How to code diabetes correctly?
E11.42 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy. The code E11.42 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code E11.42 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acute …
What is type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications?
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy E11.42 ICD-10 code E11.42 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD 10 code for diabetes with PVD?
Oct 01, 2021 · Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy Billable Code E11.42 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What are the guidelines for diabetes?
E11.69 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication E11.61 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic arthropathy E11.610 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathic... E11.62 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with skin complications E11.620 Type 2 …
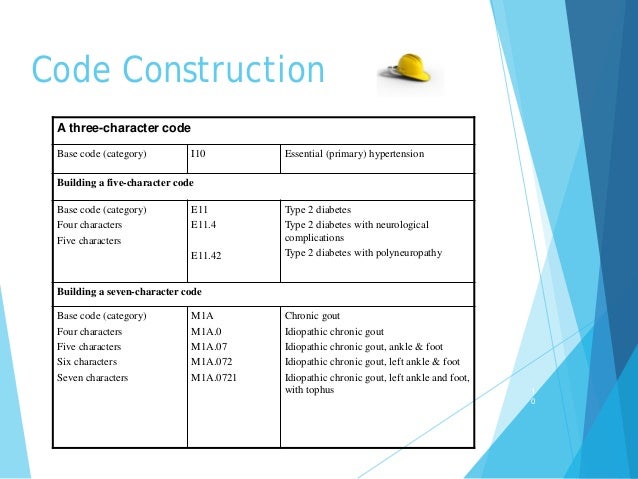
What is Type 2 diabetes mellitus with Polyneuropathy?
Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) is a complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by progressive death of nerve fibers, which leads to loss of nerves, increased sensitivity, and the development of foot ulcers. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the leading non-communicable diseases of mankind.Jun 15, 2021
How do you code diabetes with neuropathy?
ICD-10 code E11. 40 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is diabetic polyneuropathy?
Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) affects multiple peripheral sensory and motor nerves that branch out from the spinal cord into the arms, hands, legs and feet. Typically, the longest nerves — those that extend from the spine to the feet — are affected the most.
What is ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-10 Code: E11* – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the difference between polyneuropathy and neuropathy?
Polyneuropathy is when multiple peripheral nerves become damaged, which is also commonly called peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Is peripheral neuropathy the same as polyneuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy can affect one nerve (mononeuropathy), two or more nerves in different areas (multiple mononeuropathy), or many nerves (polyneuropathy). Carpal tunnel syndrome is an example of mononeuropathy. Most people with peripheral neuropathy have polyneuropathy.Jul 3, 2021
What is the difference between diabetic neuropathy and diabetic polyneuropathy?
All of the types of diabetic neuropathy above—peripheral, autonomic, and proximal—are examples of polyneuropathy. Poly means that they affect many nerves. Focal neuropathy, by contrast, affects one specific nerve; it's focused neuropathy. It can also be called mononeuropathy.Feb 19, 2021
How does diabetes cause diabetic nephropathy?
Diabetic nephropathy causes Diabetic nephropathy is a common complication of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Over time, poorly controlled diabetes can cause damage to blood vessel clusters in your kidneys that filter waste from your blood. This can lead to kidney damage and cause high blood pressure.Oct 19, 2021
What are the three types of neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy TypesMotor neuropathy. This is damage to the nerves that control muscles and movement in the body, such as moving your hands and arms or talking.Sensory neuropathy. ... Autonomic nerve neuropathy. ... Combination neuropathies.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes without complications?
ICD-10 code: E11. 9 Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications - gesund.bund.de.
What is medical code E11 8?
ICD-10 code: E11. 8 Type 2 diabetes mellitus With unspecified complications - gesund.bund.de.
What type of diabetes are included in Category E11?
TABLE 3.CodeUsed to report type 2 diabetes with:E11.2XWith kidney complicationsE11.21With diabetic nephropathyE11.22With diabetic chronic kidney diseaseE11.29With other diabetic kidney complications47 more rows
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E11. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
What is insulin resistant diabetes?
insulin resistant diabetes (mellitus) Clinical Information. A disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make a large amount of urine. This disease occurs when the body does not make enough insulin or does not use it the way it should.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is too high?
diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 2 diabetes , the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.
What is the ICD-10-CM/PCS MS-DRGv28?
Draft ICD-10-CM/PCS MS-DRGv28 Definitions Manual Appendix C: Principal diagnoses which convert CC/MCC to non-CC Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic mononeuropathy Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic polyneuropathy Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic autonomic (poly)neuropathy Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic amyotrophy Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other diabetic neurological complication Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other diabetic arthropathy Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with diabetic dermatitis Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with foot ulcer Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other skin ulcer Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other skin complications Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with periodontal disease Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other oral complications Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with hypoglycemia without coma Diabetes mellitus due to under lying condition with hyperglycemia Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with other specified complication Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition with unspecified complications Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus with neurological complications with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus with neurological complications with diabetic mononeuropathy Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus with neurological complications with diabetic polyneuropathy Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus with neurological complications with d Continue reading >>
What does it mean when your blood sugar is high?
Diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. You have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise. Having prediabetes also increases your risk. Prediabetes means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes appear slowly. Some people do not notice symptoms at all. The symptoms can include Blood tests can show if you have diabetes. One type of test, the A1C, can also check on how you are managing your diabetes. Many people can manage their diabetes through healthy eating, physical activity, and blood glucose testing. Some people also need to take diabetes medicines. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Choose More than 50 Ways to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes - NIH - Easy-to-Read (National Diabetes Education Program) Diabetes type 2 - meal planning (Medical Encyclopedia) Giving an insulin injection (Medical Encyclopedia) Type 2 diabetes - self-care (Medical Encyclopedia) Continue reading >>
What is the ICD code for diabetes mellitus?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. E11.42 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic polyneuropathy. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code E11 is used to code Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) is a complication of diabetes mellitus (predominantly type 2) in which high blood sugars cause severe dehydration, increases in osmolarity (relative concentration of solute) and a high risk of complications, coma and death. It is diagnosed with blood tests. It is related to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), another complication of diabetes more often (but not exclusively) encountered in people with type 1 diabetes; they are differentiated with measurement of ketone bodies, organic molecules that are the underlying driver for DKA but are usually not detectable in HHS. Continue reading >>

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for procedure 59.8
- 2. icd 10 cm code for post procedural state
- 3. icd code for poison ivy
- 4. icd 10 code for iol exchange
- 5. icd 10 code for ultrasound right breast
- 6. icd 10 cm code for class iii obesity
- 7. icd 10 code for basal cell carcinoma of neck
- 8. icd 10 code for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- 9. icd 10 code for aftercare cabg x 4
- 10. icd 10 code for personal history of hep c