Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene
- I00-I99 2022 ICD-10-CM Range I00-I99 Diseases of the circulatory system Type 2 Excludes certain conditions originating...
- I73 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I73 Other peripheral vascular diseases 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022...
- I73.0 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I73.0 Raynaud's syndrome 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022...
How do I code a diagnosis of Raynaud's syndrome?
Oct 01, 2021 · Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene I00-I99 2022 ICD-10-CM Range I00-I99 Diseases of the circulatory system Type 2 Excludes certain conditions originating... I73 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I73 Other peripheral vascular diseases 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022... I73.0 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code ...
What does Raynaud's disease stand for?
Raynaud's syndrome (I73.0) I73 I73.0 I73.00 ICD-10-CM Code for Raynaud's syndrome I73.0 ICD-10 code I73.0 for Raynaud's syndrome is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now
What is the ICD 10 code for Neurologic diagnosis?
ICD-10-CM Code I73.0 Raynaud's syndrome NON-BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 ICD Code I73.0 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the two child codes of I73.0 that describes the diagnosis 'raynaud's syndrome' in more detail. I73.0 Raynaud's syndrome I73.00 Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene
What is the ICD 10 code for lumbar radiculopathy?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code I73.01 Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene Billable Code I73.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
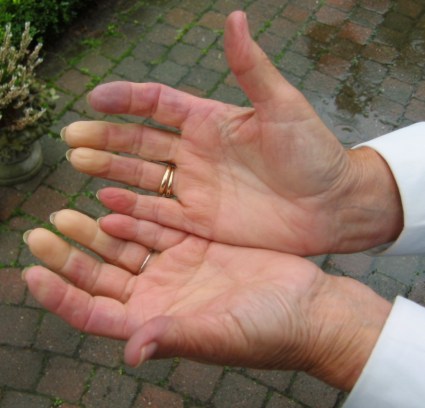
What is the meaning of Raynaud disease?
Overview. Raynaud's (ray-NOSE) disease causes some areas of your body — such as your fingers and toes — to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In Raynaud's disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin become narrow, limiting blood flow to affected areas (vasospasm).Nov 6, 2020
What is another name for Raynaud's disease?
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, eponymously named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles.
What is done for Raynaud's syndrome?
To widen blood vessels and increase blood flow, your doctor might prescribe: Calcium channel blockers. These drugs relax and open small blood vessels in your hands and feet, reducing the severity and number of attacks in most people with Raynaud's. These drugs can also help heal skin ulcers on your fingers or toes.Nov 6, 2020
What is the main cause of Raynaud?
Why does it happen? Raynaud's is usually triggered by cold temperatures, anxiety or stress. The condition occurs because your blood vessels go into a temporary spasm, which blocks the flow of blood. This causes the affected area to change colour to white, then blue and then red, as the bloodflow returns.Nov 23, 2021
Is Raynaud's a disease or a syndrome?
Raynaud's disease is a rare disorder of the blood vessels, usually in the fingers and toes. It causes the blood vessels to narrow when you are cold or feeling stressed. When this happens, blood can't get to the surface of the skin and the affected areas turn white and blue.Aug 24, 2021
Is Raynaud's an autoimmune disease or disorder?
Summary. Raynaud's phenomenon is the short-term interruption of blood flow to the extremities, such as the fingers and toes. Raynaud's phenomenon may be a sign of an underlying autoimmune disorder such as scleroderma or lupus, so it's important to see your doctor for diagnosis.
What is the difference between Raynaud's disease and Raynaud's syndrome?
Primary Raynaud's(or Raynaud's disease) happens without any other illness behind it. The symptoms are often mild. Secondary Raynaud's (Raynaud's syndrome, Raynaud's phenomenon) results from another illness. It's often a condition that attacks your body's connective tissues, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.Aug 23, 2021
What autoimmune diseases are associated with Raynaud's?
The diseases most often linked with Raynaud's are autoimmune or connective tissue diseases such as:Lupus (systemic lupus erythematous)Scleroderma.CREST syndrome (a form of scleroderma)Buerger disease.Sjögren syndrome.Rheumatoid arthritis.Occlusive vascular disease, such as atherosclerosis.Polymyositis.More items...
What is the best medication for Raynaud's?
Calcium channel blockers are the class of drugs most widely used for treatment of Raynaud syndrome—especially the dihydropyridines (eg, nifedipine, nicardipine), which are the most potent vasodilators. Nifedipine is the customary first choice.Nov 23, 2020
Why are women's hands and feet always cold?
Women's circulation is centred around the female reproductive organs, thereby leaving the extremities, such as the hands and feet, feeling colder as the blood supply in these areas is reduced. This is also the reason that women complain that their partners feet are perfect whilst theirs are not.
Is Raynaud's a neurological disorder?
(People exposed to cold weather are well aware of these mechanisms.) Cold, of course, is the main trigger in Raynaud's phenomenon, although roughly one-third of patients experience it in response to stress and anxiety -- another indication that the condition is neurological and even psychological in origin.Apr 11, 2019
What is the difference between primary and secondary Raynaud's?
A major clinical distinction between primary and secondary Raynaud's is that patients with primary Raynaud's phenomenon do not get digital ulcers, gangrene, or signs of tissue injury. Only about one-third of scleroderma patients with severe secondary Raynaud's develop ischemic digital ulcers.Feb 19, 2015
What is Raynaud's disease?
In medicine, Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's phenomenon (pronunciation: /reɪˈnoʊz/ ray-NOHZ) is excessively reduced blood flow in response to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas. This condition may also cause nails to become brittle with longitudinal ridges. Named after French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the respective regions.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
The ICD code I730 is used to code Raynaud's phenomenon
In medicine, Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's phenomenon (pronunciation: /reɪˈnoʊz/ ray-NOHZ) is excessively reduced blood flow in response to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas. This condition may also cause nails to become brittle with longitudinal ridges.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I73.00 - Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I73.00. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code I73.00 and a single ICD9 code, 443.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for family history of rheumatoid arthritis
- 2. icd 10 code for facial numbness and tingling
- 3. icd 10 code for mucocele of lip
- 4. what is the icd 10 code for cancer
- 5. icd 9 code for elbow rcl tear
- 6. icd 10 code for lac face
- 7. icd 10 code for left posterior neck skin lesion suspicious for sarcoma.
- 8. icd code for puncture wound
- 9. icd 10 code for gardnerella vaginitis
- 10. icd-10 pcs code for repeat low-cervical cesarean section and a modified pomeroy tubal ligation