What is the ICD-10 code for anorexia?
0 Anorexia nervosa. A disorder characterized by deliberate weight loss, induced and sustained by the patient.
What is diagnosis code F50 2?
2 Bulimia nervosa. A syndrome characterized by repeated bouts of overeating and an excessive preoccupation with the control of body weight, leading to a pattern of overeating followed by vomiting or use of purgatives.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of anorexia?
F50. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F50.
What is the ICD-10 code for loss of appetite?
R63. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R63. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the two types of Anorexia nervosa?
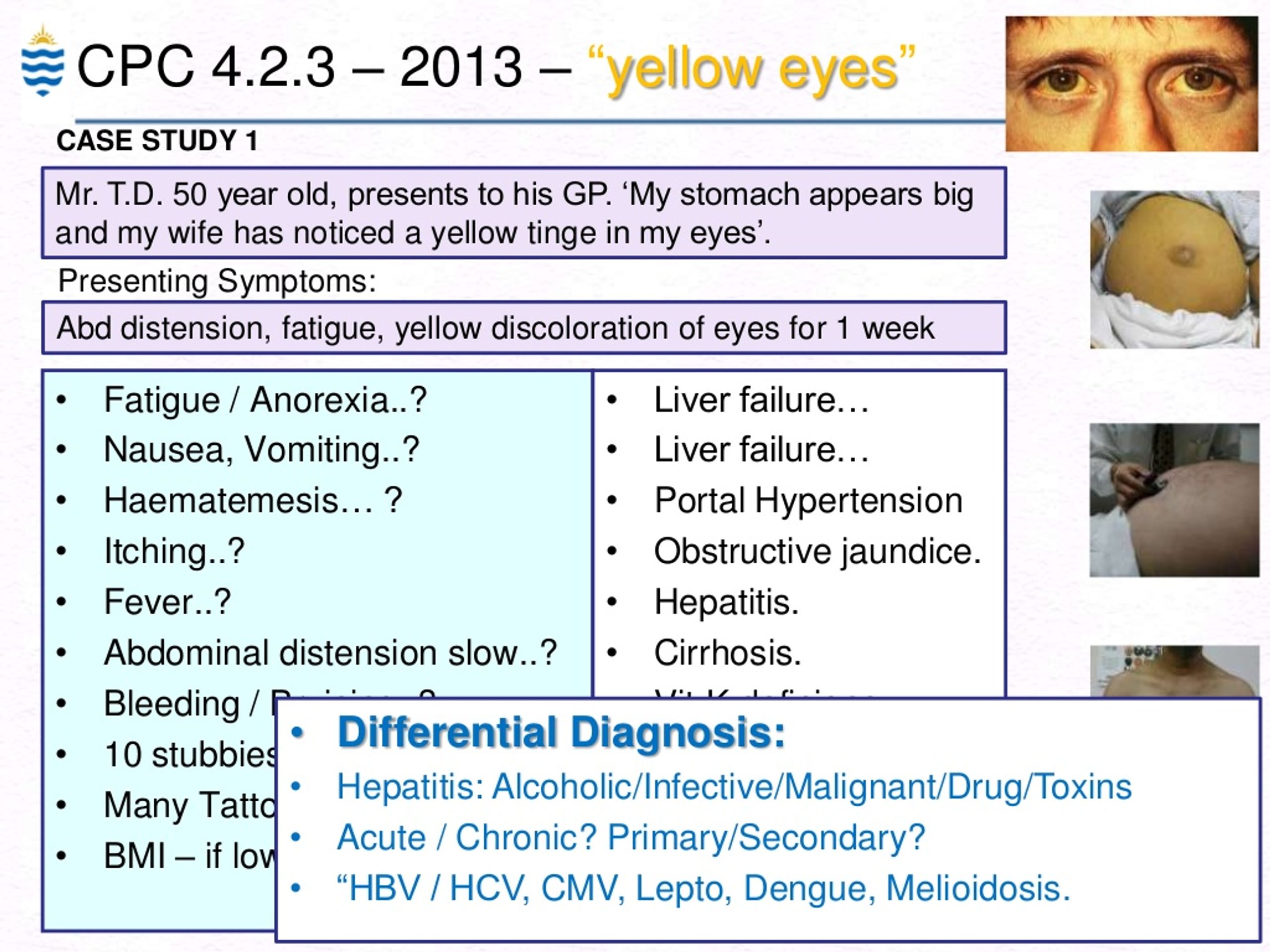
Anorexia is officially categorized into two subtypes — the restricting type and the binge eating and purging type (1).
What is the ICD-10 code for severe malnutrition?
E43Coding professionals would use ICD-10-CM code E43 to report severe malnutrition, also known as starvation edema. They would use ICD-10-CM code E42 to report severe protein-calorie malnutrition with signs of both kwashiorkor and marasmus.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is the correct code assigned for a patient with anorexia nervosa restricting type?
ICD-10-CM Code for Anorexia nervosa, restricting type F50. 01.
What is ICD-10 code for weight loss?
ICD-10 code R63. 4 for Abnormal weight loss is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
How do you code loss of appetite?
R63. 0 - Anorexia | ICD-10-CM.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
When do you use U07 1?
The following questions and answers were jointly developed and approved by the American Hospital Association's Central Office on ICD-10-CM/PCS and the American Health Information Management Association. ICD-10-CM code U07. 1, COVID-19, may be used for discharges/date of service on or after April 1, 2020.
What does unspecified PTSD mean?
