What is ICD 10 code for severe persistent asthma?
Severe persistent asthma, uncomplicated. J45.50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J45.50 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the treatment for mild asthma?
What Are the Different Types of Delivery Devices for Asthma Medicines?
- Metered dose inhalers have medicine plus a propellant. ...
- Dry powder inhalers do not have a propellant and do not spray the medicine out of the inhaler. ...
- Breath actuated inhalers have a dry powder or aerosol medicine. ...
- Soft mist inhalers do not have propellant, but they do spray the medicine out of the inhaler. ...
What is the ICD 9 code for exercise induced asthma?
ICD-9 codes 493: Asthma; 493.0: Extrinsic asthma; 493.00: Extrinsic asthma, unspecified; 493.01: Extrinsic asthma with status asthmaticus; 493.02: Extrinsic asthma with (acute) exacerbation; 493.1: Intrinsic asthma; 493.10: Intrinsic asthma, unspecified; 493.11: Intrinsic asthma with status asthmaticus; 493.12: Intrinsic asthma with (acute) exacerbation
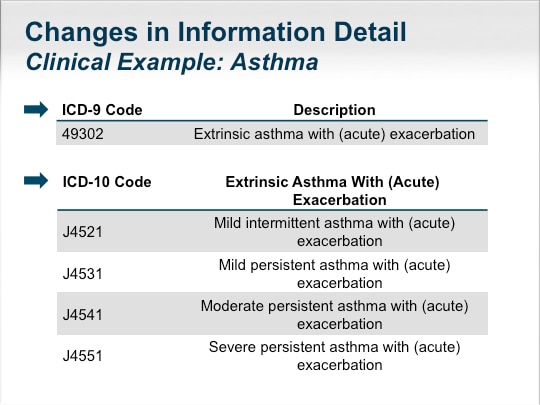
What does J45 909 mean?
Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated (J45.909)
What's considered moderate to severe asthma?
Moderate Persistent Asthma Coughing and wheezing may disrupt the child's normal activities and make it difficult to sleep. Nighttime flare-ups may occur more than once a week. In moderate persistent asthma, lung function is roughly between 60% and 80% of normal, without treatment.
What code is J45?
ICD-Code J45* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Asthma. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 493. Code J45* is the diagnosis code used for Asthma. It is a common chronic disease in which the bronchial airways in the lungs become narrowed and swollen, making it difficult to breathe.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for the bronchial asthma?
ICD-10-CM J45. 901 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 202 Bronchitis and asthma with cc/mcc.
What are the 4 categories of asthma?
Ideally, asthma severity is determined before initiating therapy. The EPR-3 guideline classification divides asthma severity into four groups: intermittent, persistent-mild, persistent-moderate, and persistent-severe.
What are the 4 levels of asthma?
Levels of AsthmaStep 1 – mild intermittent asthma. Symptoms fewer than two times a week. ... Step 2 – mild persistent asthma. Symptoms more than two times a week, but no more than once a day. ... Step 3 – moderate persistent asthma. Symptoms every day. ... Step 4 – severe persistent asthma. Constant symptoms.
What is the ICD-10 code for severe asthma?
ICD-10 code J45. 5 for Severe persistent asthma is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the ICD-10 code for J45 909?
909 Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated.
What is the ICD-9 code for unspecified asthma?
ICD-9 code 493.92 for Asthma unspecified with (acute) exacerbation is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE AND ALLIED CONDITIONS (490-496).
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for intrinsic asthma?
493.10 - Intrinsic asthma, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What qualifies as severe asthma?
Who has severe asthma and how it is diagnosed? Severe asthma is defined as someone diagnosed with asthma requiring medium or high-dose inhaled corticosteroids combined with other longer-acting medications. Asthma is also considered severe when it is uncontrolled despite proper use of these medications.
How do I know if my asthma is severe?
Seek medical attention right away if you have signs or symptoms of a serious asthma attack, which include:Severe breathlessness or wheezing, especially at night or in the early morning.The inability to speak more than short phrases due to shortness of breath.Having to strain your chest muscles to breathe.More items...•
What is the criteria for severe asthma?
Severe acute asthma Peak flow 33-50% best or predicted; Respiratory rate ≥ 25/min; Heart rate ≥ 110/min; Inability to complete sentences in one breath.
What is the most severe type of asthma?
Severe asthma is the most serious and life-threatening form of asthma. Most people with asthma can manage their symptoms well with the usual medicines like a preventer inhaler and a reliever inhaler. But someone with severe asthma struggles to manage their symptoms even with high doses of medicines.
What is asthma characterized by?
It is characterized by spasmodic contraction of airway smooth muscle, wheezing, and dyspnea (dyspnea, paroxysmal). Asthma is a chronic disease that affects your airways. Your airways are tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs. If you have asthma, the inside walls of your airways become sore and swollen.
What is bronchial disease?
A chronic respiratory disease manifested as difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of bronchial passageways. A form of bronchial disorder with three distinct components: airway hyper-responsiveness (respiratory hypersensitivity), airway inflammation, and intermittent airway obstruction.
What are the symptoms of a bronchial infection?
Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, and rapid breathing. An attack may be brought on by pet hair, dust, smoke, pollen, mold, exercise, cold air, or stress. A chronic respiratory disease manifested as difficulty breathing due to the narrowing of bronchial passageways.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What are the symptoms of asthma?
Asthma causes symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing or chest tightness. Severity differs in each person.
What is asthma exacerbation?
Asthma exacerbation: – It is nothing but an acute increase of symptoms in a person with asthma. This can be coded only with the Physician diagnosis. Status asthmatics : – Another term for this is severe asthma exacerbation. It is considered as severe as this may lead to even respiratory failure due to hypoxemia.
What happens to the lung during asthma?
What happens to our Lungs (Center of respiratory system)during asthma attack: During asthma attack, muscles around the airway gets tighten and the lining inside the airways becomes swollen and produce extra mucus. This makes airway to become narrow and partially block airflow in and out of air sacs.
How many times does asthma occur in a week?
This type of asthma occurs more than 2 times in a week with regular breathing difficulties to an extent of disturbing daily activities. Moderate persistent. These patients suffer from symptoms daily and last for several days. Severe persistent.
Why do asthmatics disappear?
Their symptoms may completely disappear after few years. Experts say this may be due to the growth of airways along with body growth. Cough variant. It is so called because of the main symptom, dry cough. Mild intermittent.
What tests are done to determine asthma?
Apart from knowing the symptoms and doing a lung physical examination the physician will also do few test measures like X-ray, spirometry, allergy testing, nitric oxide breath test or peak flow to determine the type of asthma and it’s severity. Hence a coder should definitely pay attention to these areas as well.
Can asthma be cured?
Asthma is a chronic disease, means it does not have a complete cure. Hence people with asthma should learn to live with it. Though it cannot be cured completely, symptoms can be reduced if we give proper care and treat on time.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left shoulder tendonitis and bursitis
- 2. icd 10 code for subchorionic hematoma in pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for acne adolescent
- 4. icd 10 code for genetic counseling referral
- 5. icd 10 code for hypercholesterolemia screening
- 6. icd 10 code for right upper lobe lobectomy
- 7. icd 10 code for rectal incontinence
- 8. icd 10 code for gouty arthropathy finger
- 9. icd-10 code for congenital diverticulum of bronchus
- 10. verapamil for cerebral vasospasm code icd 10