Unspecified Eustachian tube disorder, unspecified ear. H69.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H69.90 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for eustachian tube disorder?
Oct 01, 2021 · Myringotomy tube (s) status. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Z96.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z96.22 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for an ear implant?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H66.90 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Otitis media, unspecified, unspecified ear. Acute otitis media; Acute otitis media (middle ear infection); Acute persistent otitis media; Chronic otitis media; Chronic otitis media after insertion of tympanic ventilation tube; Influenza a with otitis media; Otitis media; Otitis media (middle ear infection); Otitis media (middle ear …
What is the CPT code for continued presence of a tube?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified Eustachian tube disorder, unspecified ear H69.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H69.90 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H69.90 - other ...
What is the correct DX for a PE tube replacement?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified obstruction of Eustachian tube, unspecified ear H68.109 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H68.109 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H68.109 ...
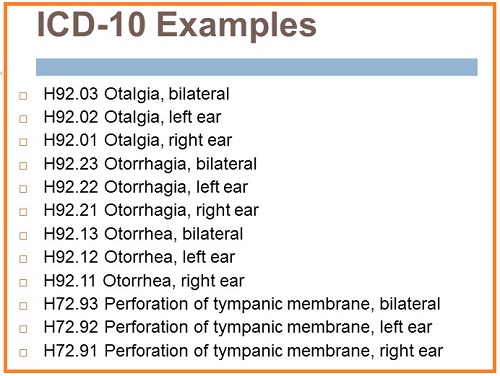
What is the ICD-10 code for presence of tympanostomy tube?
What is the difference between myringotomy and tympanostomy?
What is myringotomy with tubes?
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic Eustachian tube obstruction?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H68. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is tympanostomy tube the same as myringotomy tube?
What is it called when they put tubes in your ears?
When are tubes needed in ears?
What is the CPT code for bilateral myringotomy with insertion of tympanostomy tubes?
When do they put tubes in ears?
What helps eustachian tube dysfunction?
What does patent PE tubes mean?
What are the symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction?
- Hearing problems.
- Tinnitus, or ringing in your ears.
- Clicking or popping sounds.
- A feeling of fullness in your ears.
- Pain that mimics an ear infection.
- Dizziness, vertigo or balance problems.
- A “tickling” sensation in your ears.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for premature birth infant
- 2. icd 10 code for neoplasm of heel
- 3. icd 10 code for lymphadenopathy abdominal
- 4. icd 10 code for g
- 5. icd 9 code for neoplasm pain
- 6. icd 10 code for adhd in adults
- 7. device code icd pcs for tracheostomy tube removal
- 8. icd 10 code for right axis deviation
- 9. what is the icd 10 cm code for thoracoscopy
- 10. icd 10 cm code for stingray sting