ICD-9-CM Volume 2 Index entries containing back-references to 272.1: Elevation triglycerides 272.1 with high cholesterol 272.2 Findings, (abnormal), without diagnosis (examination) (laboratory test) 796.4 triglycerides 272.9 high 272.1 with high cholesterol 272.2 High triglycerides 272.1 with high cholesterol 272.2 Hyperglyceridemia 272.1
How do you recognize high triglyceride?
Your healthcare provider classifies high triglyceride levels as:
- Mild: 150-199 mg/dL.
- Moderate: 200-499 mg/dL.
- Severe: Greater than 500 mg/dL.
What is the ICD 10 code for high triglycerides?
What is the ICD 10 code for high triglycerides? 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM E78. 1 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E78. Click to see full answer.
Is a high triglyceride unhealthy?
Very high triglycerides can cause swelling of the pancreas. This causes severe belly pain, vomiting, and fever. If digestive juices leak outside the pancreas, it can be life-threatening. Treatment includes weight loss, diet changes, and avoiding alcohol. Very high triglycerides increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
What causes high triglycerides please?
Inherited conditions that cause high triglycerides include:
- Familial combined hyperlipidemia: This is the most common type of hyperlipidemia. ...
- Dysbetalipoproteinemia: This relatively common hereditary condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. ...
- Familial hypertriglyceridemia: This is a familial condition that causes high triglyceride levels without elevated levels of cholesterol.
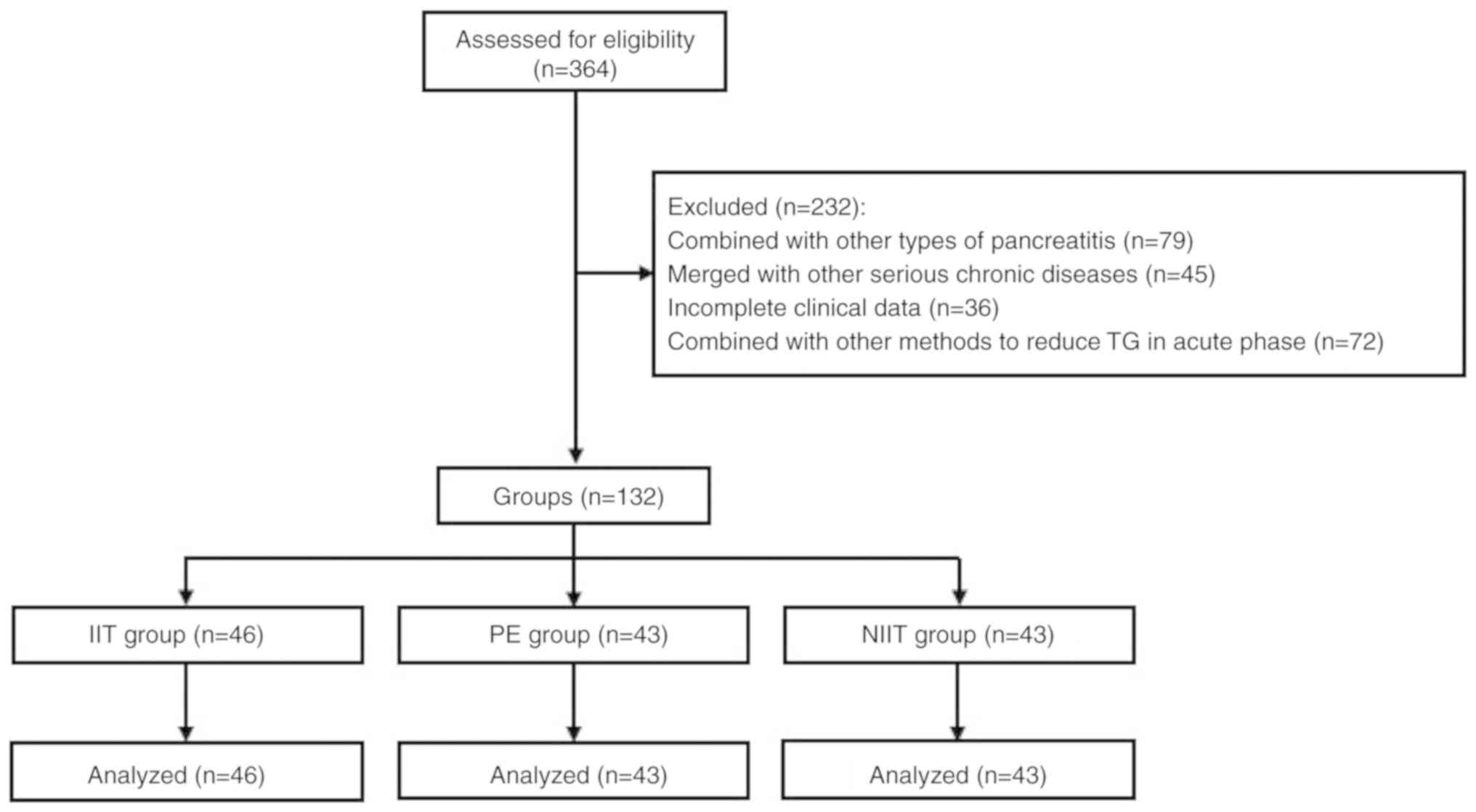
What is the ICD-10 code for high triglycerides?
1.
How do you code hypertriglyceridemia?
E78. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for dyslipidemia with hypertriglyceridemia?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E78. 2: Mixed hyperlipidemia.
How do you code dyslipidemia?
E78. 5 is still the appropriate dx is dyslipidemia NOS or hyperlipidemia NOS is what the MD diagnosis.
What is the difference between hyperlipidemia and pure hypercholesterolemia?
