Amyloidosis, unspecified. E85.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E85.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for amyloidosis?
E85- Amyloidosis › 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E85 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E85 Amyloidosis 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code E85 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the pathophysiology of TTR amyloidosis?
· E85- Amyloidosis › 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E85.82 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E85.82 Wild-type transthyretin-related (ATTR) amyloidosis 2018 - New Code 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E85.82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is there any cardiac involvement in transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR)?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E85.4 Organ-limited amyloidosis 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E85.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E85.4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is amyloidosis in microbiology?
· Amyloidosis, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E85.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What is wild-type TTR cardiac amyloidosis?
Wild-type ATTR Amyloidosis (ATTRwt) is age related and mainly affects the heart. TTR is a natural protein made mostly in the liver. Its role is to transport the hormone thyroxine and retinol (Vitamin A) around the body, hence its name transthyretin.
What is TTR cardiomyopathy?
Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR‐CA) demonstrates infiltrative cardiomyopathy caused by extracellular deposition of insoluble transthyretin (TTR) amyloid fibrils in the myocardium. 1. TTR is a plasma protein mainly synthesized in the liver, recognized as a transporter of thyroxine and retinol‐binding protein.
What is familial ATTR amyloidosis?
Familial ATTR amyloidosis is an inherited disease, where the body makes a mutant form of a protein called "transthyretin." Transthyretin is abbreviated "TTR" and is the reason this disease is called familial ATTR amyloidosis.
What is ATTR cardiac amyloidosis?
ATTR amyloidosis is a rare, progressive disease characterized by the abnormal buildup of amyloid deposits composed of misfolded transthyretin protein in the body's organs and tissues.
What is the ICD 10 code for cardiac amyloidosis?
E85. 4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E85.
How is TTR amyloidosis diagnosed?
A bone scan called a technetium pyrophosphate (TcPYP) scan can detect ATTR in the heart (see video). A positive TcPYP scan, along with blood and urine tests to rule out other forms of amyloidosis, can confirm the diagnosis without the need for a heart biopsy.
What is the difference between AL amyloidosis and ATTR amyloidosis?
More than 30 different precursor proteins may form amyloid, but only two types of amyloidosis commonly affect the heart: immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL) due to a plasma cell dyscrasia, and transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) due to misfolding of transthyretin (prealbumin), which transports thyroxine and ...
How common is TTR amyloidosis?
The exact incidence of transthyretin amyloidosis is unknown. In northern Portugal, the incidence of this condition is thought to be one in 538 people. Transthyretin amyloidosis is less common among Americans of European descent, where it is estimated to affect one in 100,000 people.
What is ATTR scan?
A technetium pyrophosphate scan is similar to an MRI in that it gives a picture of the heart. A dye is injected before the scan and will cause transthyretin amyloidosis to “light up.” If either test indicates TTR amyloidosis, genetic testing is recommended to confirm the subtype.
What are the 2 types of amyloidosis?
The most common types of amyloidosis are: AL (Primary) Amyloidosis. AA (Secondary) Amyloidosis.
What is the treatment for TTR amyloidosis?
Treatment of Amyloid Cardiomyopathy At Penn Medicine, the treatment of TTR amyloid disease involves disease modification with the FDA approved agents, tafamidis, inotersen and patisiran. Note that these medications act by slowing the progress of amyloid disease but are not a cure.
What is the most common type of amyloidosis?
The most common type of amyloidosis in developed countries, AL amyloidosis is also called primary amyloidosis. It usually affects the heart, kidneys, liver and nerves. AA amyloidosis. Also known as secondary amyloidosis, this variety is usually triggered by an inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
What is the life expectancy of someone with amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis has a poor prognosis, and the median survival without treatment is only 13 months. Cardiac involvement has the worst prognosis and results in death in about 6 months after onset of congestive heart failure. Only 5% of the patients with primary amyloidosis survive beyond 10 years.
What is amyloidosis and what causes it?
Amyloidosis is the name for a group of rare, serious conditions caused by a build-up of an abnormal protein called amyloid in organs and tissues throughout the body. The build-up of amyloid proteins (deposits) can make it difficult for the organs and tissues to work properly.
What is the difference between AL amyloidosis and ATTR amyloidosis?
More than 30 different precursor proteins may form amyloid, but only two types of amyloidosis commonly affect the heart: immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL) due to a plasma cell dyscrasia, and transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) due to misfolding of transthyretin (prealbumin), which transports thyroxine and ...
What causes AL amyloidosis?
Overview. AL Amyloidosis is caused by the accumulation of an immunoglobulin light chain protein. Typically, the protein is caused by a malignant or pre-malignant growth of identical, (clonal) lymphocytes or plasma cells that continue to produce these immunoglobulin light chain proteins.
What is amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by the localized or diffuse accumulation of amyloid protein in various anatomic sites. It may be primary, due to clonal plasma cell proliferations; secondary, due to long standing infections, chronic inflammatory disorders, or malignancies; or familial.
What organs does amyloidosis affect?
Generally, primary amyloidosis affects the nerves, skin, tongue, joints, heart, and liver; secondary amyloidosis often affects the spleen, kidneys, liver, and adrenal glands. A group of diseases in which protein is deposited in specific organs or throughout the body.
What happens when amyloid deposits enlarge?
As the amyloid deposits enlarge they displace normal tissue structures, causing disruption of function. Various signs and symptoms depend on the location and size of the deposits. Amyloidosis occurs when abnormal proteins build up and form deposits. The deposits can collect in organs such as the kidney and heart.
