| R65.21 | Severe sepsis with shock |
|---|---|
| N39.0 | UTI, site not specified |
| R30.0 | Dysuria |
| R50.81 | Fever presenting with conditions classified elsewhere |
| N17.9 | Acute kidney failure, unspecified |
How do you code recurrent UTI?
- Date of Admission
- Date (s) of indwelling urinary catheter insertion/removal if applicable
- Is patient >65 years of age?
- Collection date (s) and results of urine cultures including colony count
- Date (s) and types of UTI sign/symptoms
- Collection date (s) and results of any positive blood cultures
What is the ICD 10 code for UTI?
ICD-10-CM Code N39.0
- MS-DRG - Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Group
- Clinical Concepts. The code N39.0 can also be found in the following clinical concepts.
- Coding structure: Should you use N39.0 or N390 ( with or without decimal point )? DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected.
What is the CPT code for UTI?
N39.0 - Urinary tract infection, site not specified N39.3 - Stress incontinence (female) (male) N39.4 - Other specified urinary incontinence N39.41 - Urge incontinence N39.42 - Incontinence without sensory awareness N39.43 - Post-void dribbling N39.44 - Nocturnal enuresis N39.45 - Continuous leakage
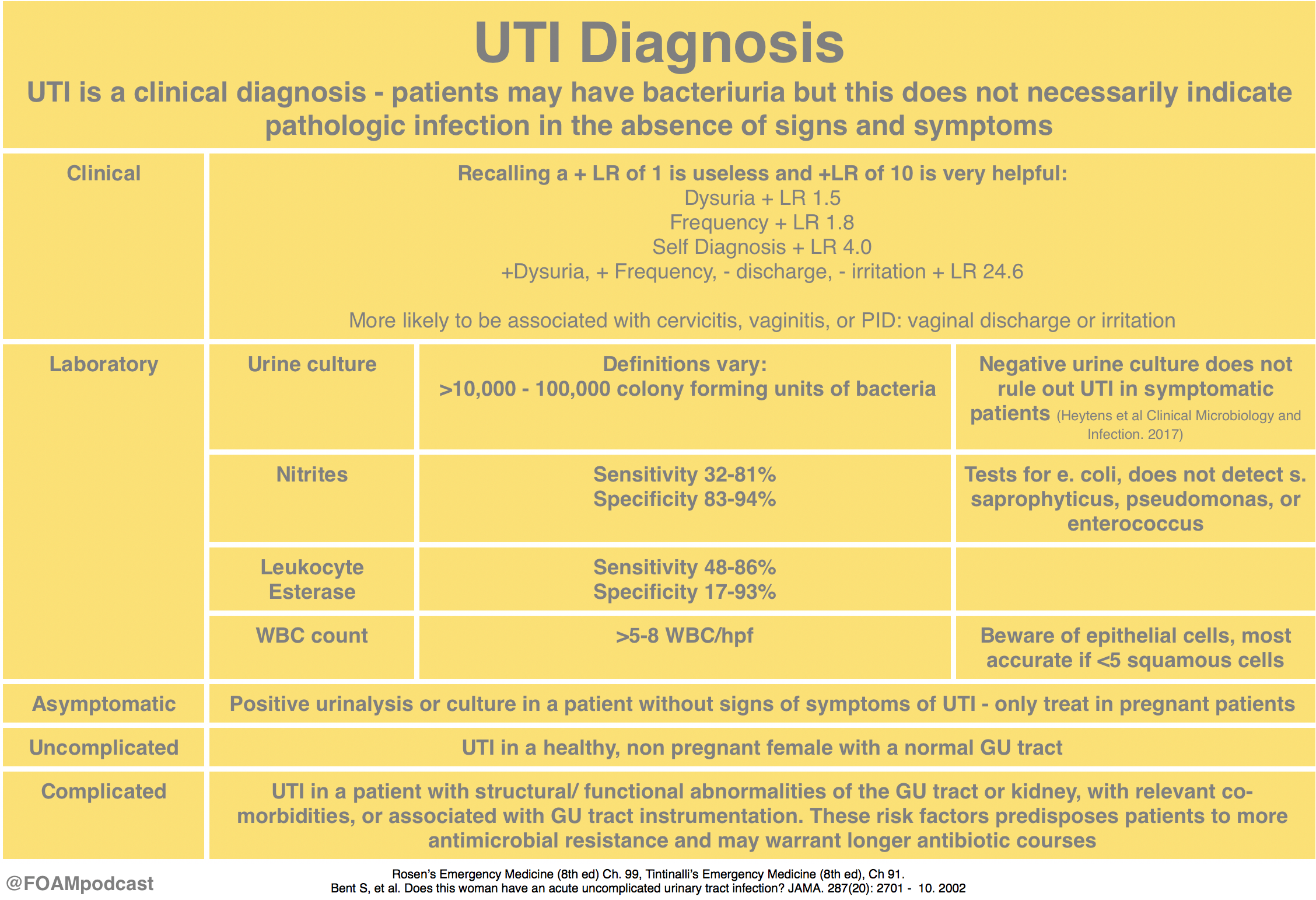
How is urinary tract infection (UTI) diagnosed?
