What is the ICD 9 code for otitis media?
2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 382.9. Unspecified otitis media. Short description: Otitis media NOS. ICD-9-CM 382.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 382.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for mastoiditis?
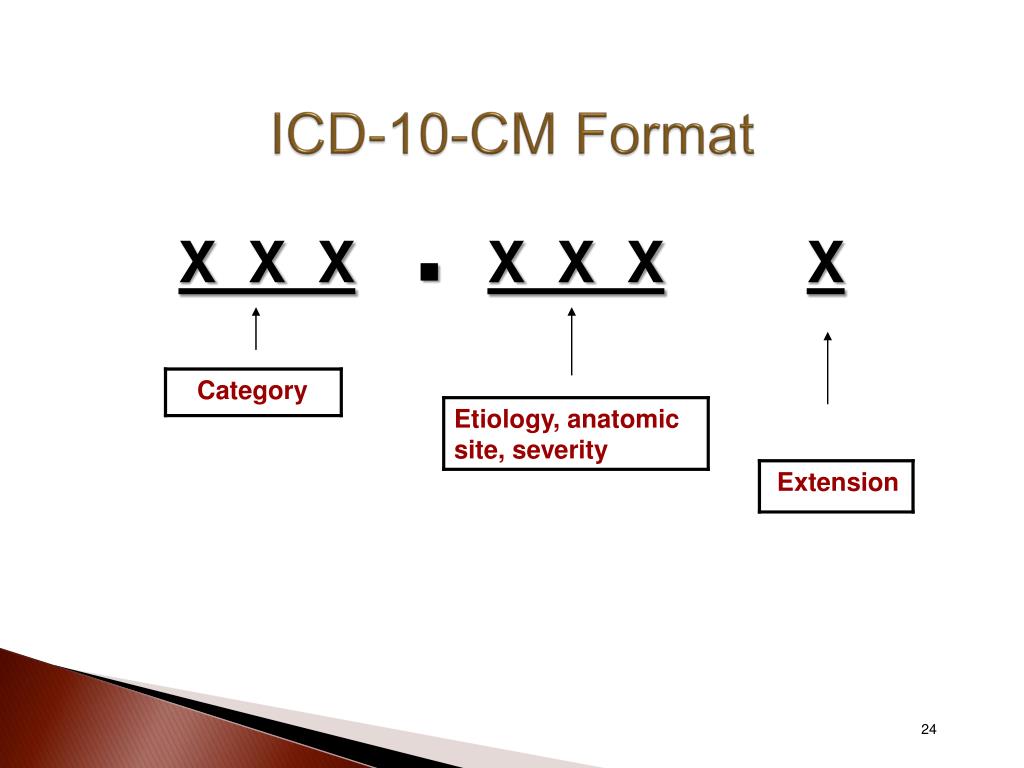
H66.90 ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66.9 ICD-10 code H66.9 for Otitis media, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process. Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for salpingitis media?
H67.3 Otitis media in diseases classified elsewhere, bilateral. H67.9 Otitis media in diseases classified elsewhere, unspecified ear. H68 Eustachian salpingitis and obstruction. H68.0 Eustachian salpingitis. Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for inflammation of the middle ear?
Inflammation of the middle ear including the auditory ossicles and the eustachian tube. Inflammation of the middle ear. ICD-10-CM H66.90 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 152 Otitis media and uri with mcc. 153 Otitis media and uri without mcc.

What is the code for bilateral otitis media?
ICD-10 code H66. 93 for Otitis media, unspecified, bilateral is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is bilateral chronic otitis media?
Chronic otitis media- This is a middle ear infection that does not go away, or happens repeatedly, over months to years. The ear may drain (have liquid coming out of the ear canal). It can often be accompanied by a tympanic membrane perforation and hearing loss. Usually chronic otitis media is not painful.
What is the ICD-10 code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral chronic and acute serous otitis media?
ICD-10 Code for Chronic serous otitis media, bilateral- H65. 23- Codify by AAPC.
What is the difference between acute and chronic otitis media?
Chronic suppurative otitis media is a long-standing, persistently draining perforation of the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Acute otitis media and blockage of a eustachian tube are among the causes of chronic suppurative otitis media.
What are the types of otitis media?
What are the different types of otitis media?Acute otitis media. This middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. ... Otitis media with effusion. Fluid (effusion) and mucus continue to accumulate in the middle ear after an initial infection subsides. ... Chronic otitis media with effusion.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for otitis media right ear?
Otitis media, unspecified, right ear H66. 91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H66. 91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for otitis media left ear?
ICD-10 Code for Otitis media, unspecified, left ear- H66. 92- Codify by AAPC.
What is acute serous otitis media bilateral?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What is the code for Chronic otitis media?
H65. 2 - Chronic serous otitis media. ICD-10-CM.
