What is the ICD 9 code for immune thrombocytopenic purpura?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Short description: Immune thrombocyt purpra. ICD-9-CM 287.31 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 287.31 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 code for immune thrombocytopenia?
D69.3 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
What is the ICD-9 code for diagnosis?
ICD-9-CM 287.31 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 287.31 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015.
What is the ICD 10 equivalent of ICD 9 code D69?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code D69.3 and a single ICD9 code, 287.39 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
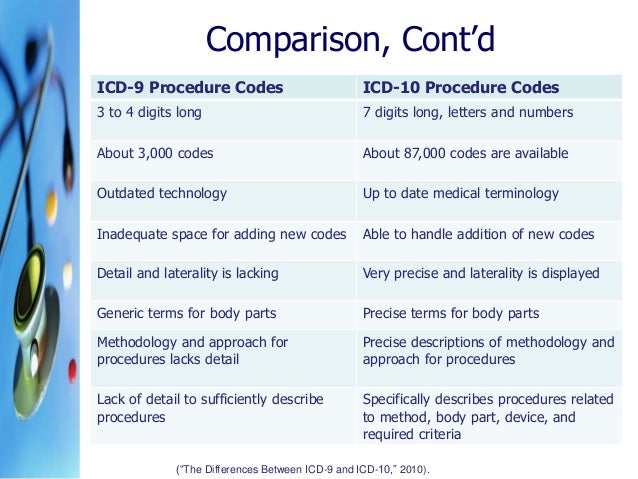
What is the ICD 10 code for ITP?
ICD-10 code D69. 3 for Immune thrombocytopenic purpura is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
What are the two types of ITP?
There are two forms of ITP:Acute thrombocytopenic purpura. This usually affects young children, ages 2 to 6 years old. ... Chronic thrombocytopenic purpura. The onset of the disorder can happen at any age, and the symptoms can last a minimum of 6 months, several years, or a lifetime.
Is ITP the same as immune thrombocytopenia?
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a disorder that can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. The bleeding results from unusually low levels of platelets — the cells that help blood clot.
Is ITP primary or secondary?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), a condition of low platelets, can occur from primary causes, often referred to as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, or secondary to an underlying disease, such as an autoimmune disorder or an infection.
Is ITP an autoimmune disease?
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune bleeding disorder characterized by abnormally low levels of blood cells called platelets, a situation referred to as thrombocytopenia.
What are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia?
What causes thrombocytopenia?Alcohol use disorder and alcoholism.Autoimmune disease which causes ITP. ... Bone marrow diseases, including aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas and myelodysplastic syndromes.Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.More items...•
What is ITP and TTP?
Both immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) are disorders that affect platelets. They may exhibit similar symptoms, however there are differences in the causes, complications, and treatments of the disorders.
What does ITP stand for?
ITP stands for Immune Thrombocytopenia, also known as Immune or Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. ITP is a rare bleeding disorder characterized by a low amount of platelets in the blood. Platelets are needed for clotting of the blood.
What does ITP look like?
One of the most common symptoms of ITP is a skin condition called petechiae. These are small red bumps on your skin caused by bleeding from underneath. Petechiae can look like a red rash at first, but the bumps are slightly raised, scattered, and the size of pinpoints. They can also have a purplish tinge.
How is ITP diagnosed?
Diagnostic Procedures for ITP Includes a special blood test called an "anti-platelet antibody test." Careful review of medications. Bone marrow aspiration: This test examines the platelet production and can rule out any abnormal cells the marrow may be producing that could lower platelet counts.
What is the most common cause of low platelet count?
One of the most common causes of low platelets is a condition called immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). You may hear it called by its old name, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Why a patient would need a splenectomy after a diagnosis of ITP?
Why remove the spleen? In people with ITP the immune system treats platelets as foreign and destroys them. The spleen is responsible for removing these damaged platelets and therefore removal of the spleen can help to keep more platelets circulating in the body.
Can ITP turn into leukemia?
ITP does not turn into a more serious blood disorder, like leukemia or aplastic anemia. It is usually not a sign that their child will later develop other autoimmune conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or “lupus”).
Is chronic ITP life threatening?
For most people with ITP, the condition isn't serious or life-threatening. For example, acute ITP in children often resolves within 6 months or less without treatment. Chronic ITP, though, can last for many years. Still, people can live for many decades with the disease, even those with severe cases.
Does ITP get worse with age?
Does it get worse over time? No, unlike autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis it is not a progressive disease, but the risk of bleeding is present from the day the disease develops. ITP can go into temporary or permanent remission.
How is chronic ITP diagnosed?
How is it diagnosed?Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures your platelet count and the number of other blood cells in your blood.Blood smear: For this test, some of your blood is put on a slide. ... Bone marrow tests: These tests check whether your bone marrow is healthy.
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2021 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
Article Guidance
This article gives guidance for billing, coding, and other guidelines in relation to local coverage policy DL38268-Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) Therapy.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
What is the ICd 9 code for Evans syndrome?
Both of these events may occur simultaneously or one may follow on from the other. Specialty: Hematology. ICD 9 Code: 287.32.
What is the ICD10 code for D69.3?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code D69.3 and a single ICD9 code, 287.39 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for thoracic compression fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for descending artery stenosis
- 3. icd 10 code for fall through floor
- 4. icd-10 code for drainage from g tube
- 5. what's the icd-10 code for laceration unspecified leg
- 6. icd 10 cm code for for subconjunctival hemorrhage.
- 7. icd 10 code for failed acl reconstruction
- 8. icd 10 code for retinal hemorrhage left eye
- 9. icd 10 code for bug bite right arm
- 10. icd 9 code for unble to site walk or take care of him self