What can cause burning with urination?
6 Causes of Non-STD Burning at the Tip of the Urethra
- Causes. In most cases, burning at the tip of the urethra is caused by bacteria entering the urethra. ...
- Other symptoms. Women with urethritis sometimes don’t show any symptoms, while men are more likely to show signs within days to a month after infection, or exposure to irritants.
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatments. ...
- The bottom line. ...
What are the causes of frequent urination and burning?
Several factors may be linked to frequent urination, such as:
- Infection, disease, injury or irritation of the bladder
- Conditions that increase urine production
- Changes in muscles, nerves or other tissues affecting bladder function
- Certain cancer treatments
- Drugs or beverages that increase urine production
What causes burning and bleeding during urination?
Burning sensation during urination and bleeding could be a sign of both intestinal and sexually transmitted bacteria. From STD’s it is usually Chlamydia that causes bleeding and burning, Chlamydia also causes bleeding after sex. Yeast infection, which is not believed to be an STD can also cause bleeding ...
Is burning during urination always UTI?
UTI is more of an umbrella term that can include urethritis, gonorrhea and chlamydia infections, and other types of infection. One common symptom of UTIs is a burning sensation during urination. They can also increase the need to urinate. Antibiotics are effective in treating UTIs.
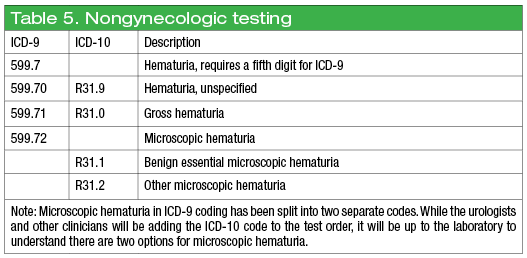
What is the ICD 10 code for painful urination?
R30. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What Dysuria means?
Definition. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Painful urination (dysuria) is discomfort or burning with urination, usually felt in the tube that carries urine out of your bladder (urethra) or the area surrounding your genitals (perineum).
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary tract symptoms?
ICD-10 Code for Urinary tract infection, site not specified- N39. 0- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary tract infection?
0 Urinary tract infection, site not specified. Use additional code (B95-B98), if desired, to identify infectious agent.
Why does it burn when I pee?
Chances are, it has happened to you: You go to the bathroom and feel a burning sensation when you urinate. That feeling is a telltale symptom of a urinary tract infection (UTI), and it's one that most women are familiar with. UTIs are incredibly common.
What is the difference between dysuria and UTI?
Dysuria is the sensation of pain, burning, or discomfort on urination. Although many physicians equate dysuria with urinary tract infection (UTI), it is actually a symptom that has many potential causes. Empiric treatment with antibiotics may be inappropriate, except in carefully selected patients.
What is the diagnosis code for lower urinary tract symptoms?
1 – Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. ICD-Code N40. 1 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms.
How do you code UTI and cystitis?
The ICD-9 code 599.0 is an unspecified urinary tract infection (ICD-10 N39. 0); each of the patients seen had the more specific diagnosis of acute cystitis (ICD-9 595.0), which has two codes in ICD-10: acute cystitis without hematuria (N30. 00), and acute cystitis with hematuria (N30. 01).
What is the best treatment for dysuria?
At-home care for painful urination often includes taking OTC anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen. A doctor will often encourage a person to drink more fluids as this dilutes urine, making it less painful to pass. Resting and taking medications as directed can usually help relieve most symptoms.
Is dysuria a STD?
Although dysuria isn't associated with all STIs, it's prudent to test for several STIs if you're experiencing symptoms or think you may have been exposed. For women, other common causes of painful urination include the following: Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Does dysuria go away?
Does dysuria go away? Yes, dysuria does go away in most cases if it's appropriately treated by a medical professional.
What antibiotics treat dysuria?
Treatment optionsPyridium.phenazopyridine.Azo Urinary Pain Relief.Uristat.Ditropan XL.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right lower quadrant abdominal mass
- 2. icd-10 code for dot physical examination
- 3. icd-10 code for autoimmune thrombocytopenia
- 4. icd 10 cm code for hormones
- 5. icd 10 code for pain in left thumb
- 6. what is icd 10 code for ibs diarrhea
- 7. icd 9 code for nausea and vomiting in pregnancy
- 8. icd 10 cm code for anemia associated with primary malignancy of the prostate
- 9. icd 10 cm code for swelling arm
- 10. icd 10 code for right axillary hidradenitis