What is serous otitis media?
Serous otitis media is a specific type of otitis media with effusion caused by transudate formation as a result of a rapid decrease in middle ear pressure relative to the atmospheric pressure. The fluid in this case is watery and clear.
What is the treatment for chronic otitis media?
Chronic Otitis Media Treatments The main form of treatment for chronic otitis media is antibiotics. Antibiotic ear drops are usually prescribed, although some patients may be given a regimen of oral antibiotics. In more advanced cases, surgery may be recommended to: Repair a damaged eardrum and/or hearing bones.
Does chronic otitis media go away?
Another cause of this condition is a block in the eustachian tube not related to the ear infection. Chronic suppurative otitis media: This is a condition in which the ear infection won't go away even with treatment. Over time, this can cause a hole to form in the eardrum.
What is the cause of most chronic otitis media?
Although viruses are the most common etiology in otitis media, bacteria often affect children with chronic suppurative otitis media. The etiology is usually polymicrobial. The most common microorganisms found in this pathology Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
How long does chronic otitis last?
Treating middle ear infections Most middle ear infections (otitis media) clear up within three to five days and don't need any specific treatment. You can relieve any pain and a high temperature using over the counter painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Known As
Acute otitis media is also known as acute left persistent otitis media, acute otitis media, acute otitis media (middle ear infection), acute persistent otitis media, acute right otitis media, bilat acute otitis media, bilat chronic otitis media, bilat chronic otitis media status post pe tubes, bilat ear infection, bilat otitis media, bilat otitis media w eardrum rupture, bilat persistent acute otitis media, bilat recurrent otitis media, bilateral acute otitis media, bilateral chronic otitis media, bilateral chronic otitis media after insertion of tympanic ventilation tube, bilateral ear infections, bilateral otitis media, bilateral perforation of tympanic membranes due to otitis media, bilateral persistent acute otitis media, bilateral recurrent otitis media, both sides acute otitis media, both sides chronic otitis media, both sides chronic otitis media status post pe tubes, both sides ear infection, both sides otitis media (ear condition), both sides otitis media with eardrum ruptures, both sides persistent acute otitis media, both sides recurrent otitis media, chronic otitis media, chronic otitis media after insertion of tympanic ventilation tube, chronic otitis media status post pe tubes, H1N1 influenza w otitis media, H1N1 influenza with otitis media, influenza A w otitis media, influenza A with otitis media, influenza w otitis media, influenza with otitis media, left acute otitis media, left chronic otitis media, left chronic otitis media after insertion of tympanic ventilation tube, left chronic otitis media status post pe tubes, left ear infection, left otitis media, left otitis media w eardrum rupture, left otitis media with eardrum rupture, left perforation of tympanic membrane due to otitis media, left persistent acute otitis media, left recurrent otitis media, otitis media, otitis media (middle ear infection), otitis media (middle ear infection) after PE tubes, otitis media (middle ear infection) persistent, otitis media (middle ear infection) acute, otitis media (middle ear infection) chronic, otitis media (middle ear infection) ear drum rupture, otitis media (middle ear infection) multiple episodes, otitis media due to H1N1 influenza, otitis media due to influenza, otitis media due to influenza A, otitis media w eardrum rupture, otitis media acute, otitis media chronic, otitis media recurrent, perforation of tympanic membrane due to otitis media, persistent acute otitis media, recurrent acute otitis media, recurrent otitis media, recurrent right otitis media, right acute otitis media, right acute persistent otitis media, right chronic otitis media, right chronic otitis media after insertion of tympanic ventilation tube, right chronic otitis media status post pe tubes, right ear infection, right otitis media, right otitis media w eardrum rupture, right otitis media with ear drum rupture, right otitis media with eardrum rupture, right persistent acute otitis media, and right recurrent otitis media..
Acute Otitis Media Definition and Symptoms
Acute otitis media is when the middle ear is inflamed and accompanied by the rapid signs of an ear infection. Acute otitis media is typically very rapidly onset with a short duration.
When will the ICd 10-CM H66.90 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H66.90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a perforated tympanic membrane?
Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by inflammation (physiologic response to irritation), swelling and redness to the middle ear. An acute or chronic inflammatory process affecting the middle ear.
Coding Notes for H66.9 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'H66.9 - Otitis media, unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code H66.9. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fall off atv
- 2. what is icd 10 code for 785.1
- 3. icd-10 code for tendonitis of right ebow
- 4. icd 10 code for class iii obesity
- 5. 2020 icd 10 code for shortness of breath with exertion
- 6. icd 9 code for medical noncompliance
- 7. icd 10 pcs code for x-ray of the left ankle with high osmolar contrast
- 8. icd 10 code for cyst sacral coccyx
- 9. icd-10 code for cat bit
- 10. icd 10 code for drug level monitoring