- Infections of the urinary tract are one of the most frequent reasons for treatment in primary medical care.
- Diagnosis solely based on clinical symptoms is often wrong.
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria only requires treatment in exceptional cases.
- Diagnostic precision can be increased by using dip sticks and clinical algorithms.
How do you code sepsis for UTI?
A41. 51 (Sepsis due to Escherichia coli), and N39. 0 (Urinary tract infection, site not specified) would be reported as additional diagnoses.
Is Urosepsis coded as sepsis?
Urosepsis isn't sepsis—not from a coding standpoint, at least. Unless you want a query, don't document it. If it was a urinary tract infection (UTI), then document that. If it was sepsis due to a UTI, please say that in your documentation.
What is the ICD-10 code for sepsis due to E coli?
ICD-10 code A41. 51 for Sepsis due to Escherichia coli [E. coli] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for acute urinary tract infection?
ICD-10 code N39. 0 for Urinary tract infection, site not specified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the rule for coding urosepsis?
Coding sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: a code for the systemic infection (e.g., 038. xx) and the code 995.91, SIRS due to infectious process without organ dysfunction. If no causal organism is documented within the medical record, query the physician or assign code 038.9, Unspecified septicemia.
Is urosepsis a specific term?
Currently: In ICD-9 Codes, you have coding conventions to follow, which is to use 599.0 (Urinary tract infection, site not specified) for "urosepsis." According to ICD-9 guidelines, "The term urosepsis is a nonspecific term.
What is the ICD-10 code for E. coli UTI?
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli infection A04. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can sepsis be coded as primary diagnosis?
According to the guidelines above, sepsis would be the appropriate principal diagnosis if it is the reason the patient is admitted, and meets the definition of principal diagnosis.
How do I code sepsis unspecified?
ICD-10-CM Code for Sepsis, unspecified organism A41. 9.
What is urosepsis?
Urosepsis is a form of sepsis that is caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs are very common, so you shouldn't worry or panic that you are going to get urosepsis if you are diagnosed with a UTI.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is diagnosis code n39?
0: Urinary tract infection, site not specified.
When to avoid coding unspecified UTI?
Avoid coding unspecified UTI (N39.0) when specific site infection is mentioned. For example if both cystitis and UTI are mentioned it is not necessary to code UTI, instead code only cystitis. Urosepsis – This does not lead to any code in the alphabetic index.
What is it called when you have a urinary infection?
Infection can happen in any part of the urinary tract – kidney, ureter, bladder or urethra. It is called as Cystitis, Urethritis and Pyelonephritis based on the site.
What is UTI in women?
Urinary Tract infection (UTI) is a very common infectious disease occurs commonly in aged women. As age goes up there will be structural changes happening in kidney. Muscles in the bladder, urethra and ureter become weaken. Urinary retention gets increased in the bladder and this creates an environment for bacterial growth.
Is it necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0?
Urethritis. It is not necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0. If the infectious organism is mentioned, place the UTI code primary and organism secondary. Site specified infection should be coded to the particular site. For example, Infection to bladder to be coded as cystitis, infection to urethra to urethritis.
What is a UTI after a procedure?
Uti (urinary tract infection) after procedure. Clinical Information. A bacterial infectious process affecting any part of the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder and the urethra. Symptoms include urinary urgency and frequency, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy urine.
How to tell if you have a UTI?
if you think you have a uti, it is important to see your doctor. Your doctor can tell if you have a uti by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with medicines to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days.
What are the infections that affect the secretion and elimination of urine?
Infections affecting stuctures participating in the secretion and elimination of urine: the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Inflammatory responses of the epithelium of the urinary tract to microbial invasions. They are often bacterial infections with associated bacteriuria and pyuria.
