied; sometimes controllable by diet alone; called also impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. The time period before the development of symptomatic diabetes.
Can diabetes cause high blood glucose levels?
Too much glucose in your blood can damage your body over time. If you have pre-diabetes, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.most people with pre-diabetes don't have any symptoms. Your doctor can test your blood to find out if your blood glucose levels are higher than normal.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for post polio syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for inpatient consultation
- 3. 2016 icd-10-cm code for abruption placenta
- 4. what is the icd 10 code for thyroid disorder
- 5. icd-10 code for lip laceration
- 6. icd-10 code for prp injection
- 7. icd 10 code for twin delivery under 38 weeks
- 8. icd 10 code for spontaneous vaginal delivery
- 9. icd 10 cm code for pyloric stenosis
- 10. icd 10 code for abscess right proximal forearm