Code F43. 10 is the diagnosis code used for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Unspecified. It is an anxiety disorder that develops in reaction to physical injury or severe mental or emotional distress, such as military combat, violent assault, natural disaster, or other life-threatening events.
What is Anorexia purging type?
The binge eating/purging type of anorexia is characterized by episodes of excessive eating followed by self-induced vomiting. Using large amounts of laxatives is another form of purging. These medications are taken in an attempt to decrease food absorption and speed up the emptying of the stomach and intestines.
What is the F code for generalized anxiety disorder?
ICD-Code F41. 1 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
Which code is used for the diagnosis of infantile autism?
In the case of code F84. 0, the inclusion terms are autism spectrum disorder, infantile autism, infantile psychosis, and Kanner's syndrome. The ICD also has Type 1 Excludes Notes, which indicate when two codes should never be diagnosed alongside each other.
What is the name of the eating disorder that is characterized by the lack or loss of appetite?
An eating disorder that is characterized by the lack or loss of appetite, known as anorexia. Other features include excess fear of becoming overweight; body image disturbance; significant weight loss; refusal to maintain minimal normal weight; and amenorrhea.
What is it called when you lose your appetite?
An eating disorder that is characterized by the lack or loss of appetite, known as anorexia.
When will the ICD-10-CM F50.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F50.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is F50.0 a reimbursement code?
Anorexia nervosa. F50.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM F50.0 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICd 10 code for insomnia?
F51 Sleep disorders not due to a substance or known physiological condition. F51.0 Insomnia not due to a substance or known physiological condition. F51.01 Primary insomnia. Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
When will the ICD-10-CM F50.01 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F50.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for eating disorders?
Below is a summary of ICD-10-CM coding for common eating disorders.#N#Anorexia Nervosa#N#Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in which the patient refuses to maintain a healthy body weight, intensely fears weight gain, and has a distorted body image. It involves self-starvation and excessive weight loss.#N#When the body is denied the essential nutrients it needs to function, it slows down all of its processes to conserve energy, which can have serious medical consequences. These include: 1 Heart failure due to an abnormally slow heart rate and hypotension 2 Bone density reduction resulting in dry, brittle bones 3 Loss of muscle and muscle weakness 4 Severe dehydration, which can cause kidney failure 5 Dry hair and skin, including hair loss 6 Development of lanugo: Lanugo is a downy layer of hair that may be present on newborns. When weight decreases drastically, the body may produce lanugo to keep warm.
What is the ICd 10 code for bulimia nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa is described by ICD-10 code F50.2 Bulimia nervosa. Pica is a compulsion to eat non-food items, such as clay, dirt, hairballs, ice, etc. According to the National Institutes of Health, as many as 32 percent of children ages one to six have this behavior.
What is the name of the eating disorder in which the patient refuses to maintain a healthy body weight?
Anorexia Nervosa. Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in which the patient refuses to maintain a healthy body weight, intensely fears weight gain, and has a distorted body image. It involves self-starvation and excessive weight loss.
What percentage of people with anorexia nervosa are female?
According to the National Eating Disorders Association fact sheet, and the National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders, approximately 90-95 percent of individuals suffering from anorexia nervosa are female, with the condition typically appearing in early to mid-adolescence.
Can laxatives cause constipation?
Chronic irregular bowel movements and constipation from regular laxative abuse. Gastric rupture is a less common but a possible side effect. Signs and symptoms include: Regular intake of large amounts of food with a sense of loss of control over eating behavior. Regular use of inappropriate compensatory behavior.
Is bulimia nervosa a female disorder?
According to the National Eating Disorders Association fact sheet, and the National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders, approximately 80 percent of people suffering from bulimia nervosa are female. Most people who are bulimic appear to be of average weight and recognize that their behaviors are unusual. The age of onset bulimia nervosa is slightly later than anorexia nervosa.
What is the code for anorexia nervosa?
Assign code 307.1, Anorexia nervosa, as the principal diagnosis. Code 261, Nutritional marasmus, should be assigned as an additional diagnosis for the severe malnutrition. For some anorexic patients, the weight loss is so severe that it leads to malnutrition. Code 261 further describes the severity of the patient's condition. However, it is appropriate to sequence the underlying condition (anorexia nervosa) as the principal diagnosis. This advice applies for both medical/surgical and psychiatric facilities and supersedes advice previously published in Coding Clinic Fourth Quarter 1989, page 11, where only code 307.1 was assigned.
What is code 307.1?
Coding Clinic Fourth Quarter 1989 advised the sequencing of code 307.1, Anorexia nervosa, as principal diagnosis for anorexia with severe malnutrition since anorexia implies malnutrition. However, at my facility, we see patients with malnutrition so severe they require medical intervention for stabilization of body function. The monitoring and treatment for these patients may extend for months. We do not have a psychiatric ward and we aren't associated with a psychiatric facility so no formalized psychiatric care is rendered beyond a psychiatric consultation. Since the primary reason for the admission is malnutrition, is it appropriate to sequence code 263.9, Unspecified protein-calorie malnutrition, as principal diagnosis? ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for medication follow up
- 2. icd 10 code for genetic susceptibility
- 3. icd 10 code for delayed laparotomy closure
- 4. icd 9 code for oral aversion
- 5. billable icd 10 code for shoulder
- 6. icd 10 code for glomus tumor of finger
- 7. icd 10 code for accident while playing drum
- 8. icd-10 code for mucinous cyst left finger
- 9. 2018 icd 10 code for dog bite left hand
- 10. icd 10 code for compression of common peroneal nerve