What is the second most common type of infection in the body?
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Infections of the urinary tract (utis) are the second most common type of infection in the body. You may have a uti if you notice.
What is systemic disease?
Systemic disease associated with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream causing a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock. Symptoms include fever, chills, tachycardia, and increased respiratory rate.
What is the term for the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues?
Urosepsis . Clinical Information. (sep-sis) the presence of bacteria or their toxins in the blood or tissues. A disorder characterized by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood stream that cause a rapidly progressing systemic reaction that may lead to shock.
What is post-procedural sepsis?
Post-procedural Sepsis and Sepsis Due to a Device, Implant, or Graft. A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to wound infection, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if severe sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
When to query a physician for sepsis?
You must query the physician when the term “sepsis syndrome” is documented as a final diagnosis. Know when to Query. Sepsis is a complicated condition to code, and it is often necessary to query the physician to code the case correctly.
Can you code for sepsis?
Documentation issues: You can code for sepsis when the physician documents the term “sepsis.”. Documentation should be consistent throughout the chart. Occasionally, during an extended length of stay, sepsis may resolve quickly and the discharging doctor may not include the diagnosis of sepsis on the discharge summary.
Is sepsis a systemic infection?
term “sepsis” must also be documented to code a systemic infection. This is a major change from ICD-9-CM. If the term “sepsis” is not documented with “SIRS” when it’s due to a localized infection, you must ask for clarification from the physician.
Is septic shock documented without sepsis?
Documentation issues: The term “septic shock” is occasionally documented without the term “sepsis.”. According to the guidelines, for all cases of septic shock the code for the underlying systemic infection is sequenced first, followed by R65.21 Severe sepsis with septic shock or T81.12- Postprocedural septic shock.
What is the most common type of infection that leads to sepsis?
Localized Infection. Almost any type of infection can lead to sepsis. Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract. When localized infections are contained, they tend to be self-limiting and resolve with antibiotics.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
How does sepsis affect the body?
Sepsis is an extreme response to infection that develops when the chemicals the immune system releases into the bloodstream to fight infection cause widespread inflammation. This inflammation can lead to blood clots and leaky blood vessels, and without timely treatment, may result in organ dysfunction and then death. Severe cases of sepsis often result from a body-wide infection that spreads through the bloodstream, but sepsis can also be triggered by an infection in the lungs, stomach, kidneys, or bladder. Thus, it is not necessary for blood cultures to be positive to code sepsis (guideline I.C.1.d.1.a.i).
How to improve sepsis documentation?
To improve sepsis documentation, coding staff needs to work closely with clinical documentation improvement specialists (CDIs), and everyone must be clear on what documentation is needed to correctly code sepsis. A physician champion can be helpful to establish guidelines for the physicians and standard terminology to use when documenting sepsis. A coding tip sheet that includes various scenarios is a helpful tool for the coding department to standardize definitions and the interpretation of the coding guidelines. A regular audit of sepsis DRGs or sepsis as a secondary code can help to identify documentation issues and coders who need more education. Sepsis is never going to be easy to code, but with continuous education and teamwork across departments, the sepsis beast can be conquered.
What is septic shock?
Septic shock refers to circulatory failure associated with severe sepsis. It is a life-threatening condition that happens when the exaggerated response to infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure (hypotension). Septic shock is a form of organ failure.
When is a localized infection coded?
If the patient is admitted with a localized infection and the patient does not develop sepsis or severe sepsis until after the admission, the localized infection is coded first, followed by the appropriate codes for sepsis or severe sepsis, if applicable .
What are the symptoms of a localized infection?
Documentation issues: A patient with a localized infection usually presents with tachycardia, leukocytosis, tachypnea, and/or fever. These are typical symptoms of any infection. It is up to the clinical judgment of the physician to decide whether the patient has sepsis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for postoperative follow up for stent
- 2. icd 10 code for bilateral macular degeneration
- 3. icd 10 code for cellulitis right foot
- 4. icd 10 code for aftercare following hemiarthroplasty
- 5. icd 10 code for injury to rib
- 6. icd 10 code for neuropathy feet
- 7. icd 10 diagnosis code for aortic stenosis
- 8. icd 10 code for graves disease with exophthalmos
- 9. icd-10 code for abnormal heart beat
- 10. icd 10 code for incontinunce