How do you describe the ruptured tympanic membrane?
A ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole or tear in the thin tissue that separates the ear canal from the middle ear (eardrum). A ruptured eardrum can result in hearing loss. It can also make the middle ear vulnerable to infections.Jan 18, 2022
What is tympanic membrane perforation called?
Tympanic membrane perforation, also known as a perforated eardrum, is a hole in the thin membrane that separates the ear canal from the middle ear.
What is left tympanic membrane?
What is the Left Tympanic Membrane? The left tympanic membrane or left eardrum is present in the left ear. It consists of the lateral process of malleus, cone of light and pars tensa, and pars flaccid similar to the right tympanic membrane.Mar 21, 2021
What causes tympanic membrane rupture?
A ruptured eardrum is often caused by a middle ear infection. With an infection fluid develops behind the drum creating pain and discomfort. This fluid buildup can create a small rupture of the drum allowing fluid to drain from the ear, appearing as pus. Bleeding may also occur.Apr 18, 2019
What is total perforation of tympanic membrane?
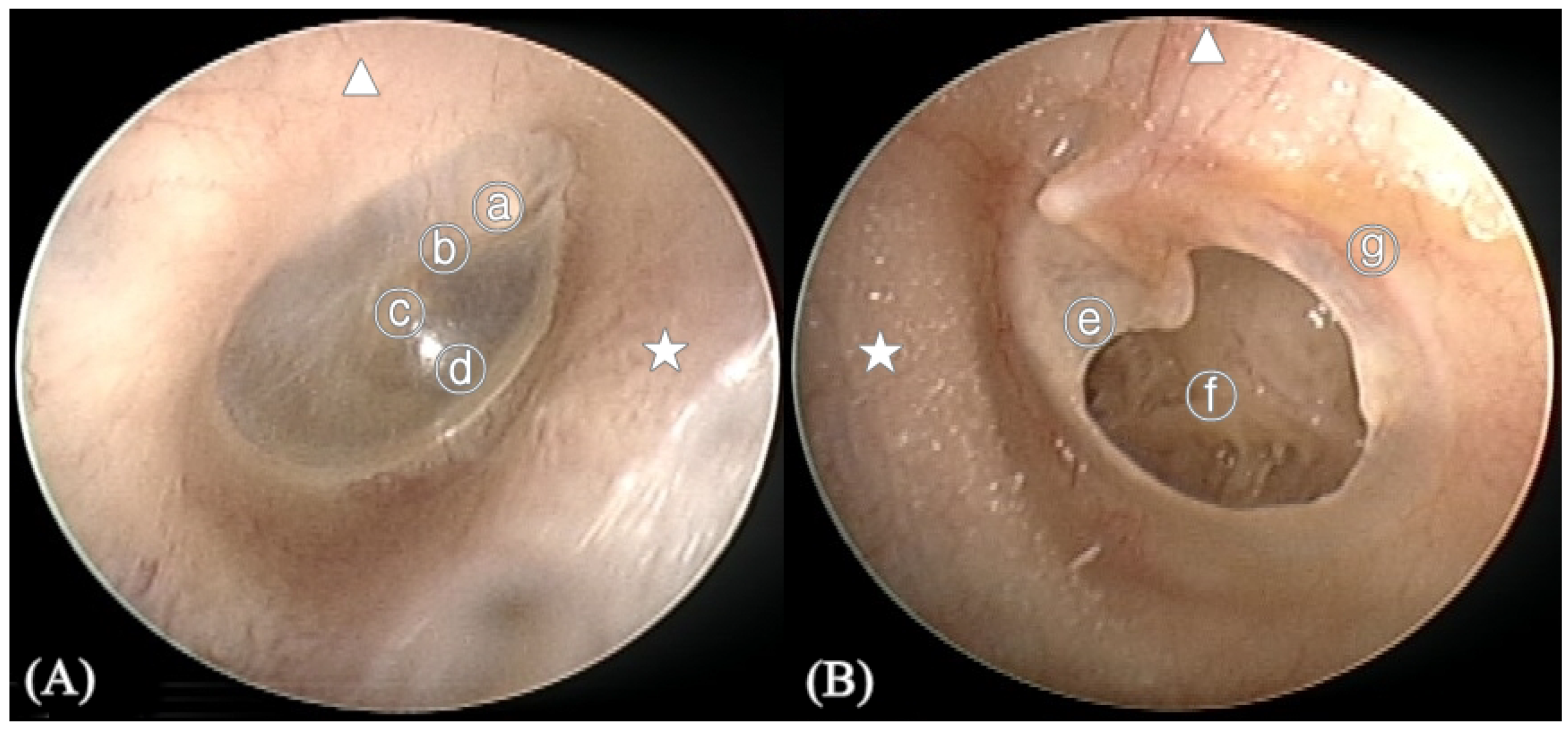
COMPLETE or "pantympanic" perforations denote total loss of the tympanic membrane with the exception of a rim of pars tensa left as a remnant which is actually the annulus of the pars tensa. This perforation usually excludes the pars flaccida of the drum.
What is meatus of ear?
external auditory canal, also called external auditory meatus, or external acoustic meatus, passageway that leads from the outside of the head to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum membrane, of each ear. The structure of the external auditory canal is the same in all mammals.
What are the three layers of the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane is thin and semi-transparent with a pearly, gray appearance. It is composed of three layers: An outer, epithelial (ectodermal)layer; a middle, fibrous layer; and an inner, mucosal(endodermal) layer that is continuous with the squamous lining of the middle ear cavity.
What is the tympanic membrane made of?
The tympanic membrane is composed of the pars flaccida and pars tensa with considerable variations in their size and thickness. Both pars flaccida and pars tensa consist of an epidermal layer, a lamina propria, and a mucosal epithelial layer.
What does tympanic mean?
the eardrumTympanic: 1. Pertaining to the tympanum (the eardrum). 2. Pertaining to the tympanic cavity. 3.
Can an ear infection cause a ruptured eardrum?
Ear infections may cause a ruptured eardrum. This occurs more often in children. The infection causes pus or fluid to build up behind the eardrum. As the pressure increases, the eardrum may break open (rupture).
What is barotrauma ear?
Ear barotrauma is a type of ear damage. It is caused by pressure differences between the inside of the ear and the outside of the ear. It can cause pain and sometimes lifelong (permanent) hearing loss. The middle ear is an air-filled space between the inner and outer parts of the ear.
Why does my ear get perforated?
by trying to clean the ear with sharp instruments), explosion, loud noise or surgery (accidental creation of a rupture). Flying with a severe cold can also cause perforation due to changes in air pressure and blocked eustachian tubes resulting from the cold. This is especially true on landing.
What is the ICd 9 code for perforation?
This is especially true on landing. ICD 9 Code: 384.2. Source: Wikipedia.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for acute bronchospasm
- 2. icd 10 code for multiple sclerosis exacerbation
- 3. icd 10 code for pneumonia due to adenovirus
- 4. icd 10 code for diarrhea second to medication induced
- 5. icd 10 code for blindness to trauma
- 6. icd 10 code for removal of nephrostomy tube
- 7. icd 10 code for periostomy ulcer
- 8. icd-9 code for diabetes with microalbuminuria
- 9. icd 10 code for bit by eel
- 10. what is icd-9cm code for raective airway