What is the ICD 10 code for primary thrombophilia?
Other primary thrombophilia. D68.59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.59 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D68.59 - other international versions of ICD-10 D68.59 may differ.
What is the new ICD 10 for thrombosis?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.59 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D68.59 - other international versions of ICD-10 D68.59 may differ. A disorder of hemostasis in which there is a tendency for the occurrence of thrombosis.
What is the ICD 10 code for thromboembolism in pregnancy?
Thromboembolism in pregnancy, third trimester. O88.213 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM O88.213 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for reticuloendothelial disease?
816 Reticuloendothelial and immunity disorders without cc/mcc. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68.5 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68.5 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68.5 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68.5 Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to D68.69: Hypercoagulable (state) D68.59 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68.59 Thrombophilia...
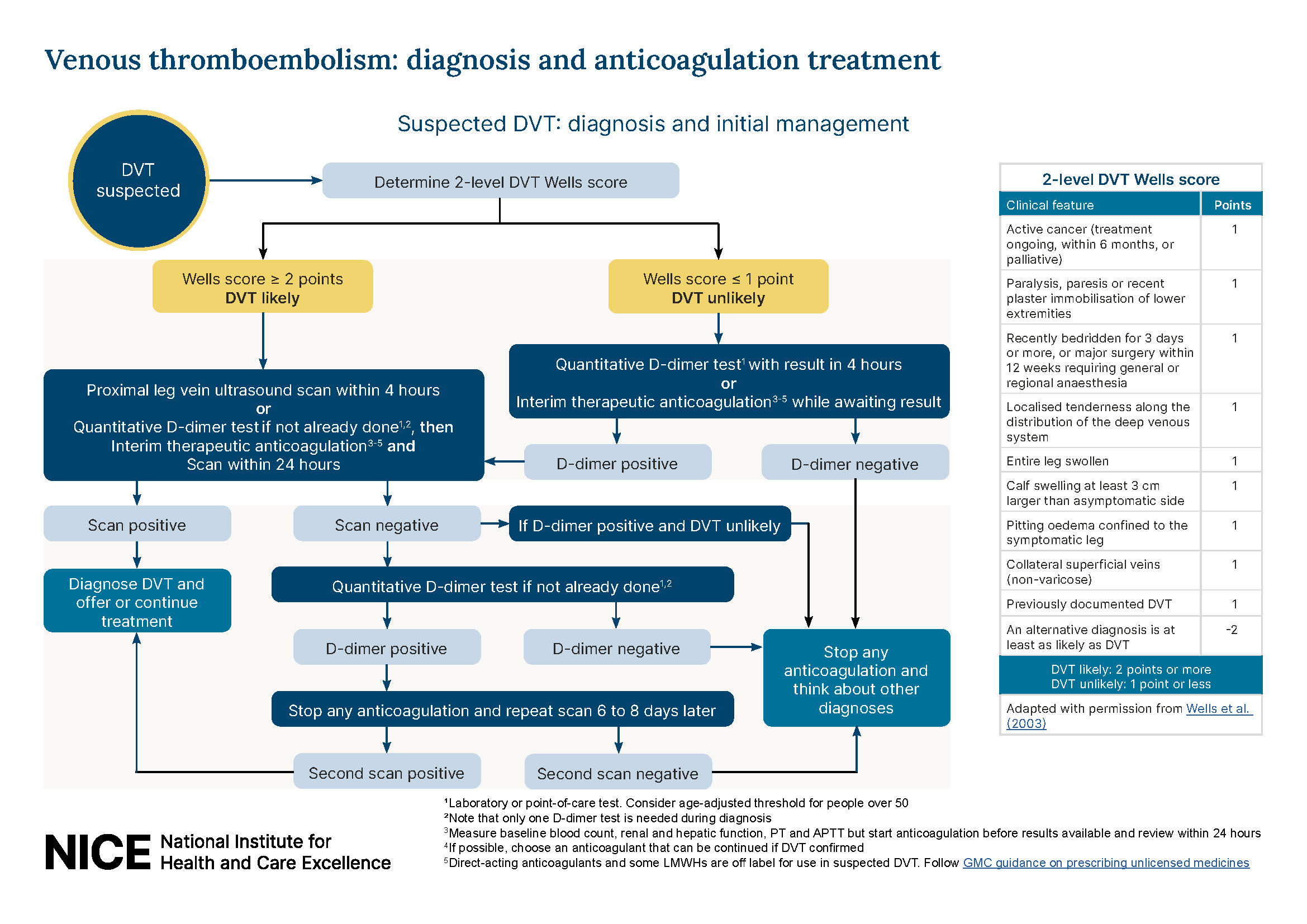
What is the ICD-10 code for thrombophilia?
ICD-10 code D68. 59 for Other primary thrombophilia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
When do you code other thrombophilia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Other thrombophilia D68. 69.
What ICD-10 code will cover factor V Leiden mutation?
Factor v leiden mutation (r506q) is the most common cause of apc resistance. An abnormality that refers to mutation of factor v leiden, which is a variant of human factor v. It results in thrombophilia, deep vein thrombosis, and a slightly increased risk of miscarriage.
What is the ICD-10 code for Factor 5?
Hereditary deficiency of other clotting factors The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D68. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D68.
What is a thrombophilia?
If you have thrombophilia, it means your blood can form clots too easily. Blood clots can be very serious and need to be treated quickly. Thrombophilia increases your risk of: deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a blood clot in a vein, usually the leg.
Is atrial fibrillation a thrombophilia?
Abstract. It is well known that atrial fibrillation is associated with high incidence of thromboembolic events, propably due to a prothrombotic or hypercoagulable state.
What is factor V Leiden heterozygous?
Heterozygous means that the 2 copies of a gene are different. In your case, one of your Factor V gene codes is for normal clotting Factor V and the other Factor V gene code is for Factor V Leiden. There is more risk of a blood clot if both gene codes are for Factor V Leiden (ie in the homozygous state).
What is Leiden?
Overview. Factor V Leiden (FAK-tur five LIDE-n) is a mutation of one of the clotting factors in the blood. This mutation can increase your chance of developing abnormal blood clots, most commonly in your legs or lungs. Most people with factor V Leiden never develop abnormal clots.
Is Factor V Leiden covered by Medicare?
This testing is considered investigational and is NOT a Medicare benefit.
What is ICD-10 code for factor VII deficiency?
D68. 2 - Hereditary deficiency of other clotting factors. ICD-10-CM.
What ICD-10 covers PT PTT?
NCD - Partial ThromboplastinTime (PTT) (190.16)
What is Factor VII deficiency?
Factor VII (seven) deficiency is a disorder caused by a lack of a protein called factor VII in the blood. It leads to problems with blood clotting (coagulation). Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for trimalleolar fracture right ankle
- 2. icd 10 code for benignrectal mass
- 3. icd 10 code for intraepithelial lymphocytes
- 4. icd 10 code for r/o pe
- 5. icd 10 code for myeloid neoplasm with eosinophilia
- 6. icd-10 code for odontogenic keratocyst
- 7. icd 9 code for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- 8. icd 10 code for left lower lobe adenocarcinoma
- 9. icd 10 code for acute urticaria
- 10. icd 10 code for mycoplasma hominis