Hyperlipidemia is above normal lipid (fat) levels in the blood, which include several types of lipids, including triglycerides. Hypercholesterolemia is above normal levels of LDL or total cholesterol in your blood. It doesn't include triglycerides.
Can you code hyperlipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia together?
Expert. You wouldn't code them together. Cholesterol is a type of lipid. If the provider diagnosed pure hypercholesterolemia, you would code that.
What is pure hypertriglyceridemia?
Primary hypertriglyceridemia, or type 4 hyperlipidemia has high concentration of triglycerides in the blood. It is also known as hypertriglyceridemia (or pure hypertriglyceridemia). Hypertriglyceridemia denotes high (hyper-) blood levels (-emia) of triglycerides, the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms.
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated lipids?
Code E78. 5 is the diagnosis code used for Hyperlipidemia, Unspecified, a disorder of lipoprotein metabolism other lipidemias. It is a condition with excess lipids in the blood.
What causes high triglyceride?
Causes include obesity, eating too much unhealthy food, genetics, certain illnesses including poorly controlled diabetes, kidney disease, and underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Some drugs, such as steroids and birth control pills, and drinking a lot of alcohol can also cause it. Most people have no symptoms.
What does diagnosis E78 2 mean?
ICD-10 code E78. 2 for Mixed hyperlipidemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is DX code e11 9?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus Without complications.
What is hyperlipidemia unspecified hyperlipidemia type?
You call it high cholesterol. Your doctor calls it hyperlipidemia. Either way, it's a common problem. The term covers several disorders that result in extra fats, also known as lipids, in your blood.
What is the meaning of hypertriglyceridemia?
Hypertriglyceridemia refers to a fasting plasma triglyceride measurement that is increased, typically above the 95th percentile for age and sex — although additional quantitative or qualitative lipoprotein abnormalities can also be present.
What is Type 4 hypertriglyceridemia?
Familial hypertriglyceridemia (type IV familial dyslipidemia) is a disorder characterized by the overproduction of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) from the liver. As a result, the patient will have an excessive number of triglycerides and VLDL on the lipid profile that can cause acute pancreatitis.
What level is hypertriglyceridemia?
Hypertriglyceridemia can be divided into moderate (TG levels from 150 mg/dL to about 1000 mg/dL) and severe (TG levels >1000 mg/dL) forms. In patients with moderate hypertriglyceridemia the focus is on the increased cardiovascular risk, in severe hypertriglyceridemia, on the increased risk of pancreatitis.
What is the first line treatment for hypertriglyceridemia?
Fibrates are the first-line treatment in patients with hypertriglyceridemia who are at risk of pancreatitis. Fibrates, niacin, and n-3 fatty acids, alone or in combination, should be considered in patients with moderate to severe hypertriglyceridemia.
What is the risk of a woman having too much triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in your blood. Too much of this type of fat may raise the risk of coronary artery disease, especially in women.
What is the ICd 10 code for hyperlipidemia?
272.4 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other and unspecified hyperlipidemia. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes Notes - A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!" An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
How to lower triglycerides?
You may be able to lower your triglycerides with a combination of losing weight, diet, and exercise. You also may need to take medicine to lower your triglycerides.
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code?
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code, it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together, when appropriate. Includes Notes - This note appears immediately under a three character code title to further define, or give examples of, the content of the category.
What is hypertriglyceridemia?
A hypertriglyceridemia disorder, often with autosomal dominant inheritance. It is characterized by the persistent elevations of plasma triglycerides, endogenously synthesized and contained predominantly in very-low-density lipoproteins (pre-beta lipoproteins). In contrast, the plasma cholesterol and phospholipids usually remain within normal limits.
When will the ICD-10-CM E78.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E78.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10?
ICD 10 – Did you know? International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a system used by clinicians and other healthcare providers to code and classify all signs, abnormal findings, symptoms and diseases. The origin of ICD is the ‘List of causes of death’, first published way back in 1893 by the International Institute of Statistics.
When was the ICD first published?
The origin of ICD is the ‘List of causes of death’, first published way back in 1893 by the International Institute of Statistics. In 1948, it was taken over by the World Health Organization (WHO), and during this sixth edition, the causes of morbidity was included in the list.
Why is hyperlipidemia a secondary disease?
Hyperlipidemia can occur due to food habit, secondary to any other underlying disease, genetic abnormalities or idiopathic (unknown cause). If it is secondary to any other disease, both primary and secondary should be coded, remember to apply combination coding guidelines if applicable.
What is the term for an increase in lipids in the blood?
Hyperlipidemia refers to increase in any type of lipid (fat) in blood. We use common name “high cholesterol” instead of saying hyperlipidemia. Though not in detail, it is important to understand the basics of lipids to code to the highest specificity. There are two types of lipids: Triglycerides. Cholesterol.
What are the risks of lipids?
Hence increase in the level of lipids is risk factors for cardiovascular problems and stroke. It may even cause obesity, fat deposits on skin, enlargement of organs like spleen, pancreas or liver. Lipid Panel – It is a lab test using specimen as blood to find any type of fat increase in blood.
Why is LDL cholesterol considered bad?
LDL cholesterol –These are called “bad cholesterol” because it gets stored in blood vessels.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 code for muscle weakness
- 2. icd 10 code for cellulitis of chest wall
- 3. icd 9 code for hip pain unspecified
- 4. icd-10 code for elevated alt
- 5. icd 10 code for major depression unspecified
- 6. icd 10 code for benign mucous membrane pemphigoid
- 7. 2015 icd 10 code for fracture left thumb
- 8. icd 10 code for foraminal narrowing cervical
- 9. icd 10 code for manic exacerbation
- 10. icd 10 code for dm type 2 with nephropathy