What is the ICD 10 code for left anterior cerebral infarction?
Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of left anterior cerebral artery. I63.322 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I63.322 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for thrombosis of the left anterior?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I63.322. Cerebral infarction due to thrombosis of left anterior cerebral artery. I63.322 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for embolism of left middle artery?
I63.412 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of cerebral infarction due to embolism of left middle cerebral artery. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. A cerebral infarction is a type of ischemic stroke resulting from a blockage in the blood vessels supplying blood to the brain.
What is the latest version of ICD 10 for transient cerebral ischemic attacks?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I67.9 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I67.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I67.9 may differ. transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes ( G45.-)
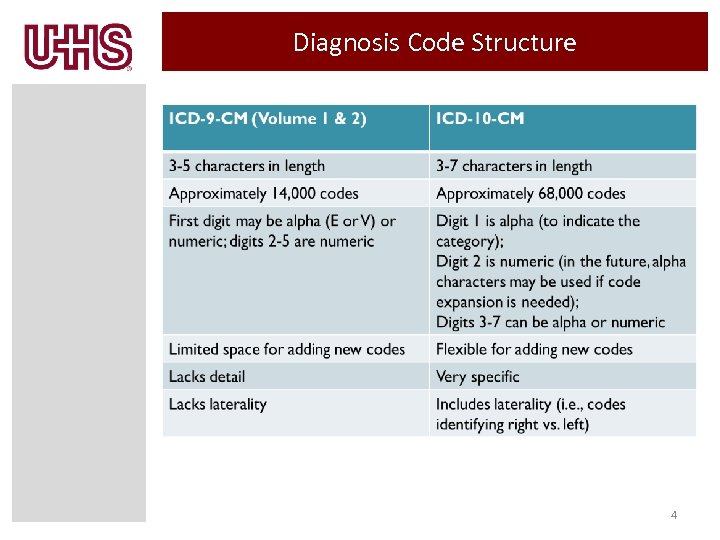
What is the ICD-10 code for ischemic stroke?
ICD-10-CM I67. 81 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 061 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with mcc.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA unspecified?
ICD-10 Code for Cerebral infarction, unspecified- I63. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What does ICD-10 code I63 9 mean?
9: Cerebral infarction, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of CVA with left sided weakness?
I69. 354 Hemiplegia and hemiparesis following cerebral infarction affecting left non-dominant side.
How do you code CVA with left sided weakness?
354 - Hemiplegia and hemiparesis following cerebral infarction affecting left non-dominant side.
How do you code a CVA?
Coding Guidelines Residual neurological effects of a stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA) should be documented using CPT category I69 codes indicating sequelae of cerebrovascular disease. Codes I60-67 specify hemiplegia, hemiparesis, and monoplegia and identify whether the dominant or nondominant side is affected.
Is CVA the same as cerebral infarction?
Obstruction in blood flow (ischemia) to the brain can lead to permanent damage. This is called a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). It is also known as cerebral infarction or stroke. Rupture of an artery with bleeding into the brain (hemorrhage) is called a CVA, too.
What is cerebrovascular accident CVA unspecified mechanism?
Listen to pronunciation. (seh-REE-broh-VAS-kyoo-ler AK-sih-dent) In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Cerebrovascular accidents are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
What is the ICD 10 code for sequelae of CVA?
ICD-10 code I69. 3 for Sequelae of cerebral infarction is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the ICD 10 code for history of CVA with right sided weakness?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hemiplegia and hemiparesis following cerebral infarction affecting right dominant side I69. 351.
What is the ICD 10 code for left sided weakness?
Hemiplegia, unspecified affecting left nondominant side The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G81. 94 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G81.
What is the difference between hemiparesis and hemiplegia?
Hemiparesis is a mild or partial weakness or loss of strength on one side of the body. Hemiplegia is a severe or complete loss of strength or paralysis on one side of the body. The difference between the two conditions primarily lies in severity.
When will ICD-10-CM I63.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I63.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does a type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I63.9) and the excluded code together.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
What is the late effect of cerebrovascular accident?
Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of left nondominant side as late effect of cerebrovascular accident
When will ICD-10-CM I69.354 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69.354 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the sequelae of traumatic intracranial injury?
sequelae of traumatic intracranial injury ( S06.-) Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of left nondominant side as late effect of cerebrovascular accident. Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of left nondominant side as late effect ...
When will ICD-10-CM I67.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I67.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is cerebral infarction?
A disorder resulting from inadequate blood flow in the vessels that supply the brain. Representative examples include cerebrovascular ischemia, cerebral embolism, and cerebral infarction. A spectrum of pathological conditions of impaired blood flow in the brain.
What is the ICD code for cerebral infarction?
The ICD code I63 is used to code Cerebral infarction. A cerebral infarction is a type of ischemic stroke resulting from a blockage in the blood vessels supplying blood to the brain. It can be atherothrombotic or embolic. Stroke caused by cerebral infarction should be distinguished from two other kinds of stroke: cerebral hemorrhage ...
What happens when a blood vessel that supplies a part of the brain becomes blocked or leakage occurs outside the vessel?
A cerebral infarction occurs when a blood vessel that supplies a part of the brain becomes blocked or leakage occurs outside the vessel walls. This loss of blood supply results in the death of tissue in that area. Cerebral infarctions vary in their severity with one third of the cases resulting in death. Specialty:
What are the synonyms for cerebral infarction?
Sequelae of cerebral infarction. Approximate Synonyms. Hemiparesis/hemiplegia (one sided weakness/paralysis) Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of right dominant side as late effect of cerebrovascular accident. Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of right dominant side as late effect of embolic cerebrovascular accident.
When will ICD-10-CM I69.351 be effective?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69.351 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the late effect of embolic cerebrovascular accident?
Hemiplegia and hemiparesis of right dominant side as late effect of embolic cerebrovascular accident
What does a type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I69.351) and the excluded code together.
What is Category I69?
Category I69 is to be used to indicate conditions in I60 - I67 as the cause of sequelae. The 'sequelae' include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition. Type 1 Excludes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of bronchiectasis
- 2. icd 10 code for neck trauma
- 3. icd-10 code for small cell lung cancer right
- 4. icd 10 cm code for cupped discs
- 5. icd 10 code for impotence of organic origin
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for cervical spondylosis
- 7. icd 10 code for hlhs
- 8. icd-10 code for diastolic heart failure
- 9. icd 9 code for liposarcoma
- 10. icd-9 code for gastrointestinal anthrax