What symptom is not related to a deficiency in PTH?
Oct 01, 2021 · E21.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.3 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E21.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 E21.3 may differ.
What is the normal range for a pth blood test?
Oct 03, 2018 · It is the provider’s responsibility to select codes carried out to the highest level of specificity and selected from the ICD-10-CM code book appropriate to the year in which the service is rendered for the claim(s) submitted. The following ICD-10-CM codes support medical necessity and provide limited coverage for CPT code: 83970. Group 1 Codes
What is the diagnosis code for hypothyroidism?
Oct 01, 2021 · E21.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.5 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E21.5 - other international versions of ICD-10 E21.5 may differ.
What is intact PTH blood test?
Apr 12, 2022 · parathyroid hormone (pth), intact a.k.a. Intact, Parathormone, PTH intact, PTH (Parathyroid Hormone), PTH Whole Molecule, Intact PTH, PTH, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Intact PTH (Parathyroid Hormone), Parathormone (parathyroid hormone), PTH Intact Molecule Test information includes: LOINC codes diseases the test is often used to detect or monitor
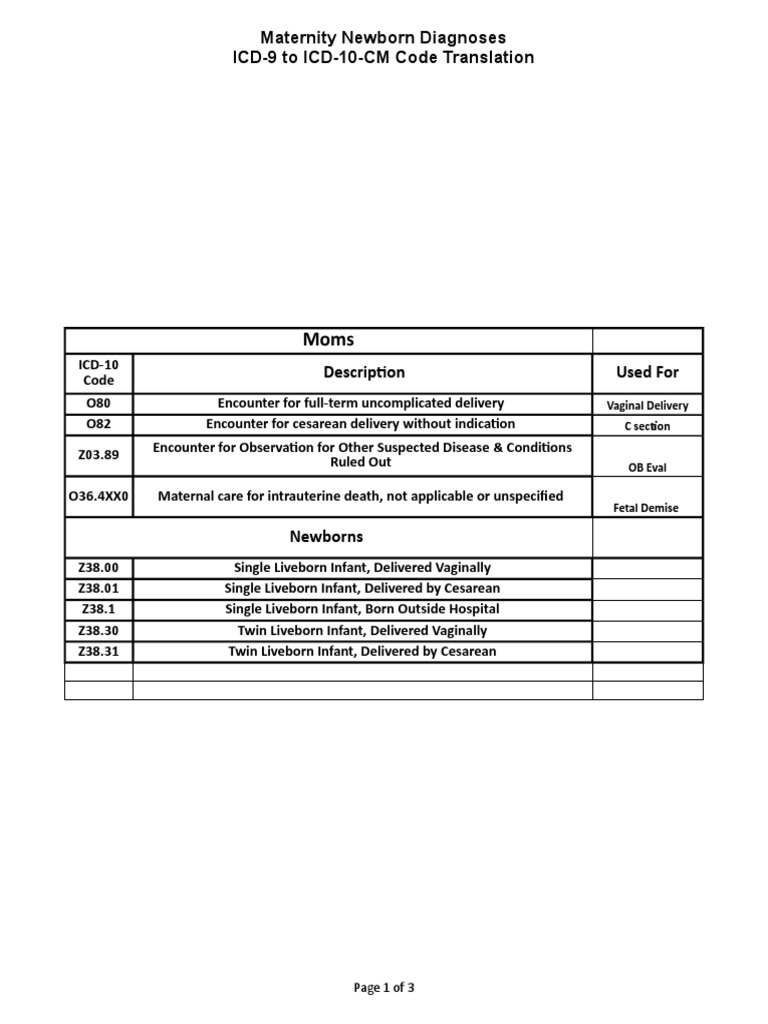
What diagnosis covers PTH?
PTH measurements are used in the differential diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, or hypercalcemia of malignancy.
What is PTH intact?
The PTH Intact test measures the amount of intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) in the body. A parathyroid test is used to diagnose certain parathyroid conditions, including hypoparathyroidism (underactive parathyroid) and hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid).
What is high intact PTH?
If your test shows you have a higher than normal level of PTH, it may mean you have: Hyperparathyroidism. A benign (noncancerous) tumor of the parathyroid gland. Kidney disease. A vitamin D deficiency.Dec 17, 2020
What is PTH disease?
