What is the synonym of hyperkalemia?
Hypokalemia ICD 9 Code Billable Medical Code for Hypopotassemia Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 276.8 Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 276.8. Known As Hypokalemia is also known as chronic hypokalemia, hypokalemia, hypokalemia (low potassium level), and hypokalemia chronic.
What are the neuromuscular manifestations of hyperkalemia?
Oct 01, 2021 · Hyperkalemia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. E87.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.5 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E87.5 - other international versions of ICD-10 E87.5 may differ.
What is the role of diuretics in the treatment of hyperkalemia?
Mar 13, 2022 · ICD-9-CM Vol. 1 Diagnostic Codes. 276.7 - Hyperpotassemia. The above description is abbreviated. This code description may also have Includes, Excludes, Notes, Guidelines, Examples and other information. Access to this feature is available in the following products: Find-A-Code Essentials. HCC Plus.

What is icd10 code for hyperkalemia?
ICD-10 | Hyperkalemia (E87. 5)
What is the ICD-9 code for hypokalemia?
Convert to ICD-10-CM: 276.8 converts directly to: 2015/16 ICD-10-CM E87. 6 Hypokalemia.
What are ICD-9 diagnosis codes?
The International Classification of Diseases Clinical Modification, 9th Revision (ICD-9 CM) is a list of codes intended for the classification of diseases and a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease.Aug 1, 2010
Are ICD-9 codes still valid?
Currently, the U.S. is the only industrialized nation still utilizing ICD-9-CM codes for morbidity data, though we have already transitioned to ICD-10 for mortality.
What do you mean by hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia is the medical term that describes a potassium level in your blood that's higher than normal. Potassium is a chemical that is critical to the function of nerve and muscle cells, including those in your heart. Your blood potassium level is normally 3.6 to 5.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
What is ICD-10 for low potassium?
ICD-10 | Hypokalemia (E87. 6)
What is an example of an ICD-9 code?
Most ICD-9 codes are three digits to the left of a decimal point and one or two digits to the right of one. For example: 250.0 is diabetes with no complications. 530.81 is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).Jan 9, 2022
What is the difference between ICD-9 and ICD-9-CM?
The current ICD used in the United States, the ICD-9, is based on a version that was first discussed in 1975. The United States adapted the ICD-9 as the ICD-9-Clinical Modification or ICD-9-CM. The ICD-9-CM contains more than 15,000 codes for diseases and disorders. The ICD-9-CM is used by government agencies.
What is an example of a diagnosis code?
A diagnosis code is a combination of letters and/or numbers assigned to a particular diagnosis, symptom, or procedure. For example, let's say Cheryl comes into the doctor's office complaining of pain when urinating.Jan 6, 2022
When did we stop using ICD-9 codes?
On October 1, 2013, the ICD-9 code sets will be replaced by ICD-10 code sets. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services issued a final rule on January 16, 2009, adopting ICD-10-CM (clinical modifier) and ICD-10-PCS (procedure coding) system.
How many codes did ICD-9 have?
The current ICD-9-CM system consists of ∼13,000 codes and is running out of numbers.
When did ICD-9 go away?
September 30, 2015CMS requires medical practices and RCM companies to make the switch from ICD-9 to ICD-10 by October 1, 2015, the last day for ICD-9 being September 30, 2015. This is not new. Organized, managed, and maintained by the World Health Organization, ICD codes are changed approximately once every 10 years.Jan 2, 2015
What is the ICd code for hyperkalemia?
The ICD code E875 is used to code Hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia (hyperkalaemia in British English, hyper- high; kalium, potassium; -emia, "in the blood") refers to an elevated concentration of the electrolyte potassium (K+) in the blood. The symptoms of elevated potassium are nonspecific, and the condition is usually discovered in a blood test ...
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
What is the difference between hyperkalemia and potassium?
Hyperkalemia results either from the shift of potassium out of cells or from abnormal renal potassium excretion. Cell shift leads to transient increases in the plasma potassium concentration, whereas decreased renal excretion of potassium leads to sustained hyperkalemia. Impairments in renal potassium excretion can be the result ...
What foods cause hyperkalemia?
Foods naturally rich in potassium include bananas (a medium-sized banana contains 451 mg or 12 mmol of potassium) and potatoes (844 mg or 22 mmol in a large baked potato with skin).
What is the effect of mineralocorticoid levels on potassium?
