What is a vault prolapse?
Vaginal prolapse, also known as vaginal vault prolapse, occurs when the top of the vagina weakens and collapses into the vaginal canal. In more serious cases of vaginal prolapse, the top of the vagina may bulge outside the vaginal opening.
What is a Viginal vault?
The vaginal vault is the expanded region of the vaginal canal at the internal end of the vagina.
How many degrees is a vault prolapse?
First-degree prolapse: The uterus droops into the lower portion of the vagina. Second-degree prolapse: The uterus falls to the level of the vaginal opening. Third-degree prolapse: The cervix, which is located at the bottom of the uterus, sags to the vaginal opening and protrudes outside the body.Aug 15, 2018
What is prolapse of vaginal vault after hysterectomy?
Vaginal Vault Prolapse (After Hysterectomy) The top of the vagina drops down, creating a bulge. In severe cases, the top of the vagina may protrude outside of the vagina. It also may occur with small intestine prolapse (shown here), anterior vaginal wall prolapse, or posterior vaginal vault prolapse.
What is pelvic prolapse?
Pelvic organ prolapse is when 1 or more of the organs in the pelvis slip down from their normal position and bulge into the vagina. It can be the womb (uterus), bowel, bladder or top of the vagina. A prolapse is not life threatening, but it can cause pain and discomfort.
What procedure is performed to treat vaginal prolapse?
Colporrhaphy—Used to treat prolapse of the anterior (front) wall of the vagina and prolapse of the posterior (back) wall of the vagina. This type of surgery is performed through the vagina. Stitches are used to strengthen the vagina so that it once again supports the bladder or the rectum.
How do you prevent a vault prolapse in a vaginal hysterectomy?
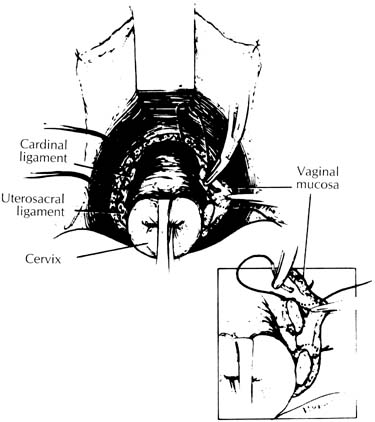
Suspension of the vaginal apex to the uterosacral ligaments (McCall culdoplasty) or to the sacrospinous ligaments at the time of vaginal hysterectomy is the mainstay for prevention of post hysterectomy vaginal vault prolapse.
How big is vaginal vault?
Introduction and hypothesis: Anterior vaginal wall length (AVL) is on average 6.1 ± 1.3 cm in women with normal support and lengthened in women with cystocele.
What happens if you have both ovaries taken out?
If you have both ovaries taken out, you will enter menopause. Your health care provider might recommend a hysterectomy if you have. Fibroids. Endometriosis that hasn't been cured by medicine or surgery. Uterine prolapse - when the uterus drops into the vagina. Cancer of the uterine, cervix, or ovaries.
What is the best treatment for a hard time getting to the bathroom?
Your health care provider diagnoses the problem with a physical exam, a pelvic exam, or special tests. Treatments include special pelvic muscle exercises called Kegel exercises. A mechanical support device called a pessary helps some women.
What is the code for a vaginal vault?
N99.3 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of prolapse of vaginal vault after hysterectomy. The code N99.3 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is a hysterectomy?
Information for Patients. Hysterectomy. A hysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's uterus or womb. The uterus is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. After a hysterectomy, you no longer have menstrual periods and can't become pregnant.
What is pelvic floor disorder?
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and other tissues that form a sling or hammock across the pelvis. In women, it holds the uterus, bladder, bowel, and other pelvic organs in place so that they can work properly.
What does it mean when you feel a heaviness in your vagina?
Seeing or feeling a "bulge" or "something coming out" of the vagina. Having a hard time starting to urinate or emptying the bladder completely. Having frequent urinary tract infections.
Why do my muscles get weaker during menopause?