What is parathyroid disease? Parathyroid disease affects the parathyroids, four pea-sized glands located in the neck near the thyroid. The glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH helps maintain the correct balance of calcium in the body. Normally, the glands release just enough PTH to keep calcium levels normal.Aug 23, 2019
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperparathyroidism?
E21.3E21. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are the 3 types of hyperparathyroidism?
There are three types of hyperparathyroidism: primary, secondary, and tertiary.Primary Hyperparathyroidism. This type occurs when you have a problem with at least one of your parathyroid glands. ... Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. ... Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism.
What causes high parathyroid hormone?
If your kidneys work poorly, usable vitamin D may decline and calcium levels drop, causing parathyroid hormone levels to go up. Chronic kidney failure is the most common cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Some medical treatments, such as vitamin D, bisphosphonates and cinacalcet, will lower PTH levels.Jun 18, 2020
What is the difference between calcitonin and parathyroid hormone?
Parathyroid hormone acts to increase blood calcium levels, while calcitonin acts to decrease blood calcium levels. When blood calcium levels drop below a certain point, calcium-sensing receptors in the parathyroid gland are activated, and the parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone into the blood.
Is parathyroid the same as thyroid?
Although the parathyroids are very close to the thyroid gland anatomically, they have no related function. The thyroid gland regulates the body's metabolism, while parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels and have no effect on metabolism.Jan 29, 2015
What is a blood typing test?
Blood typing is a screening test to determine blood groups and Rh antigen for blood transfusion and pregnancy. The four blood groups A, B, O, and AB are determined by the presence of antigens A and B or their absence (O) on a patient's red blood cells. In addition to ABO grouping, most immunohematology testing includes evaluation of Rh typing tests for Rh (D) antigen. Blood cells that express Rh (D) antigen are Rh positive. Red blood cells found lacking Rh (D) are considered Rh negative. Rh typing is also important during pregnancy because of the potential for mother and fetus Rh incompatiblity. If the mother is Rh negative but the father is Rh positive, the fetus may be positive for the Rh antigen. As a result, the mother’s body could develop antibodies against the Rh antigen. These antibodies may cross the placenta and cause destruction of the baby’s red blood cells, resulting in a condition known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
Why is it important to have blood transfusions?
Transfusion of blood components of the correct blood type is necessary in order to prevent an adverse immunologic reaction. These reactions can range from very mild and sub-clinical to very severe or fatal, depending upon the components involved and condition of the recipient.
Special Instructions
This test may exhibit interference when sample is collected from a person who is consuming a supplement with a high dose of biotin (also termed as vitamin B7 or B8, vitamin H, or coenzyme R). It is recommended to ask all patients who may be indicated for this test about biotin supplementation.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Collection
Transfer separated plasma into a plastic transport tube clearly labeled as "EDTA Plasma" and maintain at refrigerated temperature.
Causes for Rejection
Whole blood; plasma other than EDTA; hemolysis; room temperature or refrigerated serum
Use
Diagnosis of parathyroid disease and other diseases of calcium homeostasis; monitoring patients undergoing renal dialysis
Additional Information
PTH is an 84-amino-acid peptide hormone which is responsible for the regulation of serum calcium levels within a narrow range. PTH is secreted in response to decrease in serum calcium levels by increasing the renal reabsorption of calcium and lowering reabsorption of phosphorus.
Footnotes
1. Soldin SJ, Brugnara C, Gunter KC, et al. Pediatric Reference Ranges. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: AACC Press;1997:119.
Test Resources
Please visit our Clinical Education Center to stay informed on any future publications, webinars, or other education opportunities.
Reject Criteria
Gross hemolysis • Plasma in sodium heparin (green-top) tube • Plasma in lithium heparin (green-top) tube

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bleeding colon
- 2. icd 10 code for lululemon
- 3. icd 10 code for shoulder surgery
- 4. icd 10 code for post thrombotic syndrome
- 5. icd 10 code for malodorous urine
- 6. icd 10 code for alternating constipation and diarrhea
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for repair of femoral av fistula
- 8. does icd-10 code r63.8 requires the assignment of an additional code for bmi
- 9. icd 10 code for rhytides
- 10. icd 10 code for abdominal distention epigastric