When will the ICd 10 E85.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E85.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How many forms of transthyretin amyloidosis are there?
There are three major forms of transthyretin amyloidosis, which are distinguished by their symptoms and the body systems they affect.
What is the E85.82 code?
E85.82 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of wild-type transthyretin-related (attr) amyloidosis. The code E85.82 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Can transthyretin amyloidosis cause eye problems?
Eye problems similar to those in the neuropathic form may also occur. When people with leptomeningeal transthyretin amyloidosis have associated eye problems, they are said to have the oculoleptomeningeal form.The cardiac form of transthyretin amyloidosis affects the heart.
Can amyloidosis cause death?
These abnormalities can lead to progressive heart failure and death. Occasionally, people with the cardiac form of transthyretin amyloidosis have mild peripheral neuropathy.
What is ATTR cardiomyopathy?
Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) is one of the types of systemic amyloidosis in which misfolded transthyretin (TTR) protein gets deposited in the myocardium. Another pertinent etiology of cardiac amyloidosis is due to the deposition of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) aggregates. Several other amyloidogenic proteins may get deposited in various organs and tissues but rarely involve the myocardium. [1]
Where is the TTR gene found?
TTR gene is present on chromosome 18. hATTR follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. However, disease penetrance is more complicated and less understood. The age of onset of clinical disease in hATTR-CM varies widely and depends on the type of mutation. More than 100 different TTR mutations have been identified. These mutations have varied geographical distribution. The most common mutation in the USA is Val122lle. It is seen in approximately 3 to 4% of African Americans, with 1.5 million carriers. The most common mutation in the rest of the world is Val30Met. [22]
What happens when TTR is misfolded?
Misfolded TTR protein forms insoluble fibers. In the heart, they occupy interstitial spaces in the myocardium, making it stiff and rigid. TTR deposition causes further myocardial fibrosis and eventually affects its mechanical function. Due to TTR deposition, the myocardium appears thickened and hypertrophied on cardiac imaging. Compromise in ventricular compliance initially causes diastolic dysfunction. In advanced stages, myocardial dysfunction can result in globally reduced systolic dysfunction. [23]
What is the mutation in the chromosome 18?
Chromosome 18 carries the gene for TTR protein. Therefore, a mutation in the gene coding for TTR can cause structural changes in TTR, causing it to misfold. This type of ATTR is referred to as hereditary transthyretin amyloid (hATTR). In addition, it has been observed that the normal aging process can render ATTR tetramer prone to misfolding, even when the genetic sequence of the TTR is expected. [3] This type of ATTR is referred to as wild-type transthyretin amyloid (wATTR). [9]
Is ATTR a systemic disease?
Transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) is a systemic disease. Due to amyloid deposition in extracardiac tissues, patients often have associated extracardiac signs and symptoms. However, isolated cardiac involvement has been reported as well. [2] Diagnosis of ATTR-CM was often missed or delayed due to previously lacking optimal diagnostic modalities. ATTR-CM often progresses to advanced stages with minimal clinical signs and symptoms initially and is therefore associated with poor prognosis. [3]
Does Tafamidis reduce mortality?
Tafamidis has demonstrated a reduction in all-cause mortality and cardiovascular hospitalization in both hATTR-CM and wATTR-CM patients with heart failure of NYHA functional Classes I and II. Its treatment has been shown to reduce the decline in functional capacity (six-minute walk test) and quality of life (Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire). Functional improvement was seen in approximately 6 months, and mortality reduction took nearly two years.
Is transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy rare?
Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy is a rare but severe cause of restrictive cardiomyopathy, caused by the accumulation of transthyr etin fibrils in the myocardium. It can present with new or worsening heart failure or new conduction system disease. Due to the lack of knowledge and efficient diagnostic modalities, this disease was often missed in clinical settings. However, with the advent of contemporary cardiac imaging techniques and effective therapeutic options, early diagnosis and treatment are possible. This activity reviews the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and treating patients with this condition.
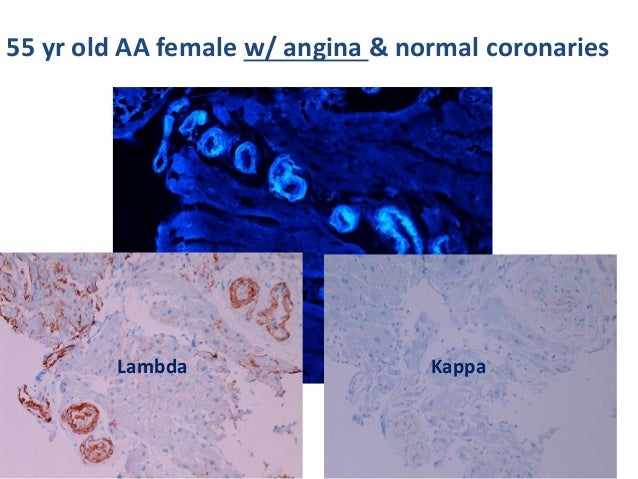
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for neck stiffness
- 2. icd 10 code for abscess left middle finger
- 3. icd-10 code for benzodiazepine use
- 4. code for screening colonoscopy but find polyps icd-10
- 5. icd 10 code for spider bite left scalp
- 6. icd 10 code for history of foley catheter
- 7. icd-10 code for non-accidental traumatic injury to child
- 8. icd 9 code for spastic quadriparesis
- 9. icd 10 cm code for toe pain
- 10. icd-10-cm code for seizure