One of the main causes of this condition is childbirth – which can easily stretch and weaken these muscles, especially for a woman who had a difficult delivery. Aging and the loss of estrogen during menopause can also weaken these muscles.
What is the N81.9?
N81.9 – Female genital prolapse, unspecified. Woman who experience any specific symptoms of vaginal prolapse (including a feeling of fullness in the lower belly or a bulge in the vagina), must visit a gynecologist for a detailed examination.
What does a gynecologist do?
He/she may test the strength of the pelvic floor, the sphincter muscles, and other muscles and ligaments that support the vaginal walls, uterus, rectum, urethra, ...
What are the risk factors for vaginal prolapse?
Other risk factors of vaginal prolapse include advanced age, abnormalities of the connective tissue, obesity, smoking, dysfunction of the nerves and tissues, and strenuous physical activity.
Why is it important to reduce body weight?
As obesity can put extra stress on the muscles and ligaments within the pelvis and vagina, it is important to reduce body weight to prevent this condition from developing or recurring. Medical billing and coding for vaginal prolapse can be challenging, as there are several codes associated with the condition.
How do you know if you have a prolapse?
Other additional symptoms include –. A feeling of heaviness or pressure in the vagina. A lump at the opening of the vagina. Urinary stress incontinence. Pain that increases during long periods of standing. Pain during sex.
What is the term for a woman's pelvis that is weakened?
January 23, 2020. by Natalie Tornese. Vaginal prolapse is a condition which occurs when the network of muscles that support the organs in a woman’s pelvis gets weakened or fall out of their normal positions. This weakening allows the uterus, urethra, bladder, or rectum to droop down into the vagina. Generally, the network of muscles, ligaments and ...
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #742-743 - Uterine and adnexa procedure for non-malignancy with CC or MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'N99.3 - Prolapse of vaginal vault after hysterectomy'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code N99.3. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 618.5 was previously used, N99.3 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Why does the pelvic floor become weak?
In women, it holds the uterus, bladder, bowel, and other pelvic organs in place so that they can work properly. The pelvic floor can become weak or be injured. The main causes are pregnancy and childbirth. Other causes include being overweight, radiation treatment, surgery, and getting older.
What part of the uterus is the place where a baby grows during pregnancy?
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, the place where a baby grows during pregnancy. The cervix has a small opening that expands during childbirth. It also allows menstrual blood to leave a woman's body.
What is the medical term for insufficient cervix?
Insufficient cervix (Medical Encyclopedia) Nabothian cyst (Medical Encyclopedia) [ Learn More in MedlinePlus ] Pelvic Floor Disorders. Also called: Cystocele, Enterocele, Pelvic prolapse, Rectocele. The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and other tissues that form a sling or hammock across the pelvis.
Why do you need a Pap test?
Your health care provider may perform a Pap test during your health checkup to look for changes to the cells of the cervix, including cervical cancer. Other problems with the cervix include: Cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix. This is usually from an infection.
What is the best treatment for a hard time getting to the bathroom?
Your health care provider diagnoses the problem with a physical exam, a pelvic exam, or special tests. Treatments include special pelvic muscle exercises called Kegel exercises. A mechanical support device called a pessary helps some women.
What is the code for utero prolapse?
N81.3 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of complete uterovaginal prolapse. The code N81.3 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What does it mean when you feel a heaviness in your vagina?
Seeing or feeling a "bulge" or "something coming out" of the vagina. Having a hard time starting to urinate or emptying the bladder completely .
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for muscle strain of right lower extremity
- 2. icd 10 code for long term use of opiods
- 3. icd-10 code for chest x ray pa and lateral
- 4. icd 10 code for acute on chronic congestive heart failure unspecified
- 5. icd-10 code for 292.89
- 6. icd 10 code for influenza a virus
- 7. icd 10 code for strep pneumoniae bacteremia
- 8. icd 10 cm code for facial trauma,
- 9. icd 10 code for l4-l5 anterolisthesis
- 10. icd 10 code for uncontrolled hypothyroidism