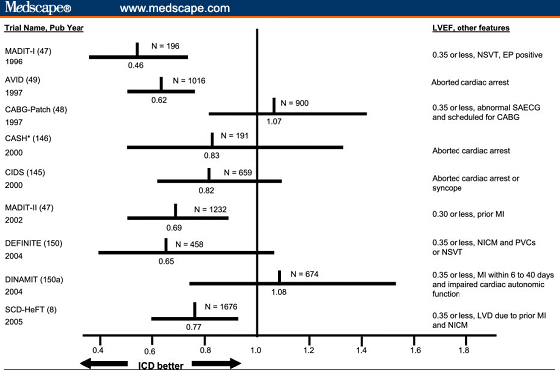
Decreased mineralocorticoid levels or activity due to disturbances in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system will impair renal potassium secretion. Such disturbances can be the result of diseases or drugs ( Figure 1 ). 13, 16, 17
How much potassium is in the body?
The body of a typical 70-kg man contains about 3,500 mmol of potassium, 98% of which is in the intracellular space; the remaining 2% is in the extracellular space. This large intracellular-to-extracellular gradient determines the cell voltage and explains why disorders in plasma potassium give rise to manifestations in excitable tissues such as the heart and nervous system.
What happens to potassium after a meal?
After a meal, release of insulin not only regulates the plasma glucose concentration, it also causes potassium to move into cells until the kidneys have had sufficient time to excrete the dietary potassium load and reestablish total-body potassium content. Exercise, beta-blockers.
What causes a spurious increase in potassium concentration?
A spurious increase in plasma potassium concentration along with a low plasma calcium concentration raises the possibility of calcium chelation and release of potassium in a sample tube contaminated with the anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid.
How does insulin affect potassium?
Insulin lowers the plasma potassium concentration by promoting its entry into cells. To avoid hypoglycemia, 10 units of short-acting insulin should be accompanied by a 50-g infusion of glucose, increased to 60 g if 20 units of insulin are given. 24. Beta-2 receptor agonists produce a similar effect.
What is hyperkalemia in neonatal?
HYPERKALEMIA-. abnormally high potassium concentration in the blood most often due to defective renal excretion. it is characterized clinically by electrocardiographic abnormalities elevated t waves and depressed p waves and eventually by atrial asystole. in severe cases weakness and flaccid paralysis may occur. dorland 27th ed#N#PSEUDOHYPOALDOSTERONISM-. a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by renal electrolyte transport dysfunctions. congenital forms are rare autosomal disorders characterized by neonatal hypertension hyperkalemia increased renin activity and aldosterone concentration. the type i features hyperkalemia with sodium wasting; type ii hyperkalemia without sodium wasting. pseudohypoaldosteronism can be the result of a defective renal electrolyte transport protein or acquired after kidney transplantation.
What is the E87.5 code?
E87.5 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of hyperkalemia. The code E87.5 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
How does kidney function help with potassium?
Your kidneys help to keep the right amount of potassium in your body. If you have chronic kidney disease, your kidneys may not remove extra potassium from the blood. Some medicines also can raise your potassium level. You may need a special diet to lower the amount of potassium that you eat.
What foods help with potassium?
Sources of potassium in the diet include. Fruit from vines, such as grapes and blackberries. Root vegetables, such as carrots and potatoes. Your kidneys help to keep the right amount of potassium in your body. If you have chronic kidney disease, your kidneys may not remove extra potassium from the blood.
How to balance water in your body?
Balance the amount of water in your body. Balance your body's acid/base (pH) level. Move nutrients into your cells. Move wastes out of your cells. Make sure that your nerves, muscles, the heart, and the brain work the way they should. Sodium, calcium, potassium, chlorine, phosphate, and magnesium are all electrolytes.
Does potassium help with blood pressure?
It also helps move nutrients into cells and waste products out of cells. A die t rich in potassium helps to offset some of sodium's harmful effects on blood pressure. Many people get all the potassium they need from what they eat and drink. Sources of potassium in the diet include.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for parasomnia
- 2. icd 10 cm code for congenital mitral stenosis 23 month old
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for transposition of great vessels with repair
- 4. icd code for renal insufficiency
- 5. icd 10 cm code for post traumatic stress disorder
- 6. icd 10 code for salmonella due to food poisoning
- 7. icd 10 code for diastolic dysfunction grade 1
- 8. icd 10 code for diabetic right ankle ulcer
- 9. icd-10 code for right foot cellulitis
- 10. icd 10 code for bilateral rhonchi